Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Suite
Last Updated :
13 Aug, 2020
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is basically an asymmetrical protocol suite for different connections or links that do not provide any framing i.e. raw bit pipes. PPP also wants other protocols to establish connection, authenticate users, and also to carry the network layer data. PPP is not a single protocol but a protocol suite that includes protocols that simply address different aspects of point-to-point layer 2 communication. There are basically 2 routers in the PPP session i.e. Initiator (mainly client) and Responder (mainly server).

PPP operation is generally made using three different parameters as given below :
1. Link Control Protocol (LCP) :
LCP is mainly responsible for establishing, maintaining, testing configuring, and terminating the physical connection. It usually works on top of layer 1. It also negotiates all of the other Wide Area Network (WAN) options that are basically controlled by NCPs. All of the LCP Packets are carried in the data field of the PPP Frame. LCP packet is shown below :
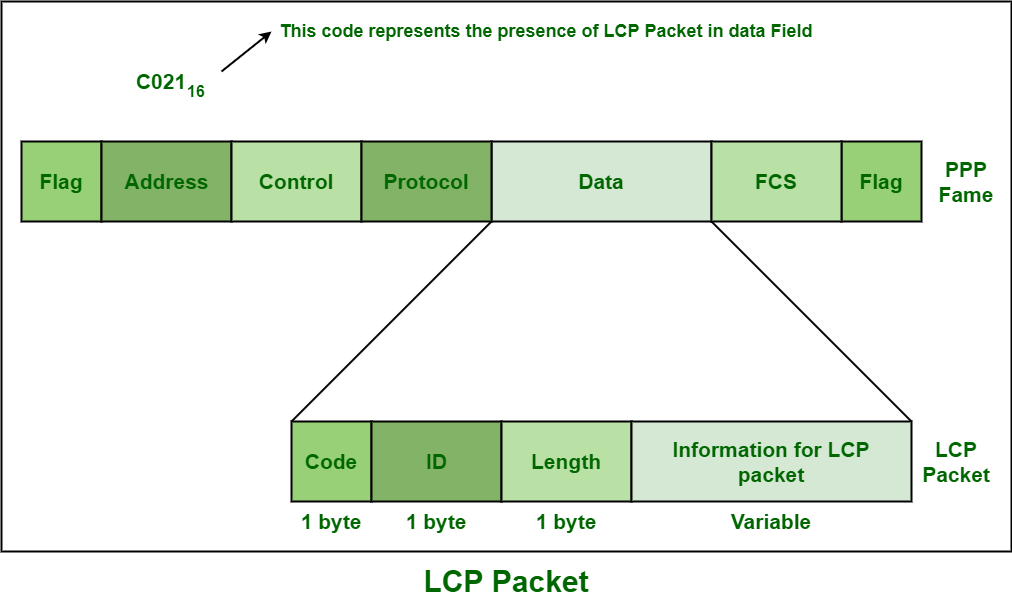
Different LCP protocols are given below :
- Bandwidth Allocation Protocol (BAP) –
BAP is basically a mechanism where any device that is communicating over an Multi-link (MP) bundle of layer, one links can request that an individual link needs to be added or removed from bundle.
- Bandwidth Allocation Control Protocol (BACP) –
BACP basically allows these devices to configure and clarify how they want to use BAP.
- Link Quality Monitoring (LQM) –
LQM is basically a process of determining the loss of the data. It is generally used for monitoring the link quality.
- Link Quality Reporting (LQR) –
LQR allows two computers to get connected to each other. It usually specifies the quality reporting mechanism, but not a particular standard for quality of connection, as there are no implementation-dependent.
2. Network Control Protocol (NCP) :
NCPs protocols are basically required to configure the various communication protocols. Each NCP is particular and specific to a network-layer protocol like IP or IPX/SPX or Apple Talk. IP is the most common layer-3 protocol that is being negotiated. At least one NCP is always present there for each and every higher-layer protocol that is supported by PPP. Different NCPs protocols are given below :
- Compression Control Protocol (CCP) –
CCP is basically responsible for configuring, enabling, disabling, or negotiating and controlling or maintaining data compression algorithms on both of the ends of the PP connection.
- Bridging Control Protocol (BCP) –
BCP is basically responsible for configuring, enabling, disabling, or negotiating and controlling or maintaining bridge control modules on both of the ends of the PP connection. It is similar to IPCP but rather than routing, it initializes bridging.
- Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) –
This protocol is especially requiring to configure, enable, also disable the IP protocol modules at every end of the connection. Routers also exchange IPCP simply to negotiate options that are specific to IP.
- Encryption Control Protocol (ECP) –
This protocol is especially requiring to configure, enable, disabling or negotiating and controlling or maintaining data encryption algorithms on both of the ends of the PP connection.
3. Authentication Protocol :
Authentication protocols simply require to validate i.e., to check the identity of the user who wants to have access to the resources. These protocols also authenticate endpoints simply for users of services. Different authentication protocols are given below :
- Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) –
There are several authentication protocols that are initiated by the client i.e. peer but EAP authentication is generally initiated by the server i.e. authentication. It is a protocol that basically supports a wide range of authentication protocols.
- Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) –
This protocol is especially required to verify the identity and password of the peer or client that might result in success or either failure. It is also symmetric and does not even allow asymmetric settings with authenticator and peer.

- Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) –
This protocol is especially required to verify the identity of the peer or client with the help of a 3-way handshake. It is asymmetric.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...