Ensuring a stable and reliable internet connection is crucial for seamless navigation and efficient communication in the world of Linux. The “ping” command is a powerful tool that allows users to check the status of their internet connection and diagnose network-related issues. In this article, we will explore how to use the ping command in Linux to verify internet connectivity and troubleshoot potential problems.
How to Check Network Connectivity Using Ping Command
The PING (Packet Internet Groper) command is used to check the network connectivity between the host and server/host. This command takes as input the IP address or the URL and sends a data packet to the specified address with the message “PING” and gets a response from the server/host this time is recorded which is called latency. Fast ping with low latency means a faster connection. Ping uses ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) to send an ICMP echo message to the specified host if that host is available then it sends an ICMP reply message. Ping is generally measured in milliseconds every modern operating system has this ping pre-installed.
Basic Syntax of the Ping Command:
The basic syntax of the ping command is as follows:
ping [options] host_or_IP_address
Here, “host_or_IP_address” represents the destination you want to ping.
Checking Internet Connection in Linux
To check your internet connection using the ping command, open the terminal and type the following command:
ping www.google.com
Replace “www.google.com” with the desired host or IP address you want to ping. If the connection is successful, you will see a series of responses displaying the round-trip time, indicating that your internet connection is working. To stop pinging we should use ctrl+c otherwise it will keep on sending packets.

testing internet connection using ping command
Here,
- min: minimum time to get a response
- avg: average time to get responses
- max: maximum time to get a response
The internet connection to www.google.com is working correctly with 0% packet loss, successful transmission and reception of 4 packets, and low round-trip time (RTT) values averaging 1.264 ms, indicating a responsive and stable connection.
Common Options Available in ping Command
1. How to Check PING Version
To get ping version installed on your system.
sudo ping -v

To get ping version
2. How to Specify the Number of Pings
Earlier we did not define the number of packets to send to the server/host by using -c option we can do so.
ping -c 2 www.geeksforgeeks.org

Specify the number of pings in Linux
3. How to Controll the Size of Packets Send Using Ping Command
Earlier a default sized packets were sent to a host but we can send light and heavy packet by using -s option.
ping -s 40 -c 5 www.geeksforgeeks.org

4. How to Change the Time Interval Using Ping Command
By default ping wait for 1 sec to send next packet we can change this time by using -i option.
ping -i 2 www.geeksforgeeks.org
Now, the ping interval will change to 2 seconds.

Changing time interval in Ping Command
5. How to Get Only Summary Using Ping Command
To only get the summary about the network use -q option.
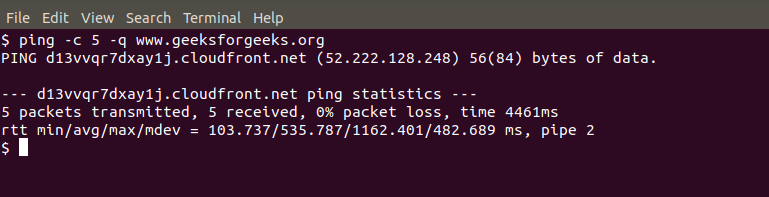
ping -c 5 -q www.geeksforgeeks.org
6. How to Timeout PING
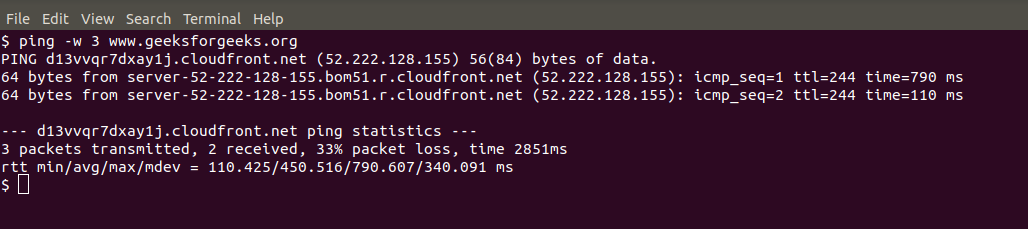
The following command demonstrates how to set a timeout for the PING command using the -w option.
ping -w 3 www.geeksforgeeks.org
This command instructs the system to stop pinging the specified website (www.geeksforgeeks.org) after waiting for 3 seconds.
7. Flooding with PING
To flood a network with PING packets for testing network performance, use the `-f` option with the PING command.
ping -f www.geeksforgeeks.org
This command floods the network with PING packets directed at www.geeksforgeeks.org, providing a means to assess and test network performance.

folding with ping
8. Add Timestamp to PING
Timestamps record the current time of an event over a network. The ping command supports three timestamp options:
- tsonly (timestamp only)
- tsandaddr (timestamp and address)
- tsprespec (timestamp pre-specified for multiple hosts)
ping -T tsonly -c 2 127.0.0.1

Adding timestamp to ping
ping -T tsandaddr -c 2 127.0.0.1

Adding timestamp to ping
9. Time to Wait for Response
Set the time to wait for a response using the `-W` option with the `ping` command
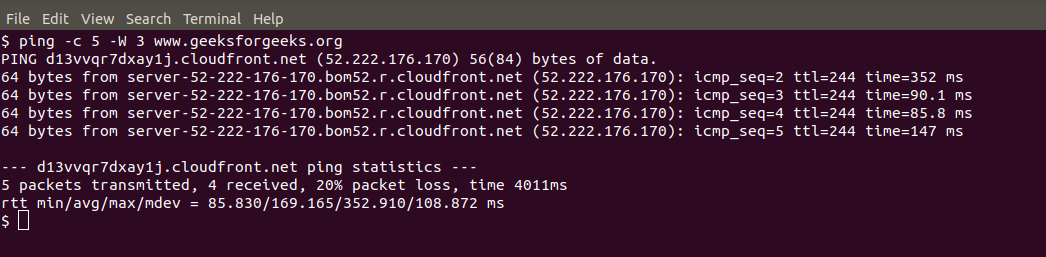
ping -c 5 -W 3 www.geeksforgeeks.org
This command configures the system to wait for a response for a maximum of 3 seconds while sending 5 PING requests to `www.geeksforgeeks.org`.
10. Fill Packet with Data
Use the `-p` option to fill a PING packet with specific data. For example, `-p ff` fills the packet with ones.
ping -c 5 -p ff www.geeksforgeeks.org
This command fills PING packets sent to `www.geeksforgeeks.org` with the specified data, in this case, ones (represented by `ff`).

Fill Packet with Data
11. Path MTU Discovery
Path MTU Discovery helps determine the maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) a TCP path can handle. Use the `-M` option with values like `do` (prohibit fragmentation), `want` (do PMTU discovery, fragment locally when packet size is large), or `dont` (do not set DF flag).
ping -c 5 -M want www.geeksforgeeks.org
This command initiates Path MTU Discovery for the specified website (`www.geeksforgeeks.org`) with the option to either prohibit fragmentation (`do`), perform PMTU discovery with local fragmentation when needed (`want`), or not set the DF flag (`dont`).

Path Mtu Discovery
12. Specify TTL (Time To Live)
The Time To Live (TTL) represents the maximum hops a packet can traverse before getting discarded. Use the `-t` option to specify the TTL value.
ping -c 5 -t 64 www.geeksforgeeks.org
This command sends 5 PING requests to www.geeksforgeeks.org with a Time To Live (TTL) set to 64, restricting the packet’s maximum allowed hops.

Specify TTL (Time To Live)
How to Check Network Connectivity in Linux | ping Command – FAQ
How do I use the ping command to check if my Linux system is connected to the internet?
You can use the ping command followed by a target host or IP address.
For example:
ping www.google.com.
If successful, you’ll see round-trip time statistics indicating a successful network connection.
What does the “ping: unknown host” error mean, and how can I resolve it?
This error occurs when the specified host or domain is not recognized. Double-check the hostname or try using an IP address instead. If using a hostname, ensure DNS resolution is working, and you have a valid internet connection.
How can I use the ping command to continuously monitor network connectivity?
The -c option in the ping command allows you to specify the number of packets to send. Use -c 4 to send four packets, or use the -f option for continuous ping.
For example:
ping -c 4 www.example.com
or
ping -f www.example.com
What does “Request timed out” or “Destination Host Unreachable” mean in the ping output?
“Request timed out” indicates that the target is not responding to ping requests. “Destination Host Unreachable” suggests that there is an issue reaching the destination network. Check your network configuration, firewall settings, and ensure the target is reachable.
Can I adjust the time interval between ping requests to reduce network load?
Yes, you can use the -i option followed by the desired interval in seconds.
For example:
ping -i 2 www.example.com
It will send ping requests every 2 seconds. Adjust the interval based on your testing requirements and to avoid unnecessary network load.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed the “ping” command which is a crucial tool in Linux for checking and maintaining a stable internet connection. This article provides a guide on using the ping command to verify connectivity, troubleshoot issues, and monitor network performance. It covers the basics of the command, important parameters, and various customization options. The inclusion of frequently asked questions addresses common concerns, making it easier for users to navigate and optimize their network connections in Linux. Ultimately, the ping command is a valuable resource for ensuring a responsive and reliable internet experience on Linux systems.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...