Parse Tree in Compiler Design
Last Updated :
14 Jul, 2022
Here we will study the concept and uses of Parse Tree in Compiler Design. First, let us check out two terms :
- Parse : It means to resolve (a sentence) into its component parts and describe their syntactic roles or simply it is an act of parsing a string or a text.
- Tree: A tree may be a widely used abstract data type that simulates a hierarchical tree structure, with a root value and sub-trees of youngsters with a parent node, represented as a group of linked nodes.
Parse Tree:
- Parse tree is the hierarchical representation of terminals or non-terminals.
- These symbols (terminals or non-terminals) represent the derivation of the grammar to yield input strings.
- In parsing, the string springs using the beginning symbol.
- The starting symbol of the grammar must be used as the root of the Parse Tree.
- Leaves of parse tree represent terminals.
- Each interior node represents productions of a grammar.
Rules to Draw a Parse Tree:
- All leaf nodes need to be terminals.
- All interior nodes need to be non-terminals.
- In-order traversal gives the original input string.
Example 1: Let us take an example of Grammar (Production Rules).
S -> sAB
A -> a
B -> b
The input string is “sab”, then the Parse Tree is:
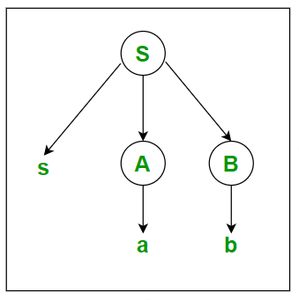
Example-2: Let us take another example of Grammar (Production Rules).
S -> AB
A -> c/aA
B -> d/bB
The input string is “acbd”, then the Parse Tree is as follows:

Uses of Parse Tree:
- It helps in making syntax analysis by reflecting the syntax of the input language.
- It uses an in-memory representation of the input with a structure that conforms to the grammar.
- The advantages of using parse trees rather than semantic actions: you’ll make multiple passes over the info without having to re-parse the input.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...