Parameter Passing Techniques in Java with Examples
Last Updated :
06 Dec, 2022
There are different ways in which parameter data can be passed into and out of methods and functions. Let us assume that a function B() is called from another function A(). In this case A is called the “caller function” and B is called the “called function or callee function”. Also, the arguments which A sends to B are called actual arguments and the parameters of B are called formal arguments.
Types of parameters:
Formal Parameter: A variable and its type as they appear in the prototype of the function or method.
Syntax:
function_name(datatype variable_name)
Actual Parameter: The variable or expression corresponding to a formal parameter that appears in the function or method call in the calling environment.
Syntax:
func_name(variable name(s));
Important methods of Parameter Passing
1. Pass By Value: Changes made to formal parameter do not get transmitted back to the caller. Any modifications to the formal parameter variable inside the called function or method affect only the separate storage location and will not be reflected in the actual parameter in the calling environment. This method is also called as call by value.
Java in fact is strictly call by value.
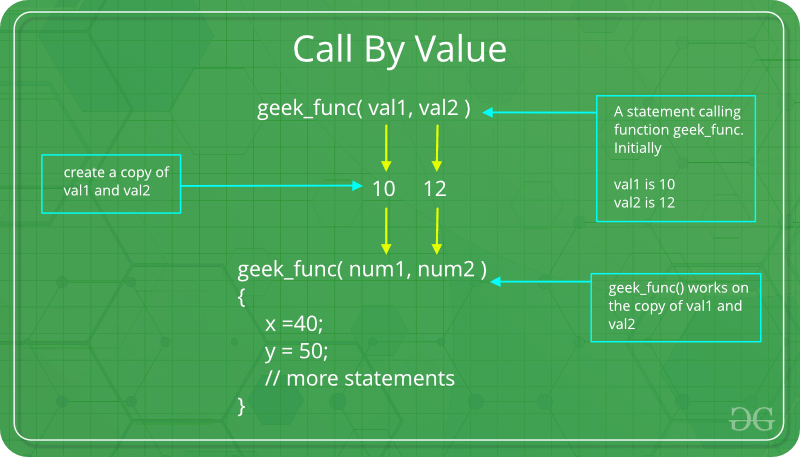
Example:
Java
class CallByValue {
public static void example(int x, int y)
{
x++;
y++;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
CallByValue object = new CallByValue();
System.out.println("Value of a: " + a
+ " & b: " + b);
object.example(a, b);
System.out.println("Value of a: "
+ a + " & b: " + b);
}
}
|
Output
Value of a: 10 & b: 20
Value of a: 10 & b: 20
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Shortcomings:
- Inefficiency in storage allocation
- For objects and arrays, the copy semantics are costly
2. Call by reference(aliasing): Changes made to formal parameter do get transmitted back to the caller through parameter passing. Any changes to the formal parameter are reflected in the actual parameter in the calling environment as formal parameter receives a reference (or pointer) to the actual data. This method is also called as call by reference. This method is efficient in both time and space.
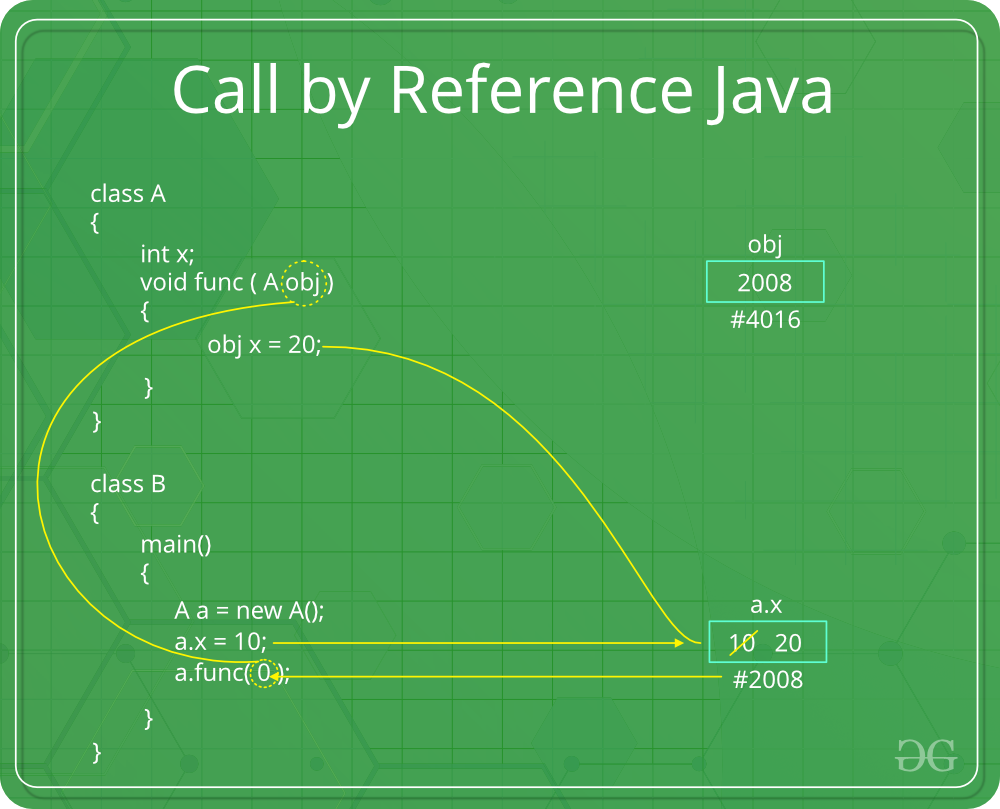
Example
Java
class CallByReference {
int a, b;
CallByReference(int x, int y)
{
a = x;
b = y;
}
void ChangeValue(CallByReference obj)
{
obj.a += 10;
obj.b += 20;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CallByReference object
= new CallByReference(10, 20);
System.out.println("Value of a: " + object.a
+ " & b: " + object.b);
object.ChangeValue(object);
System.out.println("Value of a: " + object.a
+ " & b: " + object.b);
}
}
|
Output
Value of a: 10 & b: 20
Value of a: 20 & b: 40
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Please note that when we pass a reference, a new reference variable to the same object is created. So we can only change members of the object whose reference is passed. We cannot change the reference to refer to some other object as the received reference is a copy of the original reference.
Please see example 2 in Java is Strictly Pass by Value!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...