OLAP Servers
Last Updated :
26 Jul, 2021
Online Analytical Processing(OLAP) refers to a set of software tools used for data analysis in order to make business decisions. OLAP provides a platform for gaining insights from databases retrieved from multiple database systems at the same time. It is based on a multidimensional data model, which enables users to extract and view data from various perspectives. A multidimensional database is used to store OLAP data. Many Business Intelligence (BI) applications rely on OLAP technology.
Type of OLAP servers:
The three major types of OLAP servers are as follows:
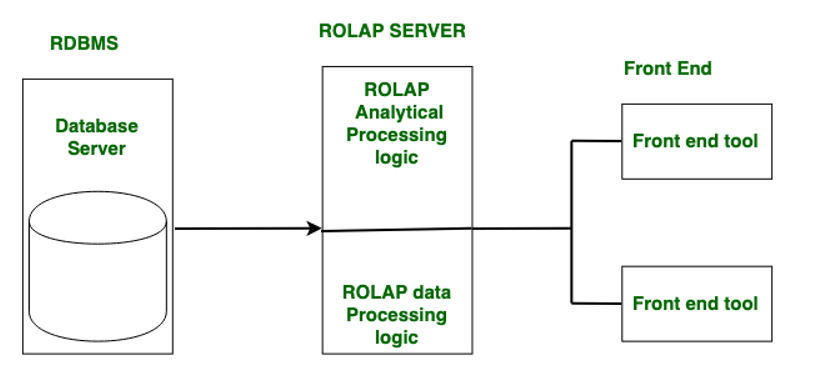
Relational OLAP (ROLAP):
Relational On-Line Analytical Processing (ROLAP) is primarily used for data stored in a relational database, where both the base data and dimension tables are stored as relational tables. ROLAP servers are used to bridge the gap between the relational back-end server and the client’s front-end tools. ROLAP servers store and manage warehouse data using RDBMS, and OLAP middleware fills in the gaps.
Benefits:
- It is compatible with data warehouses and OLTP systems.
- The data size limitation of ROLAP technology is determined by the underlying RDBMS. As a result, ROLAP does not limit the amount of data that can be stored.
Limitations:
- SQL functionality is constrained.
- It’s difficult to keep aggregate tables up to date.
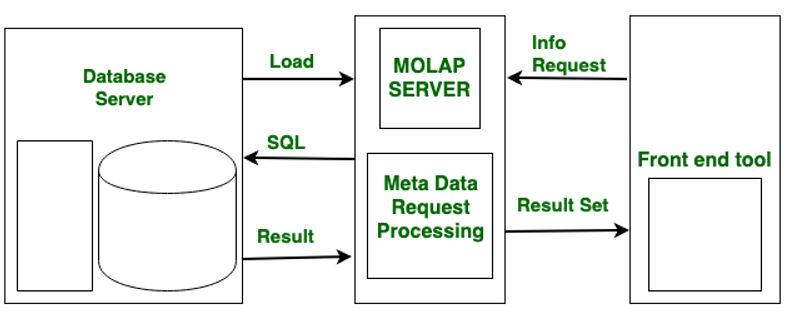
Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP):
Through array-based multidimensional storage engines, Multidimensional On-Line Analytical Processing (MOLAP) supports multidimensional views of data. Storage utilization in multidimensional data stores may be low if the data set is sparse.
MOLAP stores data on discs in the form of a specialized multidimensional array structure. It is used for OLAP, which is based on the arrays’ random access capability. Dimension instances determine array elements, and the data or measured value associated with each cell is typically stored in the corresponding array element. The multidimensional array is typically stored in MOLAP in a linear allocation based on nested traversal of the axes in some predetermined order.
However, unlike ROLAP, which stores only records with non-zero facts, all array elements are defined in MOLAP, and as a result, the arrays tend to be sparse, with empty elements occupying a larger portion of them. MOLAP systems typically include provisions such as advanced indexing and hashing to locate data while performing queries for handling sparse arrays, because both storage and retrieval costs are important when evaluating online performance. MOLAP cubes are ideal for slicing and dicing data and can perform complex calculations. When the cube is created, all calculations are pre-generated.
Benefits:
- Suitable for slicing and dicing operations.
- Outperforms ROLAP when data is dense.
- Capable of performing complex calculations.
Limitations:
- It is difficult to change the dimensions without re-aggregating.
- Since all calculations are performed when the cube is built, a large amount of data cannot be stored in the cube itself.
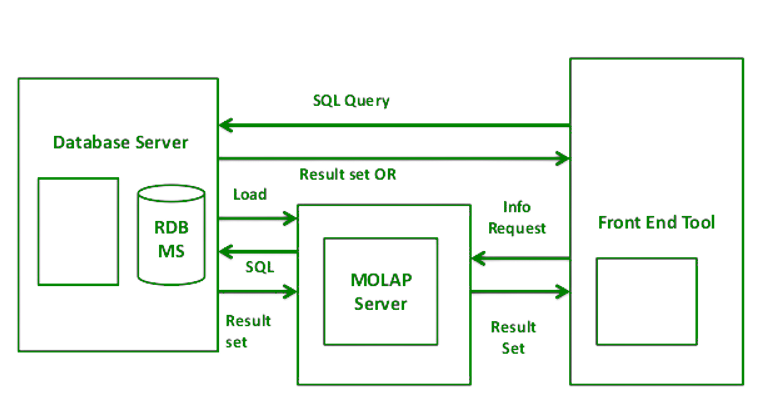
Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP):
ROLAP and MOLAP are combined in Hybrid On-Line Analytical Processing (HOLAP). HOLAP offers greater scalability than ROLAP and faster computation than MOLAP.HOLAP is a hybrid of ROLAP and MOLAP. HOLAP servers are capable of storing large amounts of detailed data. On the one hand, HOLAP benefits from ROLAP’s greater scalability. HOLAP, on the other hand, makes use of cube technology for faster performance and summary-type information. Because detailed data is stored in a relational database, cubes are smaller than MOLAP.
Benefits:
- HOLAP combines the benefits of MOLAP and ROLAP.
- Provide quick access at all aggregation levels.
Limitations
- Because it supports both MOLAP and ROLAP servers, HOLAP architecture is extremely complex.
- There is a greater likelihood of overlap, particularly in their functionalities.
Other types of OLAP include:
- Web OLAP (WOLAP): WOLAP refers to an OLAP application that can be accessed through a web browser. WOLAP, in contrast to traditional client/server OLAP applications, is thought to have a three-tiered architecture consisting of three components: a client, middleware, and a database server.
- Desktop OLAP (DOLAP): DOLAP is an abbreviation for desktop analytical processing. In that case, the user can download the data from the source and work with it on their desktop or laptop. In comparison to other OLAP applications, functionality is limited. It is less expensive.
- Mobile OLAP (MOLAP): Wireless functionality or mobile devices are examples of MOLAP. The user is working and accessing data via mobile devices.
- Spatial OLAP (SOLAP): SOLAP egress combines the capabilities of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and OLAP into a single user interface. SOLAP is created because the data can be alphanumeric, image, or vector. This allows for the quick and easy exploration of data stored in a spatial database.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...