numpy.polyder() in Python
Last Updated :
04 Dec, 2020
The numpy.polyder() method evaluates the derivative of a polynomial with specified order.
Syntax :numpy.polyder(p, m)
Parameters :
p : [array_like or poly1D]the polynomial coefficients are given in decreasing order of powers. If the second parameter (root) is set to True then array values are the roots of the polynomial equation.
For example : poly1d(3, 2, 6) = 3x2 + 2x + 6
m : [int, optional] Order of differentiation.
Return: Derivative of polynomial.
Code : Python code explaining polyder()
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
p1 = np.poly1d([1, 2])
p2 = np.poly1d([4, 9, 5, 4])
print ("P1 : ", p1)
print ("\n p2 : \n", p2)
|
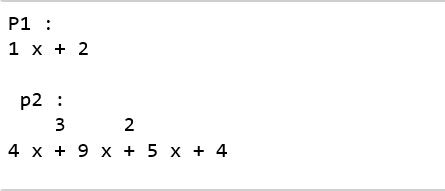
print ("\n\np1 at x = 2 : ", p1(2))
print ("p2 at x = 2 : ", p2(2))
|

a = np.polyder(p1, 1)
b = np.polyder(p2, 1)
print ("\n\nUsing polyder")
print ("p1 derivative of order = 1 : \n", a)
print ("p2 derivative of order = 1 : \n", b)
|

a = np.polyder(p1, 2)
b = np.polyder(p2, 2)
print ("\n\nUsing polyder")
print ("p1 derivative of order = 2 : ", a)
print ("p2 derivative of order = 2 : ", b)
|

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...