numpy.absolute() in Python
Last Updated :
29 Nov, 2018
numpy.absolute(arr, out = None, ufunc ‘absolute’) : This mathematical function helps user to calculate absolute value of each element. For complex input, a + ib, the absolute value is
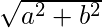
.
Parameters :
arr : [array_like] Input array or object whose elements, we need to test.
Return :
An array with absolute value of each array.
Code #1 : Working
import numpy as np
arr1 = [1, -3, 15, -466]
print ("Absolute Value of arr1 : \n",
np.absolute(arr1))
arr2 = [23 , -56]
print ("\nAbsolute Value of arr2 : \n",
np.absolute(arr2))
|
Output :
Absolute Value of arr1 :
[ 1 3 15 466]
Absolute Value of arr2 :
[23 56]
Code #2 : Working with complex numbers
import numpy as np
a = 4 + 3j
print("Absolute(4 + 3j) : ",
np.absolute(a))
b = 16 + 13j
print("\nAbsolute value(16 + 13j) : ",
np.absolute(b))
|
Output :
Absolute(4 + 3j) : 5.0
Absolute value(16 + 13j) : 20.6155281281
Code #3: Graphical Representation of numpy.absolute()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a = np.linspace(start = -5, stop = 5,
num = 6, endpoint = True)
print("Graphical Representation : \n",
np.absolute(a))
plt.title("blue : with absolute\nred : without absolute")
plt.plot(a, np.absolute(a))
plt.plot(a, a, color = 'red')
plt.show()
|
Output :
Graphical Representation :
[ 5. 3. 1. 1. 3. 5.]
 References :
https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/generated/numpy.absolute.html
References :
https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/generated/numpy.absolute.html
.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...