Number of ways to place two queens on a N*N chess-board
Last Updated :
20 Feb, 2023
Given an integer N denoting a N * N chess-board, the task is to count the number of ways to place two queens on the board such that, they do not attack each other.
Examples:
Input: N = 9
Output: 2184
Explanation:
There are 2184 ways to place two queens on 9 * 9 chess-board.
Input: N = 3
Output: 8
Explanation:
There are 8 ways to place two queens on 3 * 3 chess-board.
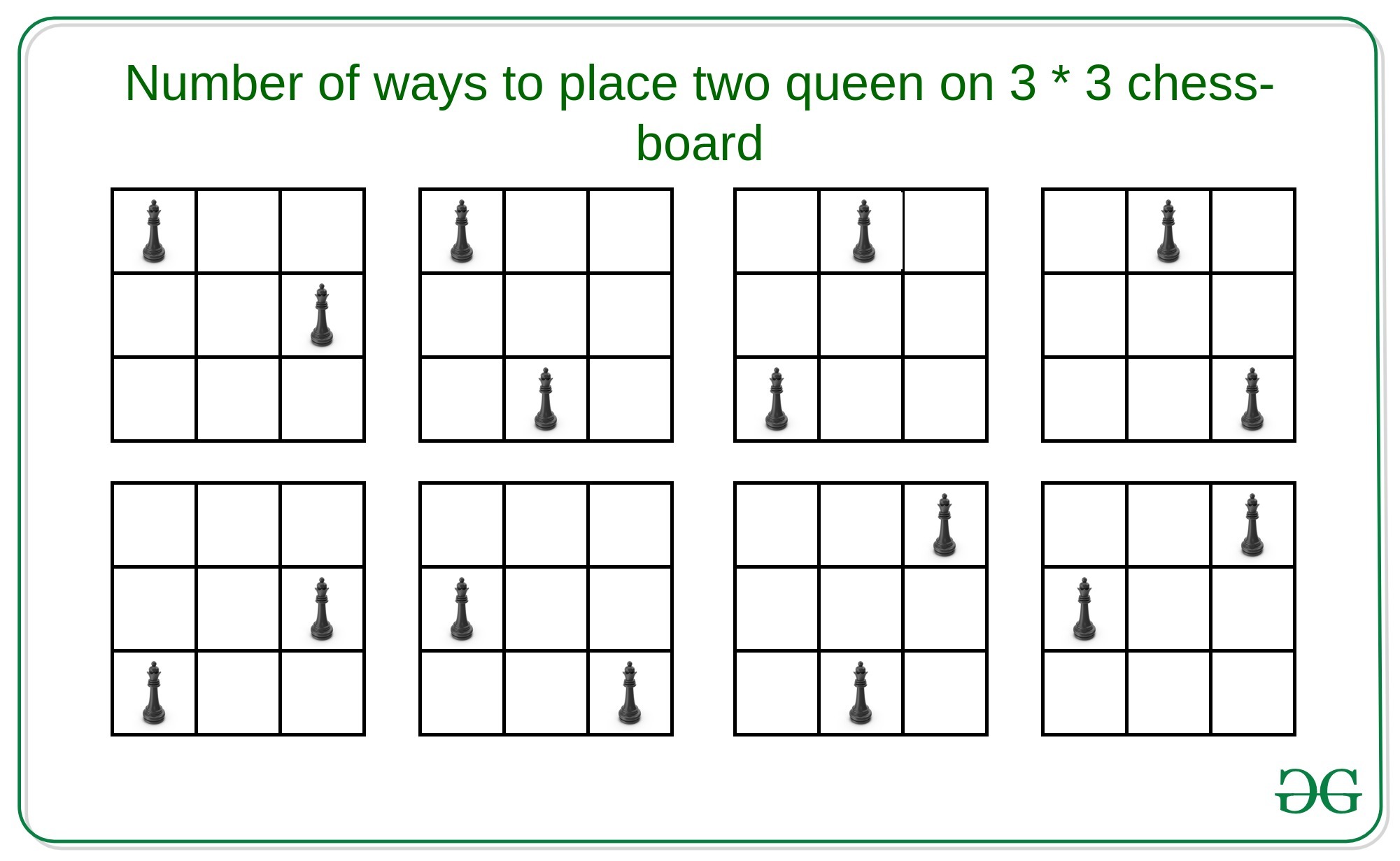
Naive Approach: A simple solution will be to choose two every possible position for the two queens on the N * N matrix and check that they are not in horizontal, vertical, positive diagonal or negative diagonal. If yes then increment the count by 1.
Time Complexity: O(N4)
Efficient Approach: The idea is to use combinations to compute the possible positions of the queens such that they do not attack each other. A useful observation is that it is quite easy to calculate the number of positions that a single queen attacks. That is –
Number of positions a queen attack = (N - 1) + (N - 1) + (D - 1)
Here,
// First N-1 denotes positions in horizontal direction
// Second N-1 denotes positions in vertical direction
// D = Number of positions in
positive and negative diagonal
If we do not place the queen on the last row and the last column then the answer will simply be the number of positions to place in a chessboard of  whereas if we place in the last column and last row then possible positions for queens will be
whereas if we place in the last column and last row then possible positions for queens will be 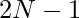 and attacking at
and attacking at 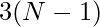 positions. Therefore, the possible positions for the other queen for each position of the queen will be
positions. Therefore, the possible positions for the other queen for each position of the queen will be 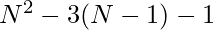 . Finally, there are
. Finally, there are 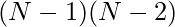 combinations where both queens are on the last row and last column. Therefore, the recurrence relation will be:
combinations where both queens are on the last row and last column. Therefore, the recurrence relation will be:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com Q(N)=Q(N-1)+(2N - 1)[N^2 - 3(N - 1) - 1] - (N - 1)(N - 2)](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c0e60622cd917d4b555f59befedcc12e_l3.png) // By Induction
// By Induction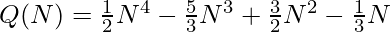
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll possiblePositions(ll n)
{
ll term1 = pow(n, 4);
ll term2 = pow(n, 3);
ll term3 = pow(n, 2);
ll term4 = n / 3;
ll ans = (ceil)(term1) / 2 -
(ceil)(5 * term2) / 3 +
(ceil)(3 * term3) / 2 - term4;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ll n;
n = 3;
ll ans = possiblePositions(n);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG{
static double possiblePositions(double n)
{
double term1 = Math.pow(n, 4);
double term2 = Math.pow(n, 3);
double term3 = Math.pow(n, 2);
double term4 = n / 3;
double ans = (Math.ceil(term1 / 2)) -
(Math.ceil(5 * term2) / 3) +
(Math.ceil(3 * term3) / 2) - term4;
return (long)ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double n;
n = 3;
double ans = possiblePositions(n);
System.out.print(ans + "\n");
}
}
|
Python3
import math
def possiblePositions(n):
term1 = pow(n, 4);
term2 = pow(n, 3);
term3 = pow(n, 2);
term4 = n / 3;
ans = ((math.ceil(term1)) / 2 -
(math.ceil(5 * term2)) / 3 +
(math.ceil(3 * term3)) / 2 - term4);
return ans;
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 3
ans = possiblePositions(n)
print(int(ans))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static double possiblePositions(double n)
{
double term1 = Math.Pow(n, 4);
double term2 = Math.Pow(n, 3);
double term3 = Math.Pow(n, 2);
double term4 = n / 3;
double ans = (Math.Ceiling(term1 / 2)) -
(Math.Ceiling(5 * term2) / 3) +
(Math.Ceiling(3 * term3) / 2) - term4;
return (long)ans;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
double n;
n = 3;
double ans = possiblePositions(n);
Console.Write(ans + "\n");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function possiblePositions(n)
{
let term1 = Math.pow(n, 4);
let term2 = Math.pow(n, 3);
let term3 = Math.pow(n, 2);
let term4 = n / 3;
let ans = (Math.ceil(term1 / 2)) -
(Math.ceil(5 * term2) / 3) +
(Math.ceil(3 * term3) / 2) - term4;
return ans;
}
let n;
n = 3;
let ans = possiblePositions(n);
document.write(Math.floor(ans));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...