NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity
Last Updated :
22 Mar, 2024
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution: This article includes free NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution. It has been developed by the subject matter experts at GFG, according to the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, and guidelines to help the students of Class 10 create a solid conceptual base for Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Science and ace their exams.
NCERT CBSE Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution of Class 10 explains the role of Heredity in the variation and evolution of organisms, over a period of time. To revise the basic concepts of Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution NCERT Class 10 Science, head over to: CBSE NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity and Evolution Notes for quick revision and class notes.
The solutions to all the exercises in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution have been collectively covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution of Page 129
Q1: If trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Answer:
According to the question, if trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and trait B exists in 60% of the same population, it means that trait A is in less number of population as compared to trait B which exists in about 60 % of the same population.
In an asexually reproducing species, a trait is expressed in a larger amount which means it has arisen earlier, existed for a long duration, and is passed on in future progeny.
Hence, trait A is a newly expressed trait in the asexually reproducing species because it is expressed in only 10% of the population while trait B is likely to have arisen earlier.
Q2: How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer:
Variation in species mostly depends on their surroundings and environmental conditions. If the environmental conditions change rapidly the survival of these species becomes difficult. In such conditions, only a few species can adapt or resist the change and survive.
For example: if the temperature of the earth’s surface increases drastically by a few degrees Celsius, then only those species which are resistant to heat would be able to survive.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution of Page 133
Q1: How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer:
To show that traits may be dominant or recessive. Mendel chose true breeding tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) pea plants for the experiment. He crossed the two breeds and observed the first filial generation(F1). He found that the seeds formed after fertilization were grown and all of them were tall (Tt).
Then, Mendel self-pollinated these plants and observed F2 generation in his observation, he found that one-fourth of F2 generation was short.
From this experiment, he concluded that the F1 generation appeared tall because the tall trait is dominant over the dwarf trait as Fi plants are not true-breeding and carry both short and tall traits.

Q2: How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer:
To show that traits are inherited independently Mendel crossed pea plants having round green seeds (RRyy) with pea plants having wrinkled yellow seeds (rrYY).
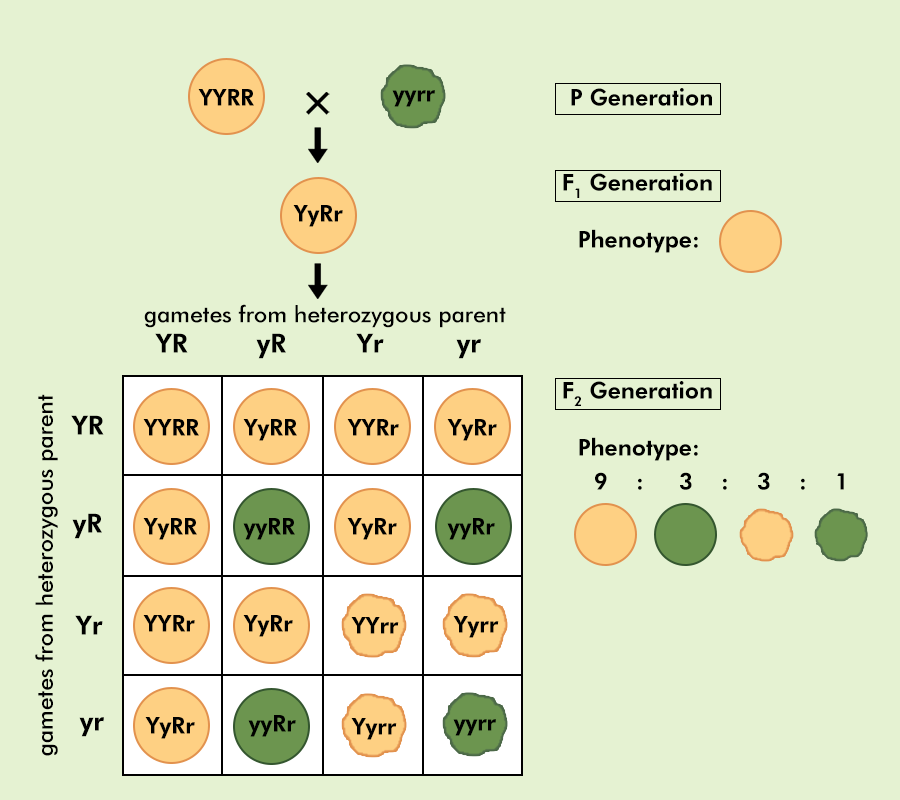
As the F1 plants are formed after crossing pea plants having green round seeds and pea plants having yellow wrinkled seeds, the F1 generation formed bore both characters in them. Although, the plants had round and yellow seed colors because they are dominant characters.
Then, F1 progeny was self-pollinated and the F2 generation have yellow round seeds, green round seeds, yellow wrinkled seeds, and green wrinkled seeds in the ratio of 9:3:3:1.
Q3: A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer:
The information given as the father having blood group A and the mother blood group O is not adequate to conclude that either the traits – blood A or O is dominant. In order to know which trait is dominant we will have to know about all the progeny of the blood group as blood group A can have genotype AA or AO.
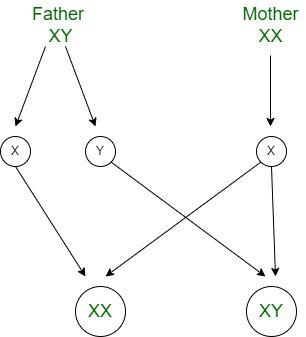
Q4: How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?
Answer:
As we know in human beings, during reproduction the gametes receive half-half chromosomes from each of their parents in equal genetic proportion. Female gametes are composed of 22 autosomes and an X chromosome and male gametes are composed of 22 autosomes and either a X or Y sex chromosome. Hence, in this process of transferring genetic materials, the mother gives only the X chromosome whereas, the father provides the X or Y chromosome which determines the sex of the child. If the X chromosome of female fuses with the X chromosome of a male it will be a girl, or if it fuses with the Y chromosome of a male it will be a boy.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Exercise
Q1: A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic makeup of the tall parent can be depicted as
(a) TTWW
(b) TTww
(c) TtWW
(d) TtWw
Answer:
From the above experiment of breeding the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as ( option c) TtWW. The Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. The experiment can be shown by the cross
TtWw × ttww
⇓
TtWw – ttww
As half of the progeny are short it means their parent plants also have a collection of short genes, whereas, all progeny bore violet flowers which means the violet color is the dominant one over white. This suggests that all the progeny are violet in color but half of them are short.
Q2: A study found that children with light-colored eyes are likely to have parents with light-colored eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye color trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
Answer:
According to the law of Dominance, when two homozygous organisms are crossed with a single pair of contrasting traits, the trait that is expressed in F1 generation is called as dominant and the one not expressed is called recessive.
In this study, to prove whether a light color trait is dominant or recessive we will have to assume that a child with light eyes can have LL or Ll or ll genotype. Let’s look into the possibilities.
- Case 1: If the child has an LL genotype then its parents are also likely to be of LL genotype.
LL × LL
⇓
LL
- Case 2: If the child with light-colored eyes has ll genotype then, his parents will also have ll genotype.
ll × ll
⇓
ll
Hence, it cannot be determined whether light eye color is dominant or recessive. It will require at least three generations to reach any conclusion.
Q3: Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat color in dogs.
Answer:
The dominant coat color in dogs is determined by their inherited genes. A dog’s coat color can be influenced by eleven identified genes which include A, B, C, D, E, F, G, M, P, S, T. To determine the dominant color a cross can be performed.
For example, in the B series, a dog can be Black(B) or Brown(b). Hence, assuming that one parent is homozygous black (BB) and one homozygous brown (bb).
| bb |
BB
|
| |
B |
B |
| b |
Bb |
Bb |
| b |
Bb |
Bb |
In this case, all the offsprings produced in the F1 generation are heterozygous Bb. So, the dominant trait can be determined by observing the offspring whether they are black or brown.
Q4: How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Answer:
During sexual reproduction in human beings, the male and female gametes fuse and the progeny receives 22 autosomes and an X (or) Y chromosome from the male and 22 autosomes and one X chromosome from the female.
This equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is possible in human beings as every somatic cell of the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes out of which, 22 pairs are autosomes, and the remaining single pair is known as sex chromosomes represented by letters X and Y.
In the female body, there are two X chromosomes (XX) which means female gametes have 22 autosomes and an X chromosome whereas, the male body has one X and one Y chromosome (XY), which means 22 autosomes and an X or Y chromosome. Later these gametes with equal chromosomes fuse during reproduction and ensure equal genetic contribution in progeny.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- They enhance the conceptual knowledge of the students.
- Clear and Comprehensible Content.
- Aid in Competitive Exam Preparation.
- The answers are provided by Top subject experts.
- Readily available and easily accessible.
- As per the revised curriculum of CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter, previously known as Chapter 9, has now been renumbered as Chapter 8.
Also Check:
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution – FAQs
Q1: What is the name of NCERT Science Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Biology?
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Biology name is Heredity and Evolution, which explains all the important processes needed for living organisms.
Q2: Where can I find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution can be found on various online platforms such as the official NCERT website, GeeksForGeeks, and more.
Q3. What are the important topics in Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution NCERT class 10?
Important topics covered in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution are as follows:
1. Laws of Inheritance
2. Mendel’s Experiments
3. Monohybrid Cross
4. Dihybrid Cross
5. Evolution and Its Theories
6. Evidence of Evolution
Q4. How can students benefit from the CBSE Free PDF Download of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution available through online free resources for their studies?
Students can benefit significantly from the CBSE Free PDF Download of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution available through online free resources at no cost. These PDFs can be valuable additions to their learning, helping them practice, and better their understanding of various subjects and topics of Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution. It offers an easy and accessible way to study and prepare for exams.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...