NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
Last Updated :
22 Mar, 2024
Control and Coordination is about control mechanisms and movement in organisms. This article includes free NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination, developed by the top Biology experts at GFG, according to the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24 and guidelines.
These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination have covered all important topics to help students in their board exams, as well as in preparing for future competitive exams.
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination of Page 105
Q1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer:
A reflex action is an involuntary action that is a rapid and automatic response to stimuli. Walking is a voluntary action, which requires our thinking and is within our control.
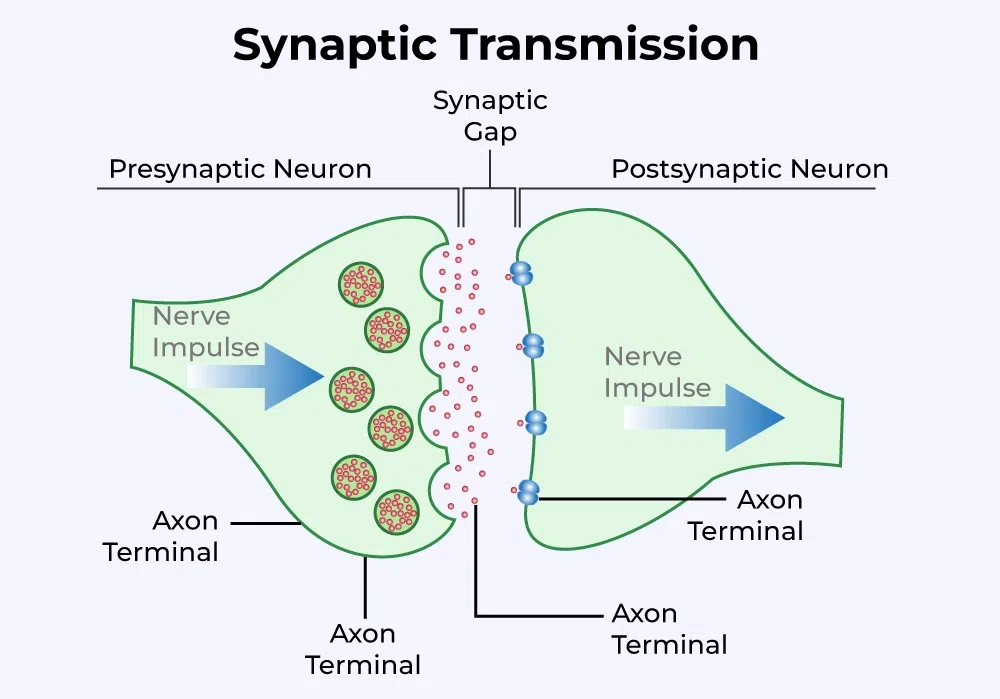
Q2: What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:
At the junction between two neurons (synapse), an action potential causes neuron A to release a chemical neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter can either help (excite) or hinder (inhibit) neuron B from firing its own action potential.
Q3: Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:
Cerebellum, part of the Hindbrain is responsible for maintaining posture and equilibrium of the body.
Q4: How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer:
Smell of an incense stick is detected by the olfactory receptors present in the nose. The receptors send the signal to the olfactory lobe present in the fore-brain where it is analyzed and reacted upon.
Q5: What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer:
The brain is not involved in a reflex action as it is an involuntary action that does not require thinking.
NCERT Solutions for Control And Coordination of Page 108
Q1: What are plant hormones?
Answer:
Plant hormones are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all the growth and development activities like cell division, enlargement, flowering, seed formation, dormancy, and abscission.
Q2: How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer:
The movement of the sensitive plant’s leaves is touch-sensitive and independent of growth, which is known as Thigmotropism. The growth-related tendency of the shoot toward light is known as Phototropism.
Q3: Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer:
Auxin is an example of a plant hormone that promotes and regulates the growth of the plant.
Q4: How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:
When a tendril is in contact with the support of a wall or any other plant, more auxin diffuses towards the side of the tendril away from the support. This auxin concentration stimulates the cells to grow longer on the tendril side which is far from the support.
Q5: Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer:
Hydrotropism is the process of growth or movement of roots toward the source of water. Here is an experiment that is performed to observe the growth of plants when water is present.
Procedure:
- Let’s take two beakers A and B.
- In beaker A, let’s add some moist soil and sow the seeds.
- In beaker B, add dry soil in one part and moist soil in another part and sow the seeds. Also, place a small beaker of water just adjacent to it.
- Keep it for some time so that the plants can grow.
Result:
It was found that in beaker A due to the presence of moist soil, plants have grown normally and roots were straight.
In beaker B, it was observed that because of, the presence of the water beaker next to it plants have grown towards the water, as shown in the below figure.
Conclusion:
This experiment states that the plants move and grow towards the source of water, hence plants show hydrotropism.

NCERT Solutions for Control And Coordination of Page 111
Q1: How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer:
Chemical coordination in multicellular organisms takes place through special chemical substances called hormones, which are produced in endocrine glands.
Q2: Why is the use of iodized salt advisable?
Answer:
Iodized salt helps create the hormones that regulate heart rate and blood pressure. It also helps to burn extra fat deposits that could lead to heart disease. Salt promotes healthy hydration levels and creates a balance of electrolytes.
Q3: How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer:
When adrenaline is secreted in large amounts it prepares our body for action. It speeds up heartbeat and breathing, raises blood pressure, and allows more glucose to go into the blood to give us a lot of energy quickly to fight or fight.
Q4: Why are some patients with diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:
Sometimes, people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes need insulin therapy if other treatments haven’t been able to keep blood glucose levels within the desired range. Insulin therapy helps prevent diabetes complications by keeping blood sugar within the target range.
NCERT Solutions for Control And Coordination Exercises
Q1: Which of the following is a plant hormone?
- a) Insulin
- b) Thyroxin
- c) Oestrogen
- d) Cytokinin
Answer:
Among the hormones listed above, Insulin, Thyroxin & Oestrogen are animal hormones. So, the correct option is d) Cytokinin. Cytokinin is a plant hormone that:
- Promotes cell division in plant roots and shoots.
- Helps to produce new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves and helps to overcome apical dominance and delay senescence.
- Breaks dormancy period of seeds.
Q2: The gap between two neurons is called a
- a) Dendrite
- b) Synapse
- c) Axon
- d) Impulse
Answer:
Correct option is b) Synapse. Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Q3: The brain is responsible for:
- a) Thinking
- b) Regulating the heartbeat
- c) Balancing the body
- d) All of the above.
Answer:
Correct answers is d) All of the above
- The brain’s frontal lobe is home to areas that manage thinking.
- The center for control of the heartbeat is present in the medulla.
- And cerebellum is associated with the functioning of balance.
Q4: What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer:
Receptors are specialized sensory nerve endings in the periphery that on stimulation generate sensory nerve impulses. They are present in all parts of our body, e.g., in the skin, nose, eyes, ears, tongue, muscle fibers, etc. Some of them are:
- Tactile corpuscles/Meissner’s corpuscles: Present in the papillae of the skin.
- Stretch receptors: Present in the alveoli & bronchioles of lungs, arteries & veins.
- Auditory/Acoustic receptors: Present in the organ of corti of the internal ear.
- Olfactory epithelium: Present in the mucous membrane of a nose.
- Taste buds: Present in the papillae of the tongue.
Some situations where receptors don’t work properly & the problems associated with them:
- In case of any damage to the skin receptor, when someone accidentally touches a hot object, his hand might get burnt as the damaged receptor cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
- When a cold occurs, humans get congested, which leads to a stop in airflow to the olfactory receptors. Without odor compounds being able to make it to olfactory receptors, the sense of smell is significantly weakened to a point where it barely works.
- In case of fever, body temperature rises up which affects the oral cavity & taste buds. Fever also leads to dehydration, because of this the moisture content of the mouth decreases and results in an alteration of taste.
Q5: Draw the structure of a neuron & explain its function.
Answer:
Neurons or nerve cells are the basic building blocks or units of the nervous system. They are highly specialized cells that act as information processing and transmitting units of the brain. A group of neurons forms a nerve. Structure of a neuron: All neurons have three main parts: Dendrites, Cell body or Soma, and Axons.
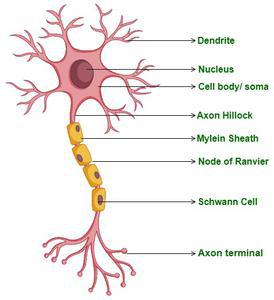
Structure of Neuron
- Dendrites: Detect chemical signals from other cells and neurons. Carrying electrical impulses toward the next part of the neuron, the cell body.
- Cell body or Soma: Supporting and organizing the functions of the whole neuron. Joining the signals received by the dendrites and passing them to the axons, the next part of the neuron.
- Axons: Axons help to receive signals from other neurons and transmit the outflow of the message to the adjacent connected neurons and also to other muscles and glands by changing the electrical potential of the cell membrane called the action potential.
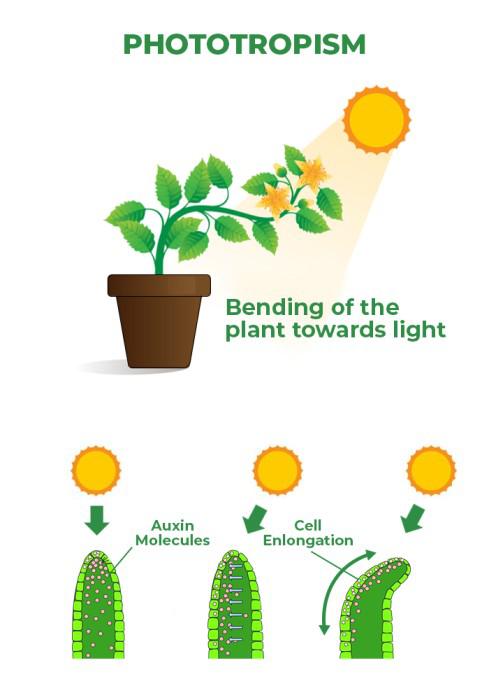
Q6: How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer:
The growth movements in plants in response to light stimulus are known as Phototropism. The shoots show positive phototropism & the roots show negative phototropism. E.g. The flower head of the sunflower is positively phototropic & hence it moves from east to west along with the sun.
Process of Phototropism:
- When sunlight falls straight on the plant, the auxin hormone synthesized at the tip of the stem spreads uniformly down the stem, and due to an equal concentration of auxin, the stem grows straight.
- When sunlight falls on only one side of the plant, the auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. The concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer. Therefore, the stem appears to bend towards the source of light.
Q7: Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer:
Spinal cord acts as a connecting link in the central nervous system. All afferent nerve paths enter through the spinal cord & all efferent nerve paths come out through it. The sympathetic fibers arise from thoracic & lumbar segments & the parasympathetic fibers arise from sacral segments of the spinal cord. Thus the spinal cord acts as the nerve center of the autonomous nervous system.
So, any injury to the spinal cord:
- Would impede the transmission of somatic motor impulses, which are the voluntary motions performed by skeletal muscle.
- A spinal cord injury would also have an effect on the body’s reflex activities because it acts as the nerve center for different reflex actions like knee jerk, postural reflex, etc.
Q8: How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer:
Chemical coordination occurs in plants with the help of phytohormones or plant hormones secreted by plants. Auxin, cytokinin, gibberellin, and abscisic acid are plant hormones. These hormones regulate the growth and development of the plants. They also regulate various metabolic activities in the plants. These hormones respond to external stimuli like light, temperature, etc. For example:
- Auxin is responsible for the growth of the plants.
- Cytokinin is responsible for cell division.
- Similarly, gibberellin is responsible for stem elongation, flowering, and fruit ripening.
- Abscisic acid is responsible for dormancy.
Q9: What is the need for a system of control & coordination in an organism?
Answer:
Control and coordination are brought about by the nervous system and chemical control and coordination occur with the help of endocrine systems. It regulates all the systems of the body to ensure proper coordination and efficient functioning of an organism.
They are important for an organism to adapt to the changes and perform important functions like metabolism, homeostasis, etc. It also helps in responding to stimuli that help in the fight, or flight responses. This occurs through the PNS and ANS that comprise the nervous system and control the musculoskeletal systems for such responses. Thus, control and coordination are important processes for the survival of an organism.
Q10: How are involuntary actions & reflex actions different from each other?
Answer:
|
Involuntary actions
|
Reflex actions
|
| Involuntary action is a set of muscle movements that do not require thinking. |
Reflex action is a sudden and involuntary response to stimuli |
| These actions are controlled by the medulla oblongata or the midbrain. |
These actions are controlled by the spinal cord. |
| The speed is relatively slower. |
The speed is relatively slower. |
| Example: Beating of heart |
Example: Blinking of eyes. |
Q11: Compare & contrast nervous & hormonal mechanisms for control & coordination in animals.
Answer:
|
Nervous Mechanism
|
Hormonal Mechanism
|
| Nerve cells take part in it |
Endocrine glands take part in it. |
| Signals travel along the neurons |
Signals are transmitted through blood. |
| Signals travel quickly & the response is quick |
Signals travel slowly, hence response is slow. |
| Signals are transferred in the form of electrical impulses |
Signals are transferred in the form of chemicals called hormones. |
Q12: What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer:
|
Plant Movement
|
Leg Movement
|
| A sensitive plant’s movement is an involuntary response to stimuli. |
Leg movement is a completely voluntary and conscious reaction. |
| It does not require any specific tissues for information transmission. |
Leg mobility is aided by a sophisticated neural system network that includes the CNS and PNS. |
| There are no specific proteins involved in the movement of the sensitive plant. |
Actin, myosin, and other proteins aid in the contraction and relaxation of leg muscles to facilitate leg movement. |
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 7 Control And Coordination
- They enhance the conceptual knowledge of the students.
- Clear and Comprehensible Content.
- Aid in Competitive Exam Preparation.
- The answers are provided by Top subject experts.
- Readily available and easily accessible.
- As per the revised curriculum of CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter, previously known as Chapter 7 Control And Coordination, has now been renumbered as Chapter 6 Control And Coordination. Stay updated with the latest changes in the CBSE curriculum.
- NCERT Solutions for Control And Coordination focuses on how organisms respond to a change in their environment. This chapter explains the controlled movement of organisms in detail. It also explains how different parts of the brain work in synchronization to carry out coordinated and controlled movements.
Also Check:
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination
What is the name of Class 10 Chapter 7 of NCERT Class 10 Biology?
NCERT Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 name is Control and Coordination which explains all the important processes needed for living organisms to coordinate or for control.
Where can I find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination can be found on various online platforms such as the official NCERT website, GeeksforGeeks, and more.
What does the concept of Synaptic Transmission entail in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination?
Synaptic transmission acts as a one way valve to transmit impulses in one direction only. It is a process through which neurons communicate with each other in the nervous system. Neurons transmit information in the form of electrical and chemical signals and synapses are the junctions where these signals are exchanged between neurons.
How can students benefit from the CBSE Free PDF Download of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination ?
Students can benefit from the CBSE Free PDF Download available through online free resources. They can get study materials, textbooks, and other educational resources for NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination at no cost. These PDFs can be great additions to their learning, helping them to review, practice, and increase their understanding of various subjects and topics. It offers an easy way to study and prepare for exams.
What are the important topics in Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination?
Following are are the important topics covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination:
- Animals – Nervous System (Reflex actions, Human brain, Nervous tissue)
- Coordination in Plants (Immediate response to stimulus, Movement due to growth)
- Hormones in animals
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...