N Queen Problem
Last Updated :
03 Oct, 2023
We have discussed Knight’s tour and Rat in a Maze problem earlier as examples of Backtracking problems. Let us discuss N Queen as another example problem that can be solved using backtracking.
What is N-Queen problem?
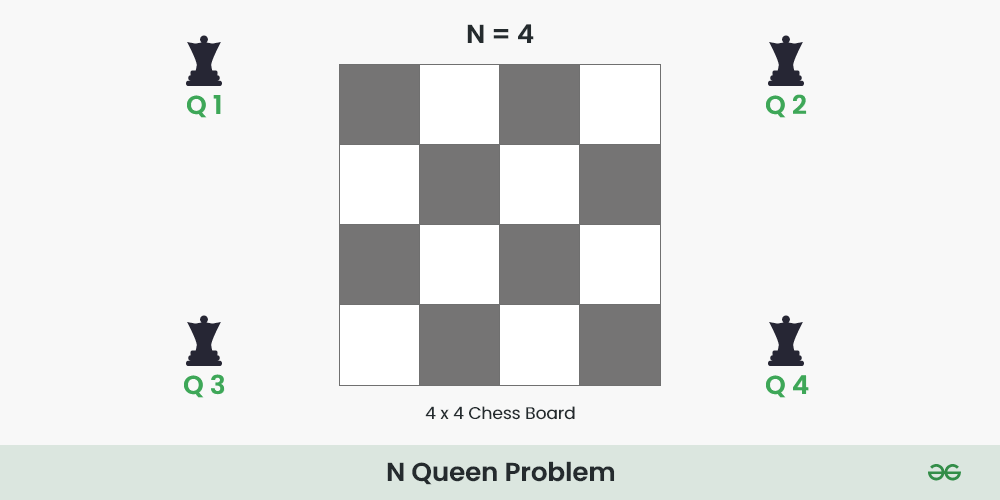
The N Queen is the problem of placing N chess queens on an N×N chessboard so that no two queens attack each other.
For example, the following is a solution for the 4 Queen problem.

The expected output is in the form of a matrix that has ‘Q‘s for the blocks where queens are placed and the empty spaces are represented by ‘.’ . For example, the following is the output matrix for the above 4-Queen solution.
. Q . .
. . . Q
Q . . .
. . Q .
The idea is to place queens one by one in different columns, starting from the leftmost column. When we place a queen in a column, we check for clashes with already placed queens. In the current column, if we find a row for which there is no clash, we mark this row and column as part of the solution. If we do not find such a row due to clashes, then we backtrack and return false.
Below is the recursive tree of the above approach:
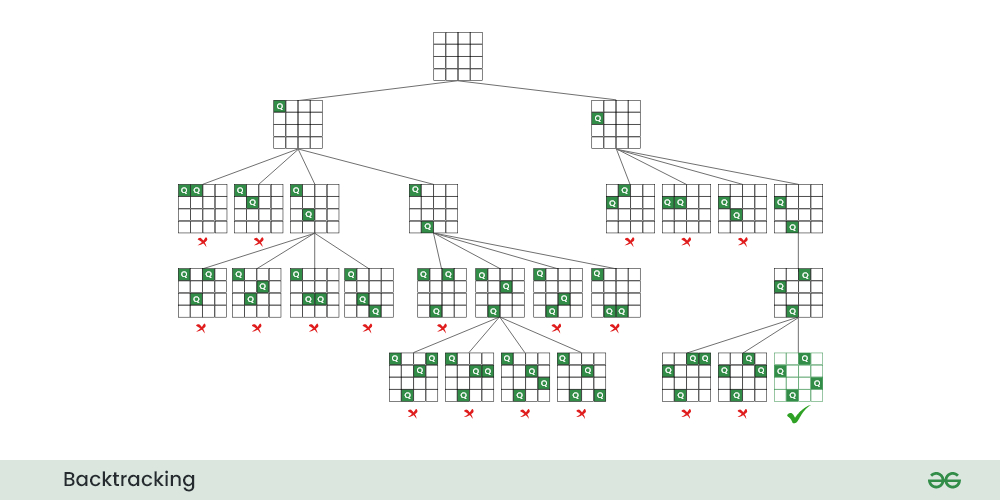
Recursive tree for N Queen problem
Follow the steps mentioned below to implement the idea:
- Start in the leftmost column
- If all queens are placed return true
- Try all rows in the current column. Do the following for every row.
- If the queen can be placed safely in this row
- Then mark this [row, column] as part of the solution and recursively check if placing queen here leads to a solution.
- If placing the queen in [row, column] leads to a solution then return true.
- If placing queen doesn’t lead to a solution then unmark this [row, column] then backtrack and try other rows.
- If all rows have been tried and valid solution is not found return false to trigger backtracking.
For better visualisation of this backtracking approach, please refer 4 Queen problem.
Note: We can also solve this problem by placing queens in rows as well.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 4
using namespace std;
void printSolution(int board[N][N])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
if(board[i][j])
cout << "Q ";
else cout<<". ";
printf("\n");
}
}
bool isSafe(int board[N][N], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i])
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false;
return true;
}
bool solveNQUtil(int board[N][N], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
board[i][col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true;
board[i][col] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int board[N][N] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false) {
cout << "Solution does not exist";
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
int main()
{
solveNQ();
return 0;
}
|
C
#define N 4
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void printSolution(int board[N][N])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if(board[i][j])
printf("Q ");
else
printf(". ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
bool isSafe(int board[N][N], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i])
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false;
return true;
}
bool solveNQUtil(int board[N][N], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
board[i][col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true;
board[i][col] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int board[N][N] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false) {
printf("Solution does not exist");
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
int main()
{
solveNQ();
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class NQueenProblem {
final int N = 4;
void printSolution(int board[][])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 1)
System.out.print("Q ");
else
System.out.print(". ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
boolean isSafe(int board[][], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i] == 1)
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j] == 1)
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j] == 1)
return false;
return true;
}
boolean solveNQUtil(int board[][], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
board[i][col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) == true)
return true;
board[i][col] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
boolean solveNQ()
{
int board[][] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false) {
System.out.print("Solution does not exist");
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
NQueenProblem Queen = new NQueenProblem();
Queen.solveNQ();
}
}
|
Python3
global N
N = 4
def printSolution(board):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if board[i][j] == 1:
print("Q",end=" ")
else:
print(".",end=" ")
print()
def isSafe(board, row, col):
for i in range(col):
if board[row][i] == 1:
return False
for i, j in zip(range(row, -1, -1),
range(col, -1, -1)):
if board[i][j] == 1:
return False
for i, j in zip(range(row, N, 1),
range(col, -1, -1)):
if board[i][j] == 1:
return False
return True
def solveNQUtil(board, col):
if col >= N:
return True
for i in range(N):
if isSafe(board, i, col):
board[i][col] = 1
if solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) == True:
return True
board[i][col] = 0
return False
def solveNQ():
board = [[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]]
if solveNQUtil(board, 0) == False:
print("Solution does not exist")
return False
printSolution(board)
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
solveNQ()
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
readonly int N = 4;
void printSolution(int [,]board)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (board[i, j] == 1)
Console.Write("Q ");
else
Console.Write(". ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
bool isSafe(int [,]board, int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row,i] == 1)
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 &&
j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i,j] == 1)
return false;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 &&
i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i, j] == 1)
return false;
return true;
}
bool solveNQUtil(int [,]board, int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (isSafe(board, i, col))
{
board[i, col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) == true)
return true;
board[i, col] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int [,]board = {{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 }};
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false)
{
Console.Write("Solution does not exist");
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
GFG Queen = new GFG();
Queen.solveNQ();
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
const N = 4
function printSolution(board)
{
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for(let j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if(board[i][j] == 1)
document.write("Q ")
else
document.write(". ")
}
document.write("</br>")
}
}
function isSafe(board, row, col)
{
for(let i = 0; i < col; i++){
if(board[row][i] == 1)
return false
}
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false
return true
}
function solveNQUtil(board, col){
if(col >= N)
return true
for(let i=0;i<N;i++){
if(isSafe(board, i, col)==true){
board[i][col] = 1
if(solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) == true)
return true
board[i][col] = 0
}
}
return false
}
function solveNQ(){
let board = [ [0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0] ]
if(solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false){
document.write("Solution does not exist")
return false
}
printSolution(board)
return true
}
solveNQ()
</script>
|
Output
. . Q .
Q . . .
. . . Q
. Q . .
Time Complexity: O(N!)
Auxiliary Space: O(N2)
Further Optimization in is_safe() function:
The idea is not to check every element in the right and left diagonal, instead use the property of diagonals:
- The sum of i and j is constant and unique for each right diagonal, where i is the row of elements and j is the
column of elements.
- The difference between i and j is constant and unique for each left diagonal, where i and j are row and column of element respectively.
Below is the implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
int ld[30] = { 0 };
int rd[30] = { 0 };
int cl[30] = { 0 };
void printSolution(int board[N][N])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout << " " << (board[i][j]==1?"Q":".") << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
bool solveNQUtil(int board[N][N], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1 && rd[i + col] != 1)
&& cl[i] != 1) {
board[i][col] = 1;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true;
board[i][col] = 0;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int board[N][N] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false) {
cout << "Solution does not exist";
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
int main()
{
solveNQ();
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int N = 4;
static int[] ld = new int[30];
static int[] rd = new int[30];
static int[] cl = new int[30];
static void printSolution(int board[][])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.printf(" %d ", board[i][j]);
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
static boolean solveNQUtil(int board[][], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1
&& rd[i + col] != 1)
&& cl[i] != 1) {
board[i][col] = 1;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i]
= 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true;
board[i][col] = 0;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i]
= 0;
}
}
return false;
}
static boolean solveNQ()
{
int board[][] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false) {
System.out.printf("Solution does not exist");
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
solveNQ();
}
}
|
Python3
N = 4
ld = [0] * 30
rd = [0] * 30
cl = [0] * 30
def printSolution(board):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
print(board[i][j], end=" ")
print()
def solveNQUtil(board, col):
if (col >= N):
return True
for i in range(N):
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1 and
rd[i + col] != 1) and cl[i] != 1):
board[i][col] = 1
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1)):
return True
board[i][col] = 0
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0
return False
def solveNQ():
board = [[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]]
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == False):
printf("Solution does not exist")
return False
printSolution(board)
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
solveNQ()
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int N = 4;
static int[] ld = new int[30];
static int[] rd = new int[30];
static int[] cl = new int[30];
static void printSolution(int[, ] board)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write(" {0} ", board[i, j]);
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
static bool solveNQUtil(int[, ] board, int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1
&& rd[i + col] != 1)
&& cl[i] != 1) {
board[i, col] = 1;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i]
= 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true;
board[i, col] = 0;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i]
= 0;
}
}
return false;
}
static bool solveNQ()
{
int[, ] board = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false) {
Console.Write("Solution does not exist");
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
solveNQ();
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let N = 4;
let ld = new Array(30);
let rd = new Array(30);
let cl = new Array(30);
function printSolution( board)
{
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++)
document.write(board[i][j] + " ");
document.write("<br/>");
}
}
function solveNQUtil(board, col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1 &&
rd[i + col] != 1) && cl[i] != 1)
{
board[i][col] = 1;
ld[i - col + N - 1] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true;
board[i][col] = 0;
ld[i - col + N - 1] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
function solveNQ()
{
let board = [[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ]];
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false)
{
document.write("Solution does not exist");
return false;
}
printSolution(board);
return true;
}
solveNQ();
</script>
|
Output
. . Q .
Q . . .
. . . Q
. Q . .
Time Complexity: O(N!)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Related Articles:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...