Muscular Tissue
Last Updated :
09 Apr, 2024
Muscular tissue is a type of tissue present in animals that is specialized for contraction and movement. Muscular tissue is one of the four main types of tissues, the others being epithelial, connective, and nervous tissue. Muscular tissue is made up of muscle fibers. There are three types of muscular tissues. In this article, we will cover muscular tissue in detail.
Muscle Tissue Definition and Meaning
Definition – Muscle tissue is a specialized animal tissue responsible for movement. It is characterized by its ability to contract and generate force, facilitating bodily movement and maintaining posture.
Muscle tissue is engaged with movements or for other body developments inside interior organs. There are three types of muscle tissue:
- Skeletal Muscles— joined to bones
- Strong Tissue—inside the middle.
- Smooth Muscle— inside the inward walls of organs like the anus, or alimentary canal.
Muscle Tissue Location
Muscle tissue is found throughout the body, attached to bones, surrounding internal organs, and even in the walls of blood vessels. Skeletal muscle, the most abundant type, is attached to bones and responsible for voluntary movements. Smooth muscle lines organs like the stomach and intestines, helping in involuntary processes like digestion. Cardiac muscle forms the heart and is crucial for pumping blood throughout the body.
Muscular Tissue Diagram
The labeled diagram of muscular tissue is given below:
Solid tissue is a particular tissue in creatures that applies powers to various pieces of the body by compression. It comprises slight and prolonged cells called muscle strands. It controls the development of a life form.
The cytoplasm in the muscle filaments is called sarcoplasm. It contains an organization of membranes called the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The membrane encompassing the muscle strands is called sarcolemma.
What are the Properties of Muscular Tissue?
Some of the properties of muscular tissue are given below:
- Contractibility: It is the capacity of muscle cells to powerfully abbreviate.
- Extensibility: A muscle can be extended.
- Elasticity: The muscles can regain their original length after stretching.
- Excitability: The muscle tissue reacts to the external stimulus carried by motor neurons.
- Highly vascularized: Muscular tissue is richly supplied with blood vessels, which provide oxygen and nutrients to the tissue and remove waste products.
- Striated or smooth appearance: Depending on the type of muscular tissue, it may have a striped or smooth appearance under a microscope. Skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue are striated, while smooth muscle tissue is not.
The characteristics of muscular tissue allow for efficient and coordinated movement, as well as the performance of other important physiological functions.
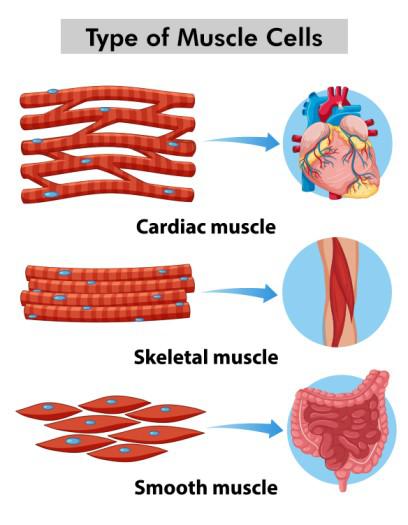
Types of Muscular Tissue
The muscular tissue is of three types:
- Skeletal muscle Tissue
- Smooth Muscle Tissue
- Cardiovascular Muscle Tissue
Skeletal/ Striated Muscle Tissue
- Skeletal Muscles are joined with the skeleton and help in the movement of the organism.
- Skeletal Muscles are also called striated muscles because of their striped appearance i.e. alternate patterns of light and dark bands in their cells under a microscope.
- Almost 40% of the body mass of a body is comprised of skeletal muscle.
- Striated muscle tissue contained myofibrils.
- Striated muscles cell are multinucleated.
- Blood vessels, elongated mitochondria, and glycogen-containing granules are present in skeletal muscles.
- Organism movement is done via skeletal muscles.

Smooth Muscle Tissue
- Smooth muscles are non-striated, controlled via Autonomous Nervous System as these are involuntary muscles
- It animates the contractility of the stomach-related, urinary, conceptive frameworks, veins, and aviation routes.
- The actin and myosin fibers are extremely thin and arranged randomly, thus no striations.
- Smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped and are single nucleated.

Also Read: Difference Between Cardiac Muscle And Skeletal Muscle
Heart/Cardiac Muscle Tissue
- As the name suggests cardiac they are only present in the heart.
- The heart pumps blood due to the contraction of cardiac muscle.
- Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles.
- The cells of the cardiovascular muscles also known as cardiomyocytes are striated.
- Cardiac muscle cells are uninucleated and single cells.
- The cardiac cells are joined together with the junction known as desmosomes. The end part of the cell is joined with another cell via a junction known as an intercalated disc.

Also Read: Cell-Cell Interaction
Muscular Tissue Function
The function of muscular tissue are given here:
- Muscular tissue is responsible for the movement of the body and its internal organs of an organism.
- Skeletal muscles are responsible for maintaining the posture of the body and supporting the weight.
- Muscular tissue produces heat as a byproduct of metabolic processes. The heat helps to maintain body temperature.
- Some muscular tissues can also provide protection to internal organs.
- Muscles can be found in and around openings in the body.
Conclusion: Muscular Tissue – Structure, Functions, Types and Characteristics
In conclusion, muscular tissue is essential for movement and bodily functions. Muscular tissue examples are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Its properties, including contractibility and excitability, facilitate coordinated movement and internal organ function. Understanding the types, properties, and functions of muscular tissue is vital for learning its role in the body’s physiology and overall health.
Also Read:
FAQs on Muscular Tissue – Structure, Functions, Types and Characteristics
What are the 3 Types of Muscular Tissue?
The 3 types of muscular tissue are: Smooth muscle, cardiac muscles, and skeletal muscle.
What are Muscle Tissue and its Importance?
Muscle tissue consists of cells specialized in contraction, enabling movement and maintaining posture, essential for bodily functions.
What is the Most Distinguishing Characteristic of Muscle Tissue?
The most distinguishing characteristic of muscle tissue is its contractility, allowing it to generate tension and produce movement.
What are the 4 Functions of Muscle Tissue?
The four functions of muscle tissue are movement (skeletal muscle contraction), stability (postural support), heat production (thermogenesis), and control of organ volume (smooth muscle contraction).
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...