Mongoose prototype.Aggregate() API
Last Updated :
27 Mar, 2023
The API.prototype.Aggregate() method of the Mongoose API is used to build aggregation pipelines. Aggregation is a method of processing many documents by sending them through multiple phases.
Syntax:
Model.aggregate()
Parameters:
- pipeline: It is an array that is an aggregation pipeline as an array of objects.
- model: It is a method to use with this aggregate.
Returns: It returns plan JavaScript Objects.
Setting up Node.js application:
Step 1: Create a Node.js application using the following command:
npm init
Step 2: After creating the NodeJS application, Install the required module using the following command:
npm install mongoose
Project Structure: The project structure will look like this:

output
Example 1: In this example, we have established a database connection using mongoose and defined a model over schema, having three columns or fields “name”, “marks” and “mobile”. In the end, we are using the aggregate() method on the User model which will use match and filter some tuples of lists from the User collection.
Database Structure: The database structure will look like this, Three documents are present in the collection over which we match the document with marks greater than 87. In collection, we have only two documents with marks greater than 87.

output2
Filename: app.js
Javascript
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
mongoose.set("strictQuery", false);
mongoose
.connect(url)
.then((ans) => {
console.log("Connected Successful");
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log("Error in the Connection");
});
let Schema = mongoose.Schema;
let schema = new Schema({
name: String,
marks: Number,
mobile: Number,
});
let Person = mongoose.model("gfgs", schema);
let find = async () => {
const aggregate = await Person.aggregate([
{ $match: { marks: { $gte: 87 } } },
]);
return aggregate;
};
find().then((x, y) => {
for (let i of x) console.log(`${i.name} got ${i.marks}`);
});
|
Output:

output3
Example 2: In this example, we are using the count pipeline inside the asynchronous function to count the matched document inside the collection.
Filename: script.js
Javascript
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
mongoose.set('strictQuery', false);
mongoose.connect(url)
.then((ans) => {
console.log("Connected Successful")
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log("Error in the Connection")
})
const Schema = mongoose.Schema;
let schema = new Schema({
firstName: String,
lastName: String,
});
let Person = mongoose.model('person', schema);
let find = async () => {
const aggregate = await Person.aggregate([
{ $match: { lastName: 'Verma' } },
{ $count: 'Matched' }
]).exec((err, fi) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(fi);
})
return aggregate;
}
find();
|
Output:
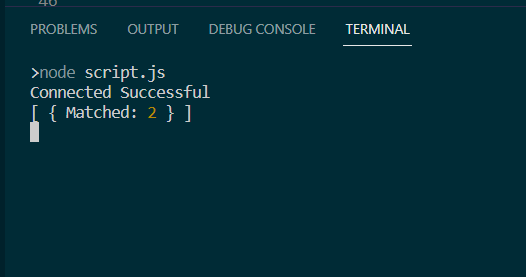
output4
Reference: https://mongoosejs.com/docs/api/mongoose.html#mongoose_Mongoose
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...