MongoDB Tutorial in Java
Last Updated :
25 Jul, 2022
MongoDB is an open-source cross-platform document database developed using C++. Some features of MongoDB are:
- High and effective performance
- Easily scalable
- High availability
- It can store high volume of data
It contains data in the form of collections and documents instead of rows and tables. A collection is a set of documents. The collection does not have schemas. It represents data in the form of a hierarchical model with which the storage of arrays and other data structures will be easy.
Components of MongoDB
The essentials components of MongoDB are listed below:
- id: This field represents a unique field in MongoDB. This field is created by default.
- Collection: It is a set of MongoDB documents. It exists with a single database.
- Database: This is the container for collections. Multiple databases can be stored in a mongoDB server.
- Document: A record in mongoDB is called a document. It contains names and values.
- Field: It is a name-value pair in a document.
Note: Make sure to install and setup MongoDB JDBC driver and Java.
Table of contents:
1. Establishing connections to database
2. Creating a MongoDb collection
3. Getting a Collection
4. Inserting Values into MongoDb
5. Displaying the list of all Documents
6. Updating documents in the MongoDB
7. Deleting a Document
8. Dropping of a Collection
9. Displaying all the collections
Establishing connections to database
For making the connection, you have to mention the database name. MongoDB creates a database by default if no name is mentioned.
- Firstly, import the required libraries for establishing the connection.
- Here, “MongoClient” is used to create the client for the database.
- “MongoCredential” is used for creating the credentials.
- And finally, to access the database “MongoDatabase” is used.
- Username will be: “GFGUser” and the database name will be “mongoDb“.
- The function “.toCharArray()” is used to convert the password into a character array.
- The function “.getDatabase()” is used for getting the database.
The following code establishes a connection to MongoDB ->
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class ConnectionDB {
public static void establishConnections()
{
try {
MongoClient db
= new MongoClient("localhost", 27017);
MongoCredential credential;
credential
= MongoCredential
.createCredential(
"GFGUser", "mongoDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println(
"Successfully Connected"
+ " to the database");
MongoDatabase database
= db.getDatabase("mongoDb");
System.out.println("Credentials are: "
+ credential);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Connection establishment failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 
Creating a MongoDb collection:
To create a collection com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase class and createCollection() method is used. Here, “database.createCollection()” creates a collection named as “GFGCollection”. Following is the code for creating collection:
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void createCollection(
String collectionName)
{
try {
establishConnections();
MongoDatabase database
= db.getDatabase("mongoDb");
database.createCollection(collectionName);
System.out.println(
"Collection created Successfully");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Collection creation failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 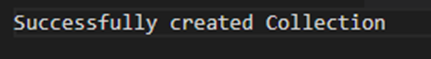
Getting a Collection
For getting a collection, MongoCollection.getCollection() method is used. Below is the implementation of this approach:
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void getCollection(
String collectionName)
{
try {
establishConnections();
MongoCollection<Document>
collection = database
.getCollection(collectionName);
System.out.println(
"Collection retrieved Successfully");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Collection retrieval failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output 
Inserting Values into MongoDb
Only a document type of data can be inserted a MongoDB. Therefore, either we can create a document with the values to be inserted using append() method or pass a document directly into the MongoDB using .insert() method. Here, first, we created a new document as “title” and then append the “about” section. Then, we have given the respective values to the documents. The function “.insertOne()” is used to insert the document into the collection. Below is the implementation of this approach:
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void insertADocIntoDb()
{
try {
establishConnections();
Document document
= new Document("title",
"MongoDB")
.append("about",
"Open-Source database")
collection.insertOne(document);
System.out.println(
"Document inserted Successfully");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Document insertion failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public static void insertManyDocsIntoDb()
{
try {
establishConnections();
Document document
= new Document("title", "MongoDB")
.append("about", "Open-Source database");
Document document1
= new Document("title", "retrieveDb")
.append("about", "Open-source database");
List<Document> dblist
= new ArrayList<Document>();
dblist.add(document);
dblist.add(document1);
collection.insertMany(dblist);
System.out.println(
"Documents inserted Successfully");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Documents insertion failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 
Displaying the list of all Documents
For displaying all documents of collection, find() method is used. Here, the database has two documents namely “document” and “document1”, which are retrieved using find() method. We use an iterator since it will iterate over each document present in the list and display it to us. Following is code for displaying all the documents:
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void displayDocuments()
{
try {
establishConnections();
System.out.println(
"Displaying the list"
+ " of Documents");
FindIterable<Document> iterobj
= collection.find();
Iterator itr = iterobj.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Could not find the documents "
+ "or No document exists");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 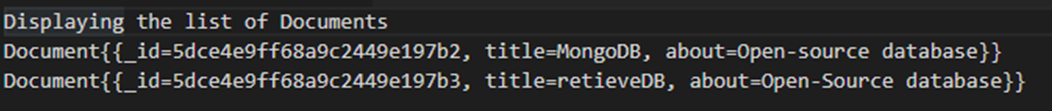
Updating documents in the MongoDb
For updating the document, updateOne() method is used. Here, “Filters.eq” creates a filter that matches all documents with the name provided as argument. “Updates.set()” is used to update the document as the given value in the argument. Following is the code for it:
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void updateDocuments()
{
try {
establishConnections();
MongoDatabase database
= mongo.getDatabase("mongoDb");
MongoCollection<Document> collection
= database.getCollection(
"GFGCollection");
collection.updateOne(
Filters.eq("title", "MongoDB"),
Updates.set("about", "Database"));
System.out.println(
"Successfully updated"
+ " the document");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Updation failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 
Deleting a Document
For deleting the document, deleteOne() method is used. Following is the code for deleting the document ->
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void deleteDocuments()
{
try {
establishConnections();
MongoDatabase database
= mongo.getDatabase("mongoDb");
MongoCollection<Document> collection
= database.getCollection(
"GFGCollection");
collection.deleteOne(
Filters.eq("title",
"Open-Source Database"));
System.out.println(
"Successfully deleted"
+ " the document");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Deletion failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 
Dropping of a Collection
“Collection.drop()” is used to drop the created collection. Following is the code for dropping the collection:
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void dropACollection()
{
try {
establishConnections();
MongoCollection<Document>
collection = database
.getCollection(
"GFGCollection");
collection.drop();
System.out.println(
"Successfully dropped"
+ " collection");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Drop failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 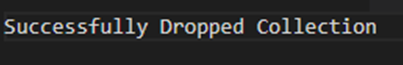
Displaying all the collections
For displaying the list of all collections, listCollectionNames() method is used. Here, we iterate over all the collections we created with the help of “for()” statement. Database.listCollectionNames() is used to display the list of all collections present in the database. Following is the code for displaying all the collections:
Java
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class Collection {
public static void displayCollections()
{
try {
establishConnections();
MongoDatabase database
= mongo.getDatabase("mongoDb");
System.out.println(
"Displaying the list"
+ " of all collections");
MongoCollection<Document> collection
= database.getCollection(
"GFGCollection");
for (String allColl : database
.listCollectionNames()) {
System.out.println(allColl);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Collections display failed");
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
|
Output: 
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...