modinfo command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
23 May, 2019
modinfo command in Linux system is used to display the information about a Linux Kernel module. This command extracts the information from the Linux kernel modules given on the command line. If the module name is not a file name, then the /lib/modules/kernel-version directory is searched by default. modinfo can understand modules from any of the Linux Kernel architecture.
Syntax:
modinfo [-0] [-F field] [-k kernel] [modulename|filename...]
Example:
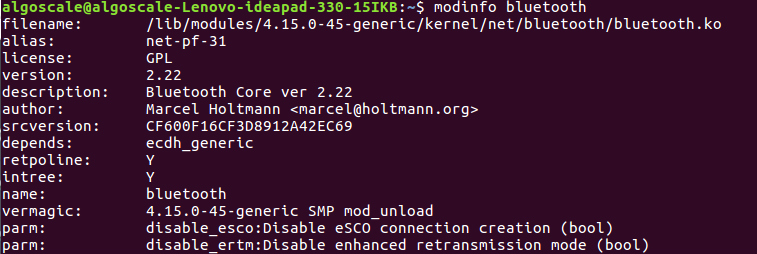
modinfo bluetooth
Options:
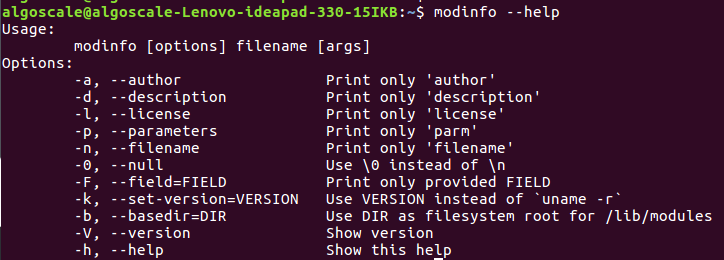
- modinfo command with help option: It will print the general syntax of the modinfo along with the various options and gives a brief description about each option.
- modinfo -V: This option gives the version information of modinfo command.
modinfo -V

- modinfo -F: This option only print this field value, one per line. Field names are case-insensitive. Common fields that may include author, description, license, parm, depends, and alias. There are possibly multiple parm, alias and depends on fields. The special field filename lists are the filename of the module.
modinfo -F modulename
- modinfo -b : This option is the root directory for modules.
modinfo -b modulename
- modinfo -k : This option provides the information about a kernel other than the running one. This option is particularly being useful for the distributions that need to extract information from a newly installed set of kernel modules. For example, to find which firmware files are needed by various modules inside a new kernel for which you need to make an initrd/initramfs image prior to booting.
modinfo -k modulename
- modinfo -0: This option use the ASCII zero character to separate field values, instead of a new line. This option is proven useful for scripts since a new line can theoretically appear inside a field.
Example:
modinfo bluetooth -0

- modinfo -a –author, -d –description, -l –license, -p –parameters, -n –filename: These are the shortcuts used for the –field flag’s author, description, license, parm and filename arguments to make the transition from the old modutils modinfo easy.
Example:
modinfo bluetooth -a

modinfo bluetooth -n

modinfo bluetooth -d

modinfo bluetooth -l

modinfo bluetooth -p

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...