ML | Random Initialization Trap in K-Means
Last Updated :
08 Jun, 2021
Random initialization trap is a problem that occurs in the K-means algorithm. In random initialization trap when the centroids of the clusters to be generated are explicitly defined by the User then inconsistency may be created and this may sometimes lead to generating wrong clusters in the dataset. So random initialization trap may sometimes prevent us from developing the correct clusters.
Example :
Suppose you have a dataset with the following points shown in the picture and you want to generate three clusters in this dataset according to their attributes by performing K-means clustering. From the figure, we can get the intuition what are the clusters that are required to be generated. K-means will perform clustering on the basis of the centroids fed into the algorithm and generate the required clusters according to these centroids.

First Trial
Suppose we choose 3 sets of centroids according to the figure shown below. The clusters that are generated corresponding to these centroids are shown in the figure below.
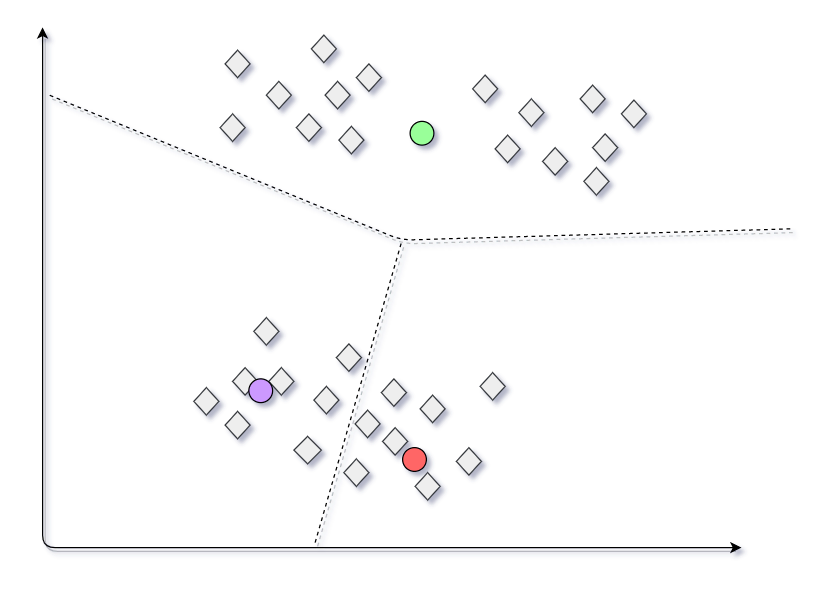
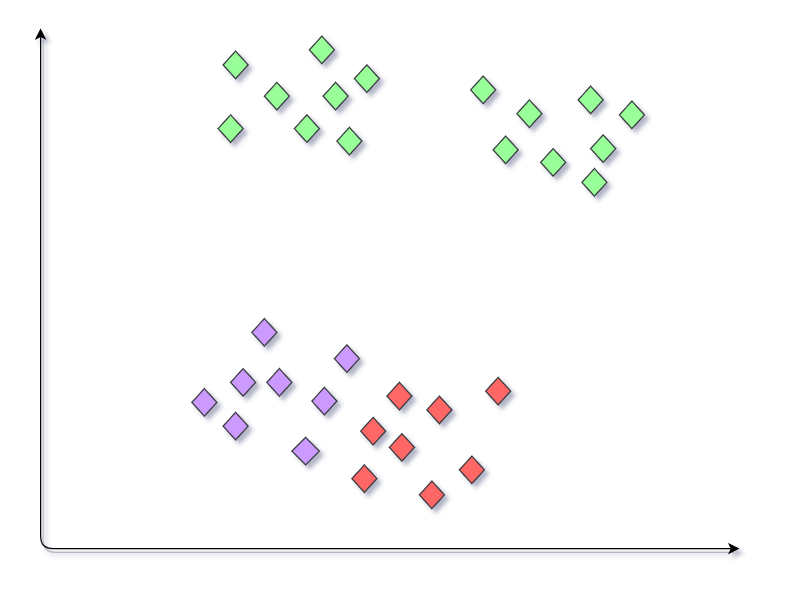
Final Model

Second Trial
Consider another case in which we choose another set of centroids for the dataset as shown. Now the set of clusters generated will be different from the clusters generated in the previous practice.
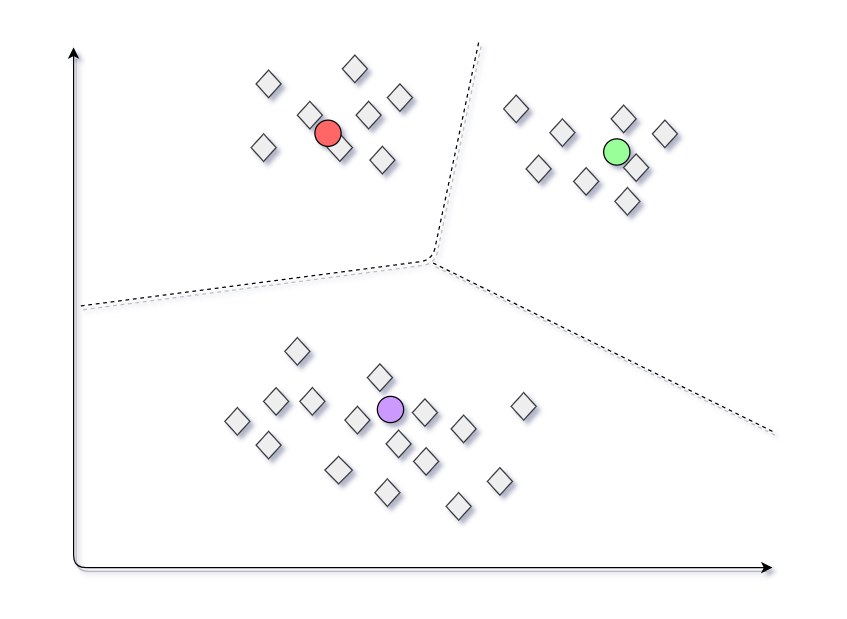
Final model
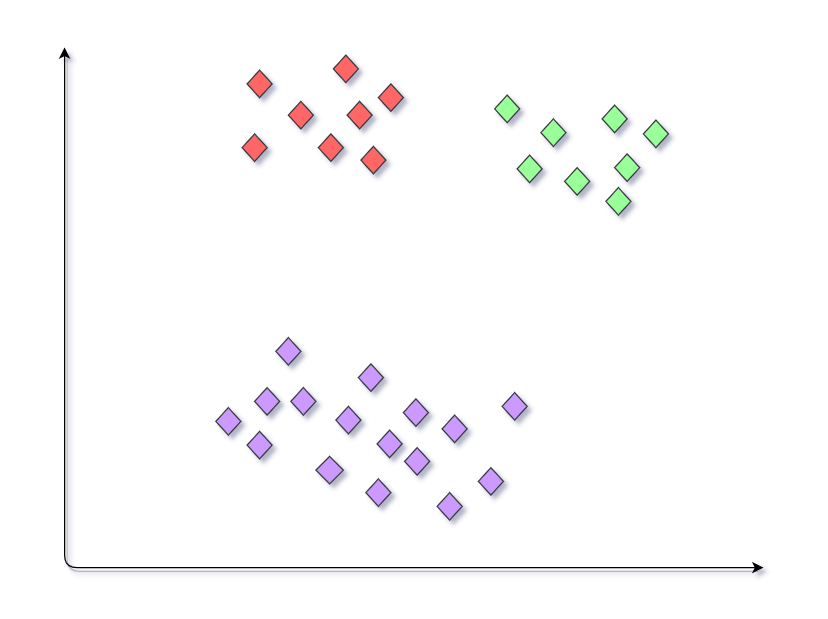
Similarly we may get different model outputs on the same dataset. This condition where a different set of clusters is generated when a different set of centroids are provided to the K-means algorithm making it inconsistent and unreliable is called the Random initialization trap.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...