ML | Kaggle Breast Cancer Wisconsin Diagnosis using KNN and Cross Validation
Last Updated :
21 Aug, 2020
Dataset :
It is given by Kaggle from UCI Machine Learning Repository, in one of its challenges.
https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/breast-cancer-wisconsin-data. It is a dataset of Breast Cancer patients with Malignant and Benign tumor.
K-nearest neighbour algorithm is used to predict whether is patient is having cancer (Malignant tumour) or not (Benign tumour).
Implementation of KNN algorithm for classification.
Code : Importing Libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
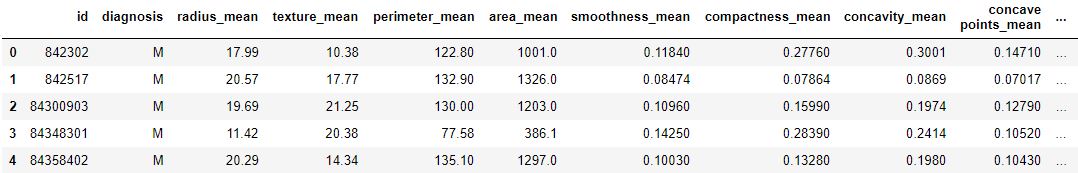
Code : Loading dataset
df = pd.read_csv("..\\breast-cancer-wisconsin-data\\data.csv")
print (data.head)
|
Output :
Code: Data Info
Output :
RangeIndex: 569 entries, 0 to 568
Data columns (total 33 columns):
id 569 non-null int64
diagnosis 569 non-null object
radius_mean 569 non-null float64
texture_mean 569 non-null float64
perimeter_mean 569 non-null float64
area_mean 569 non-null float64
smoothness_mean 569 non-null float64
compactness_mean 569 non-null float64
concavity_mean 569 non-null float64
concave points_mean 569 non-null float64
symmetry_mean 569 non-null float64
fractal_dimension_mean 569 non-null float64
radius_se 569 non-null float64
texture_se 569 non-null float64
perimeter_se 569 non-null float64
area_se 569 non-null float64
smoothness_se 569 non-null float64
compactness_se 569 non-null float64
concavity_se 569 non-null float64
concave points_se 569 non-null float64
symmetry_se 569 non-null float64
fractal_dimension_se 569 non-null float64
radius_worst 569 non-null float64
texture_worst 569 non-null float64
perimeter_worst 569 non-null float64
area_worst 569 non-null float64
smoothness_worst 569 non-null float64
compactness_worst 569 non-null float64
concavity_worst 569 non-null float64
concave points_worst 569 non-null float64
symmetry_worst 569 non-null float64
fractal_dimension_worst 569 non-null float64
Unnamed: 32 0 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(31), int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 146.8+ KB
Code: We are dropping columns – ‘id’ and ‘Unnamed: 32’ as they have no role in prediction
df.drop(['Unnamed: 32', 'id'], axis = 1)
print(df.shape)
|
Output:
(569, 31)
Code: Converting the diagnosis value of M and B to a numerical value where M (Malignant) = 1 and B (Benign) = 0
def diagnosis_value(diagnosis):
if diagnosis == 'M':
return 1
else:
return 0
df['diagnosis'] = df['diagnosis'].apply(diagnosis_value)
|
Code :
sns.lmplot(x = 'radius_mean', y = 'texture_mean', hue = 'diagnosis', data = df)
|
Output:

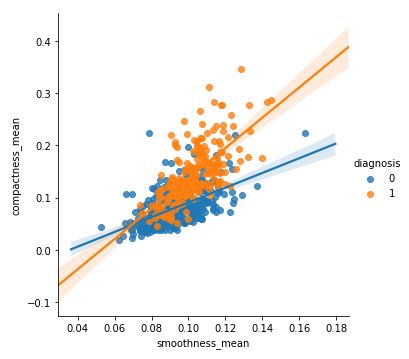
Code :
sns.lmplot(x ='smoothness_mean', y = 'compactness_mean',
data = df, hue = 'diagnosis')
|
Output:
Code : Input and Output data
X = np.array(df.iloc[:, 1:])
y = np.array(df['diagnosis'])
|
Code : Splitting data to training and testing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size = 0.33, random_state = 42)
|
Code : Using Sklearn
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 13)
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
|
Output:
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30,
metric='minkowski', metric_params=None,
n_jobs=None, n_neighbors=13, p=2,
weights='uniform')
Code : Prediction Score
knn.score(X_test, y_test)
|
Output:
0.9627659574468085
Code : Performing Cross Validation
neighbors = []
cv_scores = []
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
for k in range(1, 51, 2):
neighbors.append(k)
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = k)
scores = cross_val_score(
knn, X_train, y_train, cv = 10, scoring = 'accuracy')
cv_scores.append(scores.mean())
|
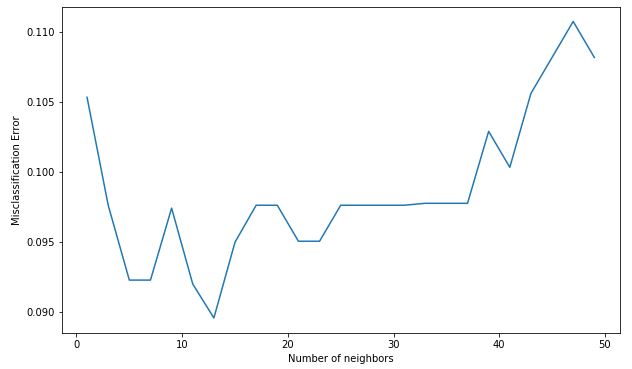
Code : Misclassification error versus k
MSE = [1-x for x in cv_scores]
optimal_k = neighbors[MSE.index(min(MSE))]
print('The optimal number of neighbors is % d ' % optimal_k)
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 6))
plt.plot(neighbors, MSE)
plt.xlabel('Number of neighbors')
plt.ylabel('Misclassification Error')
plt.show()
|
Output:
The optimal number of neighbors is 13
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...