Minimum sum after subtracting multiples of k from the elements of the array
Last Updated :
23 Aug, 2022
Given an integer 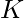 and an integer array, the task is to find the minimum possible sum of all the elements of the array after they are reduced by subtracting a multiple of
and an integer array, the task is to find the minimum possible sum of all the elements of the array after they are reduced by subtracting a multiple of 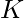 from each element (the result must be positive and every element of the array must be equal after this reduction). If the array cannot be reduced then print
from each element (the result must be positive and every element of the array must be equal after this reduction). If the array cannot be reduced then print 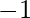
Note that an element may or may not be reduced in the final state of the array.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {2, 3, 4, 5}, K = 1
Output: 4
Subtract 1 form 2, arr[] = {1, 3, 4, 5}
Subtract 2 from 3, arr[] = {1, 1, 4, 5}
Subtract 3 from 4, arr[] = {1, 1, 1, 5}
Subtract 4 from 5 to make arr[] = {1, 1, 1, 1}, thus giving minimum possible sum as 4.Input: arr[] = {5, 6, 7}, K = 2
Output: -1
Approach: First, the array needs to be sorted as the problem can be solved using the greedy approach.
- Sort the array, if arr[0] < 0 then print -1 as every element needs to be ? 0.
- If K == 0 then no element can be reduced further. So in order to have an answer every element of the array must be equal. So the sum of elements is n * arr[0] else print -1.
- Now for the rest of the elements, run a loop from 1 to n and check whether ((arr[i] – arr[0]) % K) == 0 i.e. arr[i] can be reduced to arr[0].
- If the above condition fails for any element, print -1.
- Else if k == 1 then the answer is n i.e. every element will get reduced to 1.
- Else the answer is n * (a[0] % k).
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int min_sum(int n, int k, int a[])
{
sort(a, a + n);
if (a[0] < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0) {
if (a[0] == a[n - 1])
return (n * a[0]);
else
return -1;
}
else {
int f = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int p = a[i] - a[0];
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f)
return -1;
else {
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (a[0] % k));
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int K = 1;
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << min_sum(N, K, arr);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int min_sum(int n, int k, int a[])
{
Arrays.sort(a);
if (a[0] < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0) {
if (a[0] == a[n - 1])
return (n * a[0]);
else
return -1;
}
else {
int f = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int p = a[i] - a[0];
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f>0)
return -1;
else {
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (a[0] % k));
}
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int K = 1;
int N = arr.length;
System.out.println(min_sum(N, K, arr));
}
}
|
Python3
def min_sum(n, k, a):
a.sort(reverse = False)
if (a[0] < 0):
return -1
if (k == 0):
if (a[0] == a[n - 1]):
return (n * a[0])
else:
return -1
else:
f = 0
for i in range(1, n, 1):
p = a[i] - a[0]
if (p % k == 0):
continue
else:
f = 1
break
if (f):
return -1
else:
if (k == 1):
return n
else:
return (n * (a[0] % k))
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [2, 3, 4, 5]
K = 1
N = len(arr)
print(min_sum(N, K, arr))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int min_sum(int n, int k, int[] a)
{
Array.Sort(a);
if (a[0] < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0)
{
if (a[0] == a[n - 1])
return (n * a[0]);
else
return -1;
}
else
{
int f = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int p = a[i] - a[0];
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else
{
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f > 0)
return -1;
else
{
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (a[0] % k));
}
}
}
public static void Main ()
{
int[] arr = new int[] { 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int K = 1;
int N = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(min_sum(N, K, arr));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function min_sum($n, $k, $a)
{
sort($a);
if ($a[0] < 0)
return -1;
if ($k == 0)
{
if ($a[0] == $a[$n - 1])
return ($n * $a[0]);
else
return -1;
}
else
{
$f = 0;
for ($i = 1; $i <$n; $i++)
{
$p = $a[$i] - $a[0];
if ($p % $k == 0)
continue;
else
{
$f = 1;
break;
}
}
if ($f)
return -1;
else
{
if ($k == 1)
return $n;
else
return ($n * ($a[0] % $k));
}
}
}
$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 5 );
$K = 1;
$N = count($arr);
echo min_sum($N, $K, $arr);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function min_sum(n, k, a)
{
a.sort();
if (a[0] < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0) {
if (a[0] == a[n - 1])
return (n * a[0]);
else
return -1;
}
else {
let f = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
let p = a[i] - a[0];
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f>0)
return -1;
else {
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (a[0] % k));
}
}
}
let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
let K = 1;
let N = arr.length;
document.write(min_sum(N, K, arr));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(nlogn)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Further Optimizations:
Instead of sorting the array, we can find the minimum element in O(n) time. We can check whether all elements are the same or not also in O(n) time.
The steps involved in this approach are as follows:
- Find the minimum element in the array and store it in variable name val.
- Now if val < 0 then print -1 as every element needs to be ? 0 and if the minimum element is greater or equal to 0 then every element will be greater than 0.
- If K == 0 then no element can be reduced further. So in order to have an answer every element of the array must be equal. So we check this by iterating a loop and if all are equal then the answer will be n * val else print -1.
- Now for the rest of the elements, iterate a loop and check whether ((arr[i] – val) % K) == 0 i.e. arr[i] can be reduced to val.
- If the above condition fails for any element, print -1.
- Else if k == 1 then the answer is n i.e. every element will get reduced to 1.
- Else the answer is n * (val % k).
Below is the code for the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int min_sum(int n, int k, int a[])
{
int val=INT_MAX;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
val=min(a[i],val);
}
if (val < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(val!=a[i])
return -1;
}
return (n * val);
}
else {
int f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int p = a[i] - val;
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f)
return -1;
else {
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (val % k));
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int K = 1;
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << min_sum(N, K, arr);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int min_sum(int n,int k,int[] a)
{
int val=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
val=Math.min(a[i],val);
}
if (val < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(val!=a[i])
return -1;
}
return (n * val);
}
else {
int f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int p = a[i] - val;
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f!=0)
return -1;
else {
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (val % k));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int K = 1;
int N = arr.length;
System.out.println(min_sum(N, K, arr));
}
}
|
Python3
def min_sum(n, k, a):
val = 10000000;
for i in range(n):
val = min(a[i], val);
if (val < 0):
return -1;
if (k == 0) :
for i in range(n):
if(val != a[i]):
return -1;
return (n * val);
else :
f = 0;
for i in range(n):
p = a[i] - val;
if (p % k == 0):
continue;
else :
f = 1;
break;
if (f > 0):
return -1;
else :
if (k == 1):
return n;
else:
return (n * (val % k));
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
K = 1;
N = len(arr);
print(min_sum(N, K, arr));
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static int min_sum(int n, int k, int[] a)
{
int val = Int32.MaxValue;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
val = Math.Min(a[i],val);
}
if (val < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(val !=
a[i])
return -1;
}
return (n * val);
}
else {
int f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int p = a[i] - val;
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f!=0)
return -1;
else {
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (val % k));
}
}
}
public static void Main ()
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int K = 1;
int N = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(min_sum(N, K, arr));
}
}
|
Javascript
function min_sum(n, k, a)
{
let val = 10000000;
for(var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
val = Math.min(a[i], val);
}
if (val < 0)
return -1;
if (k == 0) {
for(var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(val != a[i])
return -1;
}
return (n * val);
}
else {
var f = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var p = a[i] - val;
if (p % k == 0)
continue;
else {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
if (f > 0)
return -1;
else {
if (k == 1)
return n;
else
return (n * (val % k));
}
}
}
let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
let K = 1;
let N = arr.length;
console.log(min_sum(N, K, arr));
|
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...