Minimum cost to sort an Array such that swapping X and Y costs XY
Last Updated :
18 Jan, 2023
Given an array of N distinct positive integers. The task is to find the minimum cost to sort the given array. The cost of swapping two elements X and Y is X*Y.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {8, 4, 5, 3, 2, 7}
Output: 57
Explanation:
Swap element at index 4 with index 5 – cost(arr[4]*arr[5]) = (2*7) = 14,
Array becomes {8, 4, 5, 3, 7, 2}
then, swap element at index 0 with 5 – cost(arr[0]*arr[5]) = (8*2) = 16,
Array becomes {2, 4, 5, 3, 7, 8}
then, swap element at index 2 with 3 – cost(arr[2]*arr[3]) = (5*3) = 15,
Array becomes {2, 4, 3, 5, 7, 8}
then, swap element at index 1 with 2 – cost(arr[1]*arr[2]) = (4*3) = 12,
Array becomes {2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8}
Array is now sorted and total cost = 14+16+15+12 = 57.
Input: arr[] = {1, 8, 9, 7, 6}
Output: 36
Approach: The idea is that for sorting a cycle we have two choices either to use only the local minimum of the cycle or to use both local and overall minimum of the array. Choose the one swap element that gives a lower cost. Below are the steps:
- Calculate the local minimum (say local_minimum) which is the minimum element in the present cycle and the overall minimum (say overall_minimum) which is the minimum element in the whole array.
- Calculate and store the cost to sort the cycle (say cost1) by using only local minimum value.
- Also, calculate and store the cost to sort the cycle (say cost2) by using both local minimum value and the overall minimum value.
- Now the minimum cost to sort this cycle will be minimum of the costs cost1 and cost2. Add this cost to the total cost.
Below is the illustration for the array arr[] = {1, 8, 9, 7, 6}:
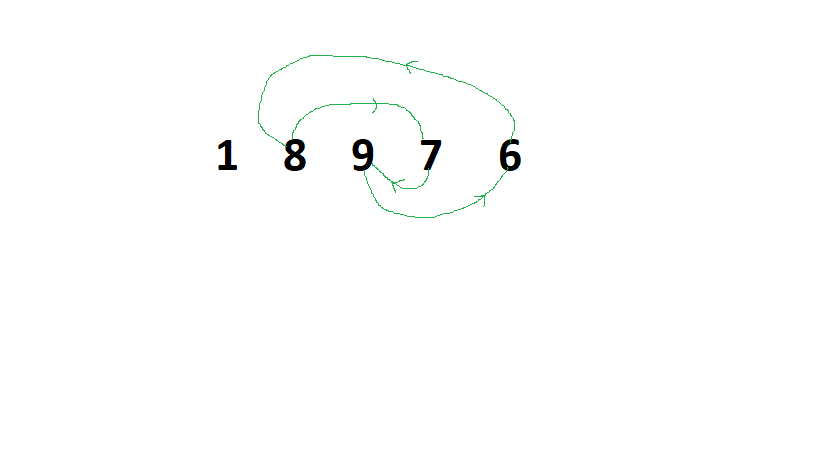
- In the above figure, cycle {8, 9, 7, 6} can be sorted using the local minimum element 6 or with overall minimum element 1. By using only local minimum element i.e., swap 6 and 9, swap 6 and 7, swap 6 and 8. Therefore, the total cost is 6*9 + 6*7 + 6*8 = 144.
- By using both overall minimum and local minimum element i.e., swap 1 and 6, swap 1 and 9, swap 1 and 7, swap 1 and 8, swap 1 and 6. Therefore, the total cost is 1*6 +1*9 +1*7 +1*8 +1*6 = 36.
- The minimum of the above cost is 36.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
pair<int, int> sorted[n];
int total_cost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sorted[i].first = arr[i];
sorted[i].second = i;
}
sort(sorted, sorted + n);
int overall_minimum = sorted[0].first;
bool vis[n] = { false };
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (vis[i] && sorted[i].second == i)
continue;
vector<int> v;
int j = i;
while (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
v.push_back(sorted[j].first);
j = sorted[j].second;
}
if (v.size() > 0) {
int local_minimum = v[0], result1 = 0,
result2 = 0;
for (int k = 1; k < v.size(); k++)
result1 += (local_minimum * v[k]);
for (int k = 0; k < v.size(); k++)
result2 += (overall_minimum * v[k]);
result2 += (overall_minimum
* local_minimum);
total_cost += min(result1, result2);
}
}
return total_cost;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 8, 9, 7, 6 };
int n = (sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
cout << minCost(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
int[][] sorted = new int[n][2];
int total_cost = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sorted[i][0] = arr[i];
sorted[i][1] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(sorted, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int overall_minimum = sorted[0][0];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (vis[i] && sorted[i][1] == i)
continue;
ArrayList<Integer> v = new ArrayList<>();
int j = i;
while (!vis[j])
{
vis[j] = true;
v.add(sorted[j][0]);
j = sorted[j][1];
}
if (v.size() > 0)
{
int local_minimum = v.get(0), result1 = 0,
result2 = 0;
for(int k = 1; k < v.size(); k++)
result1 += (local_minimum * v.get(k));
for(int k = 0; k < v.size(); k++)
result2 += (overall_minimum * v.get(k));
result2 += (overall_minimum *
local_minimum);
total_cost += Math.min(result1, result2);
}
}
return total_cost;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 8, 9, 7, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(minCost(arr, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def minCost(arr, n):
sortedarr = []
total_cost = 0
for i in range(n):
sortedarr.append([arr[i], i])
sortedarr.sort()
overall_minimum = sortedarr[0][0]
vis = [False] * n
for i in range(n):
if vis[i] and sortedarr[i][1] == i:
continue
v = []
j = i
size = 0
while vis[j] == False:
vis[j] = True
v.append(sortedarr[j][0])
j = sortedarr[j][1]
size += 1
if size != 0:
local_minimum = v[0]
result1 = 0
result2 = 0
for k in range(1, size):
result1 += local_minimum * v[k]
for k in range(size):
result2 += overall_minimum * v[k]
result2 += (overall_minimum *
local_minimum)
total_cost += min(result1, result2)
return total_cost
A = [ 1, 8, 9, 7, 6 ]
ans = minCost(A, len(A))
print(ans)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int minCost(int[] arr, int n)
{
int[][] sorted = new int[n][];
int total_cost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sorted[i] = new int[2];
sorted[i][0] = arr[i];
sorted[i][1] = i;
}
Array.Sort(sorted, (a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
int overall_minimum = sorted[0][0];
bool[] vis = new bool[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (vis[i] && sorted[i][1] == i)
continue;
List<int> v = new List<int>();
int j = i;
while (!vis[j])
{
vis[j] = true;
v.Add(sorted[j][0]);
j = sorted[j][1];
}
if (v.Count > 0)
{
int local_minimum = v[0], result1 = 0,
result2 = 0;
for (int k = 1; k < v.Count; k++)
result1 += (local_minimum * v[k]);
for (int k = 0; k < v.Count; k++)
result2 += (overall_minimum * v[k]);
result2 += (overall_minimum *
local_minimum);
total_cost += Math.Min(result1, result2);
}
}
return total_cost;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = {1, 8, 9, 7, 6};
var n = arr.Length;
Console.Write(GFG.minCost(arr, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function minCost(arr, n){
let sortedarr = []
let total_cost = 0
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++){
sortedarr.push([arr[i], i])
}
sortedarr.sort()
let overall_minimum = sortedarr[0][0]
let vis = new Array(n).fill(false)
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(vis[i] && sortedarr[i][1] == i)
continue
let v = []
let j = i
let size = 0
while(vis[j] == false){
vis[j] = true
v.push(sortedarr[j][0])
j = sortedarr[j][1]
size += 1
}
if(size != 0){
let local_minimum = v[0]
let result1 = 0
let result2 = 0
for(let k = 1; k < size; k++)
result1 += local_minimum * v[k]
for(let k = 0; k < size; k++)
result2 += overall_minimum * v[k]
result2 += (overall_minimum *
local_minimum)
total_cost += Math.min(result1, result2)
}
}
return total_cost
}
A = [ 1, 8, 9, 7, 6 ]
ans = minCost(A, A.length)
document.write(ans,"</br>")
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N*log(N))
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...