Minimum Cost to cut a board into squares
Last Updated :
13 Feb, 2023
A board of length m and width n is given, we need to break this board into m*n squares such that cost of breaking is minimum. cutting cost for each edge will be given for the board. In short, we need to choose such a sequence of cutting such that cost is minimized.
Examples:
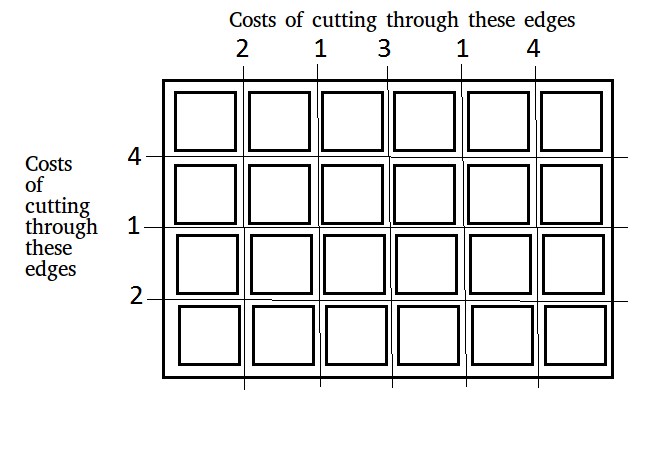
For above board optimal way to cut into square is:
Total minimum cost in above case is 42. It is
evaluated using following steps.
Initial Value : Total_cost = 0
Total_cost = Total_cost + edge_cost * total_pieces
Cost 4 Horizontal cut Cost = 0 + 4*1 = 4
Cost 4 Vertical cut Cost = 4 + 4*2 = 12
Cost 3 Vertical cut Cost = 12 + 3*2 = 18
Cost 2 Horizontal cut Cost = 18 + 2*3 = 24
Cost 2 Vertical cut Cost = 24 + 2*3 = 30
Cost 1 Horizontal cut Cost = 30 + 1*4 = 34
Cost 1 Vertical cut Cost = 34 + 1*4 = 38
Cost 1 Vertical cut Cost = 38 + 1*4 = 42
Minimum Cost to cut a board into squares using a greedy algorithm:
This problem can be solved by greedy approach . To get minimum cost , the idea is to cut the edge with highest cost first because we have less number of pieces and after every cut the number of pieces increase . As the question stated Total_cost = Total_cost + edge_cost * total_pieces .
- At first sort both the array in non-ascending order
- We keep count of two variables vert(keeps track of vertical pieces) and hzntl(keeps track of horizontal pieces). We will initialize both of them with 1.
- We will keep track of two pointers starting from 0th index of both the array
- Now we will take the highest cost edge from those pointers and multiply them with the corresponding variable. That is if we cut a horizontal cut we will add (edge_cost*hzntl) and increase vert by 1 and if we cut a vertical cut we will add(edge_cost*vert) and increase hzntl bt 1 .
- After cutting all the edges we will get the minimum cost
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int minimumCostOfBreaking(int X[], int Y[], int m, int n)
{
int res = 0;
sort(X, X + m, greater<int>());
sort(Y, Y + n, greater<int>());
int hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
vert++;
j++;
}
}
int total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
int main()
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
int X[m-1] = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
int Y[n-1] = {4, 1, 2};
cout << minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG
{
static int minimumCostOfBreaking(Integer X[], Integer Y[],
int m, int n)
{
int res = 0;
Arrays.sort(X, Collections.reverseOrder());
Arrays.sort(Y, Collections.reverseOrder());
int hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
vert++;
j++;
}
}
int total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
public static void main(String arg[])
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
Integer X[] = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
Integer Y[] = {4, 1, 2};
System.out.print(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1));
}
}
|
Python3
def minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m, n):
res = 0
X.sort(reverse = True)
Y.sort(reverse = True)
hzntl = 1; vert = 1
i = 0; j = 0
while (i < m and j < n):
if (X[i] > Y[j]):
res += X[i] * vert
hzntl += 1
i += 1
else:
res += Y[j] * hzntl
vert += 1
j += 1
total = 0
while (i < m):
total += X[i]
i += 1
res += total * vert
total = 0
while (j < n):
total += Y[j]
j += 1
res += total * hzntl
return res
m = 6; n = 4
X = [2, 1, 3, 1, 4]
Y = [4, 1, 2]
print(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int minimumCostOfBreaking(int[] X, int[] Y,
int m, int n)
{
int res = 0;
Array.Sort<int>(X, new Comparison<int>(
(i1, i2) => i2.CompareTo(i1)));
Array.Sort<int>(Y, new Comparison<int>(
(i1, i2) => i2.CompareTo(i1)));
int hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
vert++;
j++;
}
}
int total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
public static void Main(String []arg)
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
int []X = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
int []Y = {4, 1, 2};
Console.WriteLine(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m, n)
{
let res = 0;
X.sort();
X.reverse();
Y.sort();
Y.reverse();
let hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
let i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
vert++;
j++;
}
}
let total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
let m = 6, n = 4;
let X = [2, 1, 3, 1, 4];
let Y = [4, 1, 2];
document.write(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(mlogm + nlogn), where n and m are the sizes of the given arrays.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...