Minimize cost of painting N houses such that adjacent houses have different colors
Last Updated :
24 Apr, 2023
Given an integer N and a 2D array cost[][3], where cost[i][0], cost[i][1], and cost[i][2] is the cost of painting ith house with colors red, blue, and green respectively, the task is to find the minimum cost to paint all the houses such that no two adjacent houses have the same color.
Examples:
Input: N = 3, cost[][3] = {{14, 2, 11}, {11, 14, 5}, {14, 3, 10}}
Output: 10
Explanation:
Paint house 0 as blue. Cost = 2. Paint house 1 as green. Cost = 5. Paint house 2 as blue. Cost = 3.
Therefore, the total cost = 2 + 5 + 3 = 10.
Input: N = 2, cost[][3] = {{1, 2, 3}, {1, 4, 6}}
Output: 3
Naive Approach: The simplest approach to solve the given problem is to generate all possible ways of coloring all the houses with the colors red, blue, and green and find the minimum cost among all the possible combinations such that no two adjacent houses have the same colors.
Time Complexity: (3N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Efficient Approach: The above approach can be optimized by using Dynamic Programming as there are overlapping subproblems that can be stored to minimize the number of recursive calls. The idea is to find the minimum cost of painting the current house by any color on the basis of the minimum cost of the other two colors of previously colored houses. Follow the steps below to solve the given problem:
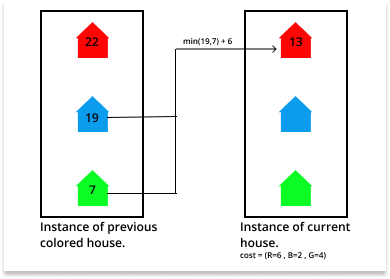
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create an auxiliary 2D dp[][3] array to store the minimum cost of previously colored houses.
- Initialize dp[0][0], dp[0][1], and dp[0][2] as the cost of cost[i][0], cost[i][1], and cost[i][2] respectively.
- Traverse the given array cost[][3] over the range [1, N] and update the cost of painting the current house with colors red, blue, and green with the minimum of the cost other two colors in dp[i][0], dp[i][1], and dp[i][2] respectively.
- After completing the above steps, print the minimum of dp[N – 1][0], dp[N – 1][1], and dp[N – 1][2] as the minimum cost of painting all the houses with different adjacent colors.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int minCost(vector<vector<int> >& costs,
int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return 0;
vector<vector<int> > dp(
N, vector<int>(3, 0));
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
dp[i][0] = min(dp[i - 1][1],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][0];
dp[i][1] = min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][1];
dp[i][2] = min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][1])
+ costs[i][2];
}
cout << min(dp[N - 1][0],
min(dp[N - 1][1],
dp[N - 1][2]));
}
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > costs{ { 14, 2, 11 },
{ 11, 14, 5 },
{ 14, 3, 10 } };
int N = costs.size();
minCost(costs, N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void minCost(int costs[][], int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return;
int dp[][] = new int[N][3];
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][0];
dp[i][1] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][1];
dp[i][2] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1])
+ costs[i][2];
}
System.out.println(
Math.min(dp[N - 1][0],
Math.min(dp[N - 1][1], dp[N - 1][2])));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int costs[][] = { { 14, 2, 11 },
{ 11, 14, 5 },
{ 14, 3, 10 } };
int N = costs.length;
minCost(costs, N);
}
}
|
Python3
def minCost(costs, N):
if (N == 0):
return 0
dp = [[0 for i in range(3)] for j in range(3)]
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0]
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1]
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2]
for i in range(1, N, 1):
dp[i][0] = min(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][0]
dp[i][1] = min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][1]
dp[i][2] = min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1]) + costs[i][2]
print(min(dp[N - 1][0], min(dp[N - 1][1],dp[N - 1][2])))
if __name__ == '__main__':
costs = [[14, 2, 11],
[11, 14, 5],
[14, 3, 10]]
N = len(costs)
minCost(costs, N)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int minCost(List<List<int>>costs,
int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return 0;
List<int> temp = new List<int>();
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
temp.Add(0);
List<List<int>> dp = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
dp.Add(temp);
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.Min(dp[i - 1][1],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][0];
dp[i][1] = Math.Min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][1];
dp[i][2] = Math.Min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][1])
+ costs[i][2];
}
return (Math.Min(dp[N - 1][0], Math.Min(dp[N - 1][1],dp[N - 1][2])))-11;
}
public static void Main()
{
List<List<int>>costs = new List<List<int>>();
costs.Add(new List<int>(){14, 2, 11});
costs.Add(new List<int>(){11, 14, 5 });
costs.Add(new List<int>(){14, 3, 10 });
int N = 3;
Console.WriteLine((int)(minCost(costs, N)));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function minCost(costs, N)
{
if (N == 0)
return 0;
let dp = new Array(N);
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
dp[i] = new Array(3);
for(let j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for(let i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
dp[i][0] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][0];
dp[i][1] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][1];
dp[i][2] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1]) + costs[i][2];
}
document.write(Math.min(dp[N - 1][0], Math.min(dp[N - 1][1],dp[N - 1][2])));
}
let costs = [[14, 2, 11],
[11, 14, 5],
[14, 3, 10]];
let N = costs.length;
minCost(costs, N);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Efficient Approach using Dp with Constant Space: If we see the efficient approach that’s discussed above we can observe one thing for painting current house you only required information of paint house just before that is for painting ith house you only required information for i-1th house so we rather than making a dp of size 3*N we can just make 6 variable that is 3 for current and 3 for last and space complexity will reduce to O(1)
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void minCost(vector<vector<int>> costs, int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return;
int previous_red = costs[0][0];
int previous_blue = costs[0][1];
int previous_green = costs[0][2];
int current_red;
int current_blue;
int current_green;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
current_red = min(previous_blue, previous_green) + costs[i][0];
current_blue = min(previous_red, previous_green) + costs[i][1];
current_green = min(previous_red, previous_blue) + costs[i][2];
previous_red = current_red;
previous_blue = current_blue;
previous_green = current_green;
}
cout << (min(previous_red, min(previous_blue,previous_green)));
}
int main(){
vector<vector<int>> costs = { { 14, 2, 11 },
{ 11, 14, 5 },
{ 14, 3, 10 } };
int N = costs.size();
minCost(costs, N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void minCost(int costs[][], int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return;
int previous_red = costs[0][0];
int previous_blue = costs[0][1];
int previous_green = costs[0][2];
int current_red;
int current_blue;
int current_green;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
current_red
= Math.min(previous_blue, previous_green)
+ costs[i][0];
current_blue
= Math.min(previous_red, previous_green)
+ costs[i][1];
current_green
= Math.min(previous_red, previous_blue)
+ costs[i][2];
previous_red = current_red;
previous_blue = current_blue;
previous_green = current_green;
}
System.out.println(
Math.min(previous_red,
Math.min(previous_blue,previous_green)));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int costs[][] = { { 14, 2, 11 },
{ 11, 14, 5 },
{ 14, 3, 10 } };
int N = costs.length;
minCost(costs, N);
}
}
|
Python3
def minCost(costs, N):
if N == 0:
return
previous_red = costs[0][0]
previous_blue = costs[0][1]
previous_green = costs[0][2]
current_red = 0
current_blue = 0
current_green = 0
for i in range(1, N):
current_red = min(previous_blue, previous_green) + costs[i][0]
current_blue = min(previous_red, previous_green) + costs[i][1]
current_green = min(previous_red, previous_blue) + costs[i][2]
previous_red = current_red
previous_blue = current_blue
previous_green = current_green
print(min(previous_red, min(previous_blue, previous_green)))
costs = [[14, 2, 11], [11, 14, 5], [14, 3, 10]]
N = len(costs)
minCost(costs, N)
|
Javascript
function minCost(costs, N)
{
if (N == 0)
{
return;
}
let previous_red = costs[0][0];
let previous_blue = costs[0][1];
let previous_green = costs[0][2];
let current_red = 0;
let current_blue = 0;
let current_green = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < N; i++) {
current_red = Math.min(previous_blue, previous_green) + costs[i][0];
current_blue = Math.min(previous_red, previous_green) + costs[i][1];
current_green = Math.min(previous_red, previous_blue) + costs[i][2];
previous_red = current_red;
previous_blue = current_blue;
previous_green = current_green;
}
console.log(Math.min(previous_red, Math.min(previous_blue, previous_green)));
}
let costs = [[14, 2, 11], [11, 14, 5], [14, 3, 10]];
let N = costs.length;
minCost(costs, N);
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static void minCost(int[][] costs, int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return;
int previous_red = costs[0][0];
int previous_blue = costs[0][1];
int previous_green = costs[0][2];
int current_red;
int current_blue;
int current_green;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
current_red = Math.Min(previous_blue, previous_green) + costs[i][0];
current_blue = Math.Min(previous_red, previous_green) + costs[i][1];
current_green = Math.Min(previous_red, previous_blue) + costs[i][2];
previous_red = current_red;
previous_blue = current_blue;
previous_green = current_green;
}
Console.WriteLine(Math.Min(previous_red, Math.Min(previous_blue, previous_green)));
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[][] costs = { new int[] { 14, 2, 11 },
new int[] { 11, 14, 5 },
new int[] { 14, 3, 10 } };
int N = costs.Length;
minCost(costs, N);
}
}
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...