Maximize the number of segments of length p, q and r
Last Updated :
23 Apr, 2024
Given a rod of length L, the task is to cut the rod in such a way that the total number of segments of length p, q, and r is maximized. The segments can only be of length p, q, and r.
Examples:
Input: l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5
Output: 5
Explanation: Segments of 2, 2, 2, 2 and 3
Input: l = 7, p = 2, q = 5, r = 5
Output: 2
Explanation: Segments of 2 and 5
BRUTE METHOD(Recursion)
Intuition:
- We look for all possibilities for every individual length and send the remaining value in recursion.
- Once the base case is hit, i.e n becomes 0, we return 0;
- And this continues till all the lengths x,y,z are looked whether they will contribute to it or not.
Implementation:
C++
// C++ Code to find maximum number of cut segments
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int maximizeCuts(int n, int x, int y, int z)
{
// Your code here
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n < 0)
return INT_MIN;
int a = maximizeCuts(n - x, x, y, z) + 1;
int b = maximizeCuts(n - y, x, y, z) + 1;
int c = maximizeCuts(n - z, x, y, z) + 1;
int d = max(a, max(b, c));
return d;
}
int main()
{
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
cout << maximizeCuts(l, p, q, r) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Raunak Singh
// Java Code to find maximum number of cut segments
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static int maximizeCuts(int n, int x, int y, int z)
{
// Your code here
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n < 0)
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int a = maximizeCuts(n - x, x, y, z) + 1;
int b = maximizeCuts(n - y, x, y, z) + 1;
int c = maximizeCuts(n - z, x, y, z) + 1;
int d = Math.max(a, Math.max(b, c));
return d;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
System.out.println(maximizeCuts(l, p, q, r));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Raunak Singh
# function to find the maximum number of cuts
def maximize_cuts(n, x, y, z):
# if the rod length is 0, no more cuts can be made
if n == 0:
return 0
# if the rod length becomes negative, return negative infinity
if n < 0:
return float('-inf')
# Calculate the number of cuts using each possible cut length (x, y, z)
a = maximize_cuts(n - x, x, y, z) + 1
b = maximize_cuts(n - y, x, y, z) + 1
c = maximize_cuts(n - z, x, y, z) + 1
# Find the maximum number of cuts among the three possibilities
d = max(a, max(b, c))
return d
if __name__ == "__main__":
l = 11
p = 2
q = 3
r = 5
# Call the maximize_cuts function and print the result
print(maximize_cuts(l, p, q, r))
using System;
class Program {
// Function to find the maximum number of cut segments
static int MaximizeCuts(int n, int x, int y, int z)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n < 0)
return int.MinValue;
// Recursively calculate the maximum cuts for each
// option
int a = MaximizeCuts(n - x, x, y, z) + 1;
int b = MaximizeCuts(n - y, x, y, z) + 1;
int c = MaximizeCuts(n - z, x, y, z) + 1;
// Return the maximum of the three options
return Math.Max(a, Math.Max(b, c));
}
static void Main()
{
// Given lengths and cuts
int length = 11, cut1 = 2, cut2 = 3, cut3 = 5;
// Print the maximum number of cut segments
Console.WriteLine(
MaximizeCuts(length, cut1, cut2, cut3));
}
}
// JavaScript code to find maximum number of cut segments
// Function to find maximum cuts
function maximizeCuts(n, x, y, z) {
// Base cases
if (n === 0)
return 0;
if (n < 0)
return Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER; // Represents negative infinity in JavaScript
// Recursively find the maximum cuts for each possibility
let a = maximizeCuts(n - x, x, y, z) + 1;
let b = maximizeCuts(n - y, x, y, z) + 1;
let c = maximizeCuts(n - z, x, y, z) + 1;
// Find the maximum of the three possibilities
let d = Math.max(a, Math.max(b, c));
return d;
}
// Main function
function main() {
let l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5; // Length of rod and lengths of cuts
console.log(maximizeCuts(l, p, q, r)); // Output the maximum cuts
}
// Call the main function to execute the code
main();
Time Complexity: O(3^n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Maximize the number of segments of length p, q, and r using Memoization:
This can be visualized as a classical recursion problem, which further narrows down to the memoization ( top-down ) method of Dynamic Programming.
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Initially, we have length l present with us, we’d have three size choices to cut from this, either we can make a cut of length p, q, or r
- Let’s say we made a cut of length p, so the remaining length would be l-p, and similarly, with cuts q & r resulting in remaining lengths l-q & l-r respectively.
- We will call the recursive function for the remaining lengths and at any subsequent instance, we’ll have these three choices.
- We will store the answer from all these recursive calls & take the maximum out of them +1 as at any instance we’ll have 1 cut from this particular call as well.
Note: The recursive call would be made if and only if the available length is greater than the length we want to cut i.e. suppose p=3, and after certain recursive calls the available length is 2 only, so we can’t cut this line in lengths of p anymore.
Below is the pseudocode for the above approach:
C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
// Recursive function to maximize cuts
int maximizeCuts(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
// Base Case
if (l == 0) {
return 0;
}
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
// Check if cut of length p is possible
if (p <= l) {
a = maximizeCuts(l - p, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length q is possible
if (q <= l) {
b = maximizeCuts(l - q, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length r is possible
if (r <= l) {
c = maximizeCuts(l - r, p, q, r);
}
// Return 1 + maximum of a, b, c
return 1 + std::max({ a, b, c });
}
int main()
{
// Test cases
int l1 = 11, p1 = 2, q1 = 3, r1 = 5;
int l2 = 7, p2 = 2, q2 = 5, r2 = 5;
// Output the result for each case
std::cout << maximizeCuts(l1, p1, q1, r1)
<< std::endl; // Output: 5
std::cout << maximizeCuts(l2, p2, q2, r2)
<< std::endl; // Output: 2
return 0;
}
if (l == 0) // Base Case
return 0;
int a, b, c;
if (p <= l)
a = func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l)
b = func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l)
c = func(l - r, p, q, r);
return 1 + max({ a, b, c });
public class MaximizeCuts {
// Recursive function to maximize cuts
private static int maximizeCuts(int l, int p, int q, int r) {
// Base Case
if (l == 0) {
return 0;
}
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
// Check if cut of length p is possible
if (p <= l) {
a = maximizeCuts(l - p, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length q is possible
if (q <= l) {
b = maximizeCuts(l - q, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length r is possible
if (r <= l) {
c = maximizeCuts(l - r, p, q, r);
}
// Return 1 + maximum of a, b, c
return 1 + Math.max(Math.max(a, b), c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test cases
int l1 = 11, p1 = 2, q1 = 3, r1 = 5;
int l2 = 7, p2 = 2, q2 = 5, r2 = 5;
// Output the result for each case
System.out.println(maximizeCuts(l1, p1, q1, r1)); // Output: 5
System.out.println(maximizeCuts(l2, p2, q2, r2)); // Output: 2
}
}
# Recursive function to maximize cuts
def maximize_cuts(l, p, q, r):
# Base Case
if l == 0:
return 0
# Initialize counts for each cut type
a, b, c = 0, 0, 0
# Check if cut of length p is possible
if p <= l:
a = maximize_cuts(l - p, p, q, r)
# Check if cut of length q is possible
if q <= l:
b = maximize_cuts(l - q, p, q, r)
# Check if cut of length r is possible
if r <= l:
c = maximize_cuts(l - r, p, q, r)
# Return 1 + maximum of a, b, c
return 1 + max(a, b, c)
# Main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Test cases
l1, p1, q1, r1 = 11, 2, 3, 5
l2, p2, q2, r2 = 7, 2, 5, 5
# Output the result for each case
print(maximize_cuts(l1, p1, q1, r1)) # Output: 5
print(maximize_cuts(l2, p2, q2, r2)) # Output: 2
# This code is contributed by shivamgupta0987654321
using System;
class Program {
// Recursive function to maximize cuts
static int MaximizeCuts(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
// Base Case
if (l == 0) {
return 0;
}
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
// Check if cut of length p is possible
if (p <= l) {
a = MaximizeCuts(l - p, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length q is possible
if (q <= l) {
b = MaximizeCuts(l - q, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length r is possible
if (r <= l) {
c = MaximizeCuts(l - r, p, q, r);
}
// Return 1 + maximum of a, b, c
return 1 + Math.Max(a, Math.Max(b, c));
}
static void Main()
{
// Test cases
int l1 = 11, p1 = 2, q1 = 3, r1 = 5;
int l2 = 7, p2 = 2, q2 = 5, r2 = 5;
// Output the result for each case
Console.WriteLine(
MaximizeCuts(l1, p1, q1, r1)); // Output: 5
Console.WriteLine(
MaximizeCuts(l2, p2, q2, r2)); // Output: 2
}
}
// Recursive function to maximize cuts
function maximizeCuts(l, p, q, r) {
// Base Case
if (l === 0) {
return 0;
}
let a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
// Check if cut of length p is possible
if (p <= l) {
a = maximizeCuts(l - p, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length q is possible
if (q <= l) {
b = maximizeCuts(l - q, p, q, r);
}
// Check if cut of length r is possible
if (r <= l) {
c = maximizeCuts(l - r, p, q, r);
}
// Return 1 + maximum of a, b, c
return 1 + Math.max(a, Math.max(b, c));
}
// Test cases
const l1 = 11, p1 = 2, q1 = 3, r1 = 5;
const l2 = 7, p2 = 2, q2 = 5, r2 = 5;
// Output the result for each case
console.log(maximizeCuts(l1, p1, q1, r1)); // Output: 5
console.log(maximizeCuts(l2, p2, q2, r2)); // Output: 2
Below is the recursion tree for Input: l=4,p=2,q=1 and r=1:
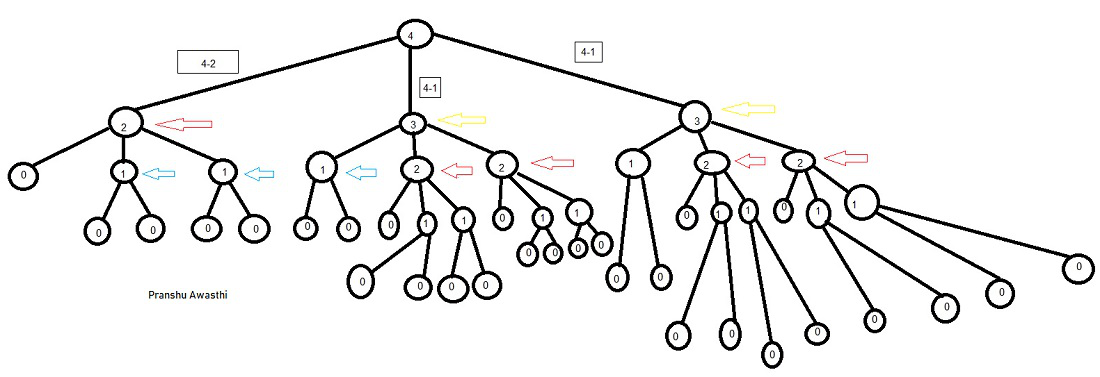
Recursion Tree for l=4 , p=2 ,q=1 and r=1 2
One can clearly observe that at each call, the given length ( 4 initially ) is divided into 3 different subparts. Also, we can see that the recursion is being repeated for certain entries (The red arrow represents a repetitive call for l=2, Yellow for l=3, and Blue for l=1). Therefore, we can memoize the results in any container or array, so that repetition of the same recursive calls is avoided.
Now, the above pseudocode changes to:
C++
vector<int> dp(10005,-1); // Initialise DP Table ( Array can also be used )
if(l==0) // Base Case
return 0;
if(dp[l]!=-1) // If already memoized , return from here only
return dp[l];
int a,b,c;
if(p<=l)
a=func(l-p,p,q,r);
if(q<=l)
b=func(l-q,p,q,r);
if(r<=l)
c=func(l-r,p,q,r);
return dp[l]=1+max({a,b,c}); // Memoize the result in the dp table & return
import java.util.Arrays;
public class DPExample {
static int[] dp = new int[10005];
// Initialize DP Table
static {
Arrays.fill(dp, -1);
}
// Function to calculate the maximum value
static int func(int l, int p, int q, int r) {
// Base Case
if (l == 0)
return 0;
// If already memoized, return from here only
if (dp[l] != -1)
return dp[l];
int a = Integer.MIN_VALUE, b = Integer.MIN_VALUE, c = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (p <= l)
a = func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l)
b = func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l)
c = func(l - r, p, q, r);
// Memoize the result in the dp table and return
return dp[l] = 1 + Math.max(Math.max(a, b), c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int l = 10;
int p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
int result = func(l, p, q, r);
System.out.println("Maximum value: " + result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by akshitaguprzj3
# Initialize a memoization table
dp = [-1] * 10005
# Function to calculate the maximum value
def func(l, p, q, r):
# Base Case
if l == 0:
return 0
# If already memoized, return from here only
if dp[l] != -1:
return dp[l]
a, b, c = float("-inf"), float("-inf"), float("-inf")
if p <= l:
a = func(l - p, p, q, r)
if q <= l:
b = func(l - q, p, q, r)
if r <= l:
c = func(l - r, p, q, r)
# Memoize the result in the dp table and return
dp[l] = 1 + max(a, b, c)
return dp[l]
if __name__ == "__main__":
l = 10
p, q, r = 2, 3, 5
result = func(l, p, q, r)
print("Maximum value:", result)
using System;
class Program {
// Initialize a memoization table
static int[] dp = new int[10005];
// Function to calculate the maximum value
static int Func(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
// Base Case
if (l == 0)
return 0;
// If already memoized, return from here only
if (dp[l] != -1)
return dp[l];
int a = int.MinValue, b = int.MinValue,
c = int.MinValue;
if (p <= l)
a = Func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l)
b = Func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l)
c = Func(l - r, p, q, r);
// Memoize the result in the dp table and return
dp[l] = 1 + Math.Max(a, Math.Max(b, c));
return dp[l];
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int l = 10;
int p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
// Initialize the memoization table with -1
for (int i = 0; i < dp.Length; i++) {
dp[i] = -1;
}
int result = Func(l, p, q, r);
Console.WriteLine("Maximum value: " + result);
}
}
const dp = new Array(10005).fill(-1);
// Function to calculate the maximum value
function func(l, p, q, r) {
// Base Case
if (l === 0)
return 0;
// If already memoized, return from here only
if (dp[l] !== -1)
return dp[l];
let a = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER, b = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER, c = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
if (p <= l)
a = func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l)
b = func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l)
c = func(l - r, p, q, r);
// Memoize the result in the dp table and return
return dp[l] = 1 + Math.max(Math.max(a, b), c);
}
// Driver code
const l = 10;
const p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
const result = func(l, p, q, r);
console.log("Maximum value: " + result);
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ Code to find maximum number of cut segments
// Memoization DP
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum number of cuts.
int dp[10005];
int func(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
if (l == 0)
return 0; // Base Case
if (dp[l] != -1) // If already memoized
return dp[l];
int a(INT_MIN), b(INT_MIN),
c(INT_MIN); // Intitialise a,b,& c with INT_MIN
if (p <= l) // If Possible to make a cut of length p
a = func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length q
b = func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length r
c = func(l - r, p, q, r);
return dp[l] = 1 + max({ a, b, c }); // Memoize & return
}
int maximizeTheCuts(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp)); // Set Lookup table to -1
int ans = func(l, p, q, r); // Utility function call
if (ans < 0)
return 0; // If returned answer is negative , that
// means cuts are not possible
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
cout << maximizeTheCuts(l, p, q, r) << endl;
return 0;
}
// Java Code to find maximum number of cut segments
// Memoization DP
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Function to find the maximum number of cuts.
static int[] dp;
static int func(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
if (l == 0)
return 0; // Base Case
if (dp[l] != -1) // If already memoized
return dp[l];
int a, b, c; // Intitialise a,b,& c with INT_MIN
a = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
b = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
c = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (p <= l) // If Possible to make a cut of length p
a = func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length q
b = func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length r
c = func(l - r, p, q, r);
return dp[l] = 1
+ Math.max(Math.max(a, b),
c); // Memoize & return
}
static int maximizeTheCuts(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
Arrays.fill(dp, -1); // Set Lookup table to -1
int ans = func(l, p, q, r); // Utility function call
if (ans < 0)
return 0; // If returned answer is negative ,
// that means cuts are not possible
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
dp = new int[10005];
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
System.out.println(maximizeTheCuts(l, p, q, r));
}
}
# Python Code to find maximum number of cut segments
# Memoization DP
import sys
# Function to find the maximum number of cuts.
dp = [0]*10005
def func(l, p, q, r):
# Base Case
if (l == 0):
return 0
# If already memoized
if (dp[l] != -1):
return dp[l]
# Intitialise a,b,& c with INT_MIN
a, b, c = -1*sys.maxsize,-1*sys.maxsize,-1*sys.maxsize
# If Possible to make a cut of length p
if (p <= l):
a = func(l - p, p, q, r)
# If possible to make a cut of length q
if (q <= l):
b = func(l - q, p, q, r)
# If possible to make a cut of length r
if (r <= l):
c = func(l - r, p, q, r)
# Memoize & return
dp[l] = 1 + max(max(a, b),c)
return dp[l]
def maximizeTheCuts(l, p, q, r):
# Set Lookup table to -1
for i in range(len(dp)):
dp[i]=-1
# Utility function call
ans = func(l, p, q, r)
# If returned answer is negative , that
# means cuts are not possible
if (ans < 0):
return 0
return ans
# Driver code
l = 11
p = 2
q = 3
r = 5
print(maximizeTheCuts(l, p, q, r))
# This code is contributed by Utkarsh
// C# Code to find maximum number of cut segments
// Memoization DP
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to find the maximum number of cuts.
static int[] dp;
static int func(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
if (l == 0)
return 0; // Base Case
if (dp[l] != -1) // If already memoized
return dp[l];
int a, b, c; // Intitialise a,b,& c with INT_MIN
a = Int32.MinValue;
b = Int32.MinValue;
c = Int32.MinValue;
if (p <= l) // If Possible to make a cut of length p
a = func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length q
b = func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length r
c = func(l - r, p, q, r);
return dp[l] = 1
+ Math.Max(Math.Max(a, b),
c); // Memoize & return
}
static int maximizeTheCuts(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
// Set Lookup table to -1
for(int i=0;i<dp.Length;i++)
{
dp[i]=-1;
}
int ans = func(l, p, q, r); // Utility function call
if (ans < 0)
return 0; // If returned answer is negative ,
// that means cuts are not possible
return ans;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main ()
{
dp = new int[10005];
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
Console.WriteLine(maximizeTheCuts(l, p, q, r));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Pushpesh Raj.
// Javascript Code to find maximum number of cut segments
// Memoization DP
// Function to find the maximum number of cuts.
let dp=new Array(10005);
function func( l, p, q, r)
{
if (l == 0)
return 0; // Base Case
if (dp[l] != -1) // If already memoized
return dp[l];
// Intitialise a,b,& c with INT_MIN
let a=Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
let b=Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
let c=Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
if (p <= l) // If Possible to make a cut of length p
a = func(l - p, p, q, r);
if (q <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length q
b = func(l - q, p, q, r);
if (r <= l) // If possible to make a cut of length r
c = func(l - r, p, q, r);
return dp[l] = 1 + Math.max(Math.max(a, b),c); // Memoize & return
}
function maximizeTheCuts(l, p, q, r)
{
// Set Lookup table to -1
for (let i = 0; i < dp.length; i++)
dp[i] = -1;
let ans = func(l, p, q, r); // Utility function call
if (ans < 0)
return 0; // If returned answer is negative , that
// means cuts are not possible
return ans;
}
// Driver code
let l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
console.log(maximizeTheCuts(l, p, q, r));
// This code is contributed by Aman Kumar
Time Complexity: O(N) where n is the length of the rod or line segment that has to be cut
Auxiliary Space: O(N) where n is the length of the rod or line segment that has to be cut
Maximize the number of segments of length p, q, and r using Dynamic Programming (DP):
As the solution for the maximum number of cuts that can be made in a given length depends on the maximum number of cuts previously made in shorter lengths, this question could be solved by the approach of Dynamic Programming. Suppose we are given a length ‘l’. For finding the maximum number of cuts that can be made in length ‘l’, find the number of cuts made in shorter previous length ‘l-p’, ‘l-q’, ‘l-r’ lengths respectively.
The required answer would be the max(l-p,l-q,l-r)+1 as one more cut should be needed after this to cut length ‘l‘. So for solving this problem for a given length, find the maximum number of cuts that can be made in lengths ranging from ‘1’ to ‘l’.
Example:
l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5
Analysing lengths from 1 to 11:
- Not possible to cut->0
- Possible cut is of lengths 2->1 (2)
- Possible cut is of lengths 3->1 (3)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[4-2],arr[4-3])+1->2 (2,2)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[5-2],arr[5-3])+1->2 (2,3)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[6-2],arr[6-3],arr[6-5])+1->3 (2,2,2)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[7-2],arr[7-3],arr[7-5])+1->3 (2,3,2) or (2,2,3)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[8-2],arr[8-3],arr[8-5])+1->4 (2,2,2,2)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[9-2],arr[9-3],arr[9-5])+1->4 (2,3,2,2) or (2,2,3,2) or (2,2,2,3)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[10-2],arr[10-3],arr[10-5])+1->5 (2,2,2,2,2)
- Possible cuts are of lengths max(arr[11-2],arr[11-3],arr[11-5])+1->5 (2,3,2,2,2) or (2,2,3,2,2) or (2,2,2,3,2) or (2,2,2,2,3)
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Initialise an array DP[]={-1} and DP[0]=0.
- Run a loop from ‘1’ to ‘l’
- If DP[i]=-1 means it’s not possible to divide it using giving segments p,q,r so continue
- DP[i+p]=max(DP[i+p],DP[i]+1)
- DP[i+q]=max(DP[i+q],DP[i]+1)
- DP[i+r]=max(DP[i+r],DP[i]+1)
- print DP[l]
Pseudo-Code:
C++
DP[l+1]={-1}
DP[0]=0
for(i from 0 to l)
if(DP[i]==-1)
continue
DP[i+p]=max(DP[i+p],DP[i]+1)
DP[i+q]=max(DP[i+q],DP[i]+1)
DP[i+r]=max(DP[i+r],DP[i]+1)
print(DP[l])
public class MaxSteps {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int l = 10; // replace 10 with your desired value of l
int p = 2; // replace 2 with your desired value of p
int q = 3; // replace 3 with your desired value of q
int r = 5; // replace 5 with your desired value of r
int[] DP = new int[l + 1];
DP[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
if (DP[i] == -1)
continue;
if (i + p <= l)
DP[i + p] = Math.max(DP[i + p], DP[i] + 1);
if (i + q <= l)
DP[i + q] = Math.max(DP[i + q], DP[i] + 1);
if (i + r <= l)
DP[i + r] = Math.max(DP[i + r], DP[i] + 1);
}
System.out.println(DP[l]);
}
}
#pseudo code in python for better understanding
DP = [-1] * (l + 1)
DP[0] = 0
for i in range(l + 1):
if DP[i] == -1:
continue
DP[i + p] = max(DP[i + p], DP[i] + 1)
DP[i + q] = max(DP[i + q], DP[i] + 1)
DP[i + r] = max(DP[i + r], DP[i] + 1)
print(DP[l])
let l = /* assign the value of l */;
let p = /* assign the value of p */;
let q = /* assign the value of q */;
let r = /* assign the value of r */;
let DP = new Array(l + 1).fill(-1);
DP[0] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
if (DP[i] == -1) {
continue;
}
if (i + p <= l) {
DP[i + p] = Math.max(DP[i + p], DP[i] + 1);
}
if (i + q <= l) {
DP[i + q] = Math.max(DP[i + q], DP[i] + 1);
}
if (i + r <= l) {
DP[i + r] = Math.max(DP[i + r], DP[i] + 1);
}
}
console.log(DP[l]);
//this code is contributed by adarsh
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to maximize the number
// of segments of length p, q and r
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function that returns the maximum number
// of segments possible
int findMaximum(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
// Array to store the cut at each length
int dp[l + 1];
// All values with -1
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
// if length of rod is 0 then total cuts will be 0
// so, initialize the dp[0] with 0
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
// if certain length is not possible
if (dp[i] == -1)
continue;
// if a segment of p is possible
if (i + p <= l)
dp[i + p] = max(dp[i + p], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of q is possible
if (i + q <= l)
dp[i + q] = max(dp[i + q], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of r is possible
if (i + r <= l)
dp[i + r] = max(dp[i + r], dp[i] + 1);
}
// if no segment can be cut then return 0
if (dp[l] == -1) {
dp[l] = 0;
}
// return value corresponding to length l
return dp[l];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
// Calling Function
int ans = findMaximum(l, p, q, r);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
// Java program to maximize
// the number of segments
// of length p, q and r
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Function that returns
// the maximum number
// of segments possible
static int findMaximum(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
// Array to store the
// cut at each length
int dp[] = new int[l + 1];
// All values with -1
for (int i = 0; i < l + 1; i++)
dp[i] = -1;
// if length of rod is 0
// then total cuts will
// be 0 so, initialize
// the dp[0] with 0
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
// if certain length
// is not possible
if (dp[i] == -1)
continue;
// if a segment of
// p is possible
if (i + p <= l)
dp[i + p] = Math.max(dp[i + p], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of
// q is possible
if (i + q <= l)
dp[i + q] = Math.max(dp[i + q], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of
// r is possible
if (i + r <= l)
dp[i + r] = Math.max(dp[i + r], dp[i] + 1);
}
// if no segment can be cut then return 0
if (dp[l] == -1) {
dp[l] = 0;
}
// return value corresponding
// to length l
return dp[l];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
// Calling Function
int ans = findMaximum(l, p, q, r);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by anuj_67.
# Python 3 program to
# maximize the number
# of segments of length
# p, q and r
# Function that returns
# the maximum number
# of segments possible
def findMaximum(l, p, q, r):
# Array to store the cut
# at each length
# All values with -1
dp = [-1]*(l + 1)
# if length of rod is 0 then
# total cuts will be 0
# so, initialize the dp[0] with 0
dp[0] = 0
for i in range(l+1):
# if certain length is not
# possible
if (dp[i] == -1):
continue
# if a segment of p is possible
if (i + p <= l):
dp[i + p] = (max(dp[i + p],
dp[i] + 1))
# if a segment of q is possible
if (i + q <= l):
dp[i + q] = (max(dp[i + q],
dp[i] + 1))
# if a segment of r is possible
if (i + r <= l):
dp[i + r] = (max(dp[i + r],
dp[i] + 1))
# if no segment can be cut then return 0
if dp[l] == -1:
dp[l] = 0
# return value corresponding
# to length l
return dp[l]
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
l = 11
p = 2
q = 3
r = 5
# Calling Function
ans = findMaximum(l, p, q, r)
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by
# ChitraNayal
// C# program to maximize
// the number of segments
// of length p, q and r
using System;
class GFG {
// Function that returns
// the maximum number
// of segments possible
static int findMaximum(int l, int p, int q, int r)
{
// Array to store the
// cut at each length
int[] dp = new int[l + 1];
// All values with -1
for (int i = 0; i < l + 1; i++)
dp[i] = -1;
// if length of rod is 0
// then total cuts will
// be 0 so, initialize
// the dp[0] with 0
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
// if certain length
// is not possible
if (dp[i] == -1)
continue;
// if a segment of
// p is possible
if (i + p <= l)
dp[i + p] = Math.Max(dp[i + p], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of
// q is possible
if (i + q <= l)
dp[i + q] = Math.Max(dp[i + q], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of
// r is possible
if (i + r <= l)
dp[i + r] = Math.Max(dp[i + r], dp[i] + 1);
}
// if no segment can be cut then return 0
if (dp[l] == -1) {
dp[l] = 0;
}
// return value corresponding
// to length l
return dp[l];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
// Calling Function
int ans = findMaximum(l, p, q, r);
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by anuj_67.
// Javascript program to maximize
// the number of segments
// of length p, q and r
// Function that returns
// the maximum number
// of segments possible
function findMaximum(l,p,q,r)
{
// Array to store the
// cut at each length
let dp = new Array(l + 1);
// All values with -1
for (let i = 0; i < l + 1; i++)
dp[i] = -1;
// if length of rod is 0
// then total cuts will
// be 0 so, initialize
// the dp[0] with 0
dp[0] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
// if certain length
// is not possible
if (dp[i] == -1)
continue;
// if a segment of
// p is possible
if (i + p <= l)
dp[i + p] = Math.max(dp[i + p], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of
// q is possible
if (i + q <= l)
dp[i + q] = Math.max(dp[i + q], dp[i] + 1);
// if a segment of
// r is possible
if (i + r <= l)
dp[i + r] = Math.max(dp[i + r], dp[i] + 1);
}
// if no segment can be cut then return 0
if (dp[l] == -1) {
dp[l] = 0;
}
// return value corresponding
// to length l
return dp[l];
}
// Driver Code
let l = 11, p = 2, q = 3, r = 5;
// Calling Function
let ans = findMaximum(l, p, q, r);
console.log(ans);
// This code is contributed by rag2127
Time Complexity: O(N). Use of a single for-loop till length ‘N’.
Auxiliary Space: O(N). Use of an array ‘DP’ to keep track of segments
Note: This problem can also be thought of as a minimum coin change problem because we are given a certain length to acquire which is the same as the value of the amount whose minimum change is needed. Now the x,y, and z are the same as the denomination of the coin given. So length is the same as the amount and x y z are the same as denominations, thus we need to change only one condition that is instead of finding the minimum we need to find the maximum and we will get the answer. As the minimum coin change problem is the basic dynamic programming question so this will help to solve this question also.
The condition we need to change in the minimum coin change problem is:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main() {
ll n = 10; // Example value of n
ll dp[1000]; // Assuming the size of dp array
ll a[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3}; // Example values for a array
fill(dp, dp + 1000, -1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (ll j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i >= a[j] && dp[i - a[j]] != -1) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], 1 + dp[i - a[j]]);
}
}
}
// Printing the dp array
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << "dp[" << i << "] = " << dp[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long n = 10; // Example value for n
long[] a = {0, 1, 2, 3}; // Example values for a array
long[] dp = new long[(int) (n + 1)]; // Array dp initialized with size n + 1
// Initialize dp array with -1
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = -1;
}
dp[0] = 0;
// Nested loops to iterate through i and j values
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
// Check conditions and update dp[i]
if (i >= a[j] && dp[i - (int) a[j]] != -1) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], 1 + dp[i - (int) a[j]]);
}
}
}
// Printing dp array values
System.out.println("Values of dp array:");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.println("dp[" + i + "] = " + dp[i]);
}
}
}
//this code is contributed by Utkkarsh.
n = 10 # Example value of n
a = [0, 1, 2, 3] # Example values for a array
dp = [-1] * (n + 1)
dp[0] = 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, 4):
if i >= a[j] and dp[i - a[j]] != -1:
dp[i] = max(dp[i], 1 + dp[i - a[j]])
# Printing the dp array
for i in range(1, n + 1):
print("dp[{}] = {}".format(i, dp[i]))
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
long n = 10; // Example value for n
long[] a = { 0, 1, 2, 3 }; // Example values for a array
long[] dp = new long[n + 1]; // Array dp initialized with size n + 1
// Initialize dp array with -1
for (long i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
dp[i] = -1;
}
dp[0] = 0;
// Nested loops to iterate through i and j values
for (long i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (long j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
{
// Check conditions and update dp[i]
if (i >= a[j] && dp[i - a[j]] != -1)
{
dp[i] = Math.Max(dp[i], 1 + dp[i - a[j]]);
}
}
}
// Printing dp array values
Console.WriteLine("Values of dp array:");
for (long i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("dp[" + i + "] = " + dp[i]);
}
}
}
function main() {
const n = 10; // Example value of n
const dp = new Array(1000).fill(-1); // Assuming the size of dp array
const a = [0, 1, 2, 3]; // Example values for a array
dp[0] = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i >= a[j] && dp[i - a[j]] !== -1) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], 1 + dp[i - a[j]]);
}
}
}
// Printing the dp array
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
console.log(`dp[${i}] = ${dp[i]}`);
}
}
main();
Outputdp[1] = 1
dp[2] = 2
dp[3] = 3
dp[4] = 4
dp[5] = 5
dp[6] = 6
dp[7] = 7
dp[8] = 8
dp[9] = 9
dp[10] = 10
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...