Matlab | Dilation of an Image
Last Updated :
23 Mar, 2022
Morphology is known as the broad set of image processing operations that process images based on shapes. It is also known as a tool used for extracting image components that are useful in the representation and description of region shape.
The basic morphological operations are:
Dilation:
- Dilation expands the image pixels i.e. it is used for expanding an element A by using structuring element B.
- Dilation adds pixels to object boundaries.
- The value of the output pixel is the maximum value of all the pixels in the neighborhood. A pixel is set to 1 if any of the neighboring pixels have the value 1.
Approach:
- Read the RGB image.
- Using function im2bw(), convert the RGB image to a binary image.
- Create a structuring element or you can use any predefined mask eg. special(‘sobel’).
- Store the number of rows and columns in an array and loop through it.
- Create a zero matrix of the size same as the size of our image.
- Leaving the boundary pixels start moving the structuring element on the image and start comparing the pixel with the pixels present in the neighborhood.
- If the value of the neighborhood pixel is 1, then change the value of that pixel to 1.
Example:
MATLAB
I=imread('lenna.png');
I=im2bw(I);
se=ones(5, 5);
[P, Q]=size(se);
In=zeros(size(I, 1), size(I, 2));
for i=ceil(P/2):size(I, 1)-floor(P/2)
for j=ceil(Q/2):size(I, 2)-floor(Q/2)
on=I(i-floor(P/2):i+floor(P/2), j-floor(Q/2):j+floor(Q/2));
nh=on(logical(se));
In(i, j)=max(nh(:));
end
end
imshow(In);
|
Output:

Figure: Input image
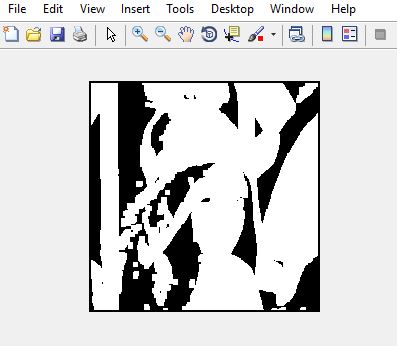
Figure: Output image
Let’s take another example for dilation.
Syntax:
- imread() function is used to read the image.
- strel() function is used to define the structuring element. We have chosen a disk-shaped SE, of radius 5.
- imdialate() function is used to perform the dilation operation.
- imtool() function is used to display the image.
Example:
Matlab
k=imread("dilation.png");
SE=strel('disk',5);
d=imdilate(k,SE);
imtool(k,[]);
imtool(d,[]);
imtool(d-k,[]);
|
Output:

Figure: Left: Original image, Right: Dilated image

Figure: Expansion in the original image
Code Explanation:
- k=imread(“dilation_exmp.png”); this line reads the image.
- SE=strel(‘disk’,5); this line defines the structuring element.
- d=imdilate(k,SE); this line applies the dilation operation.
- imtool(k,[]); this line displays the original image.
- imtool(e,[]); this line displays the dilated image.
- imtool(d-k,[]); this line shows the effective expansion in original image.
The last image shows the extent to which the original image got dilated. We have used the Structuring element of disk-shaped and the image we used is also circular in shape. This gives us the very desired output to understand erosion.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...