Mathematics | Ring Homomorphisms
Last Updated :
02 Jan, 2023
Prerequisite : Rings
Ring Homomorphism :
A set 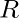 with any two binary operations on set
with any two binary operations on set 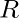 let denoted by
let denoted by 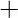 and
and 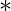 is called ring denoted as
is called ring denoted as 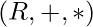 , if
, if 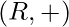 is abelian group, and
is abelian group, and 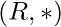 is semigroup, which also follow right and left distributive laws.
is semigroup, which also follow right and left distributive laws.
for two rings 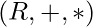 and
and 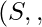 [Tex]\times [/Tex]
[Tex]\times [/Tex]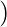 a mapping
a mapping 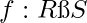 is called ring homomorphism if
is called ring homomorphism if
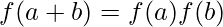 , ∀a, b ∈
, ∀a, b ∈ 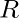 .
.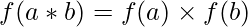 , ∀a, b ∈
, ∀a, b ∈ 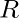 .
.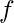 [Tex]( [/Tex]IR
[Tex]( [/Tex]IR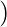
 IS , if IR and IS are identities (if they exist which in case of Ring with unity) of set
IS , if IR and IS are identities (if they exist which in case of Ring with unity) of set 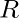 over
over 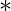 and set
and set 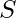 over
over 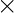 operations respectively.
operations respectively.
NOTE : Ring 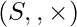 is called homomorphic image of ring
is called homomorphic image of ring 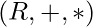 .
.
Examples :
- Function f(x) = x mod(n) from group (
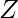 ,+,*) to (
,+,*) to (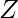 n,+,*) ∀x ∈
n,+,*) ∀x ∈ 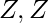 is group of integers. + and * are simple addition and multiplication operations respectively.
is group of integers. + and * are simple addition and multiplication operations respectively. - Function f(x) = x for any two groups (R,+,*) and (S,⨁,
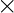 ) ∀x ∈ R, which is called identity ring homomorphism.
) ∀x ∈ R, which is called identity ring homomorphism. - Function f(x) = 0 for groups (N,*,+) and (Z,*,+) for ∀x ∈ N.
- Function f(x) = which is complex conjugate form group (C,+,*) to itself, here C is set of complex numbers. + and * are simple addition and multiplication operations respectively.
NOTE : If f is homomorphism from (R,+,*) and (S,⨁,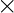 ) then f(OR) = f(OS) where OR and OS are identities of set R over + and set S over ⨁ operations respectively.
) then f(OR) = f(OS) where OR and OS are identities of set R over + and set S over ⨁ operations respectively.
NOTE : If f is ring homomorphism from (R,+,*) and (S,⨁,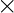 ) then f : (R,+) → (S,⨁) is group homomorphism.
) then f : (R,+) → (S,⨁) is group homomorphism.
Ring Isomorphism :
A one and onto homomorphism from ring 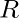 to ring
to ring 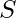 is called Ring Isomorphism, and
is called Ring Isomorphism, and 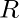 and
and 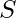 are Isomorphic.
are Isomorphic.
Ring Automorphism :
A homomorphism from a ring to itself is called Ring Automorphism.
Field Homomorphism :
For two fields 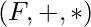 and
and 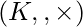 a mapping
a mapping 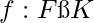 is called field homomorphism if
is called field homomorphism if
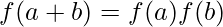 , ∀a, b ∈
, ∀a, b ∈ 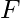 .
.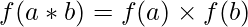 , ∀a, b ∈
, ∀a, b ∈ 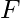 .
.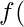 IF
IF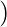
 IK , where IF and IK are identities of set
IK , where IF and IK are identities of set 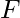 over
over 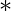 and set
and set 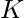 over
over 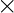 operations respectively.
operations respectively.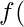 OF
OF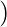
 OK , where OF and OK are identities of set
OK , where OF and OK are identities of set 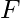 over
over 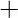 and set
and set 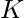 over
over  operations respectively.
operations respectively.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...