Mahotas – Eroding Image
Last Updated :
29 Jul, 2021
In this article we will see how we can erode the image in mahotas. Erosion (usually represented by ?) is one of two fundamental operations (the other being dilation) in morphological image processing from which all other morphological operations are based. It was originally defined for binary images, later being extended to grayscale images, and subsequently to complete lattices.
In this tutorial we will use “luispedro” image, below is the command to load it.
mahotas.demos.load('luispedro')
Below is the luispedro image

In order to do this we will use mahotas.morph.erodemethod
Syntax : mahotas.morph.erode(image)
Argument :It takes image object as argument
Return : It returns image object
Note : Input image should be filtered or should be loaded as grey
In order to filter the image we will take the image object which is numpy.ndarray and filter it with the help of indexing, below is the command to do this
image = image[:, :, 0]
Below is the implementation
Python3
import mahotas
import mahotas.demos
from pylab import gray, imshow, show
import numpy as np
luispedro = mahotas.demos.load('luispedro')
luispedro = luispedro.max(2)
T_otsu = mahotas.otsu(luispedro)
img = luispedro > T_otsu
print("Image threshold using Otsu Method")
imshow(img)
show()
new_img = mahotas.morph.erode(img)
print("Eroded Image")
imshow(new_img)
show()
|
Output :
Image threshold using Otsu Method
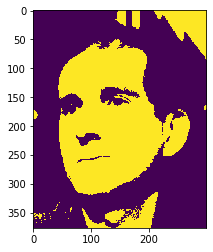
Eroded Image

Another example
Python3
import mahotas
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
img = mahotas.imread('dog_image.png')
img = img[:, :, 0]
T_otsu = mahotas.otsu(img)
img = img > T_otsu
print("Image threshold using Otsu Method")
imshow(img)
show()
new_img = mahotas.morph.erode(img)
print("Eroded Image")
imshow(new_img)
show()
|
Output :
Image threshold using Otsu Method
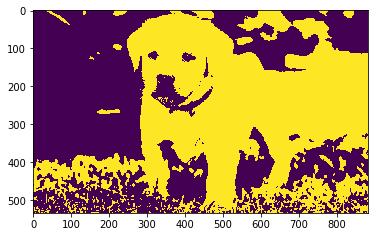
Eroded Image

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...