lsmod command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
23 May, 2019
lsmod command is used to display the status of modules in the Linux kernel. It results in a list of loaded modules. lsmod is a trivial program which nicely formats the contents of the /proc/modules, showing what kernel modules are currently loaded.
Syntax:
lsmod
Example: Run lsmod at the command line to list all active kernel modules.
lsmod
Output:
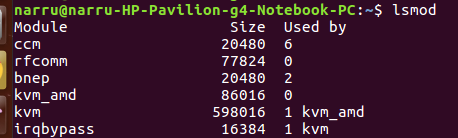
Output Format: There are three columns in output.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...