List All Available Commands and Aliases in Linux
Last Updated :
15 Sep, 2023
There might be sometimes a need to list all the commands and aliases supported by the current system. As we already know, an alias is a custom shortcut that references a command. It can be very useful to replace long commands with a small alternative command. While a command is a program that we can run in the terminal to produce some output or change the status of the system. In this article, we are going to talk about how we can list all the available commands and aliases in the Linux system.
Three methods for listing all the available commands and aliases in Linux:
- Method 1: Using compgen command
- Method 2: Using the alias command
- Method 3: Using bash script
Method 1: Using compgen command
We can list all the available commands and aliases supported by the system using the compgen command. Following is the excerpt from the help page about the compgen command
help compgen
.png)
1. List commands
To list all the commands supported by the system we can use the -c option
compgen -c
The following screenshot shows five of the commands supported:
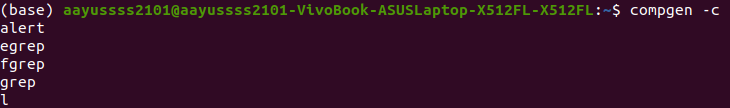
2. List aliases
To list all the aliases, we can use the -a option.
compgen -a
The following screenshot lists all the aliases in my system:

Method 2: Using the alias command
We can use the alias command to list all the aliases in the system. Following is the excerpt from the help page about the alias command
help alias

We can use the -p command to print all the defined aliases like
alias -p
.png)
To get a better and clear output we can pipe this output from the alias command to the cut command like
alias -p | cut -d' ' -f2

Method 3: Using bash script
We can also write a bash script to list all the commands. The following will suffice to do the job:
#!/bin/bash
echo $PATH | tr : '\n' |
while read e; do
for i in $e/*; do
if [[ -x "$i" && -f "$i" ]]; then
echo $i
fi
done
done
The following output lists five of the commands listed using the bash script.
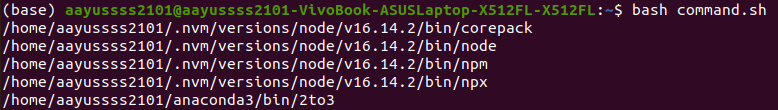
Now let us try to understand the above script. Using the $PATH environment variable, we have first obtained all of the directory paths that lead to executable files. The output is then piped to the tr command. Then, the while loop receives the output of the tr command, which converts the: from the input to a new line. The while loop puts the contents of each step in $e after reading each line using the read command. We traverse through each directory using the for loop, and we use the -x option to determine whether each file is executable. The -f option verifies a file’s existence and its regularity. Once the filename passes both checks, the echo command is used to show the path on the console.
Conclusion:
In this article, we learned how to list every command and alias available in Linux by using the compgen function. We also learned how to use a Bash script to list all the available commands and aliases using the alias command.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...