LinkedList remove() Method in Java
Last Updated :
06 Feb, 2023
LinkedList as we all know is a way of storing data that contains sets of nodes where each node contains data and address part where address part is responsible for linking of nodes and hence forming a List over which now we can perform operations. Now here we want to remove a node/s using the remove() method of LinkedList class only.
Illustration:
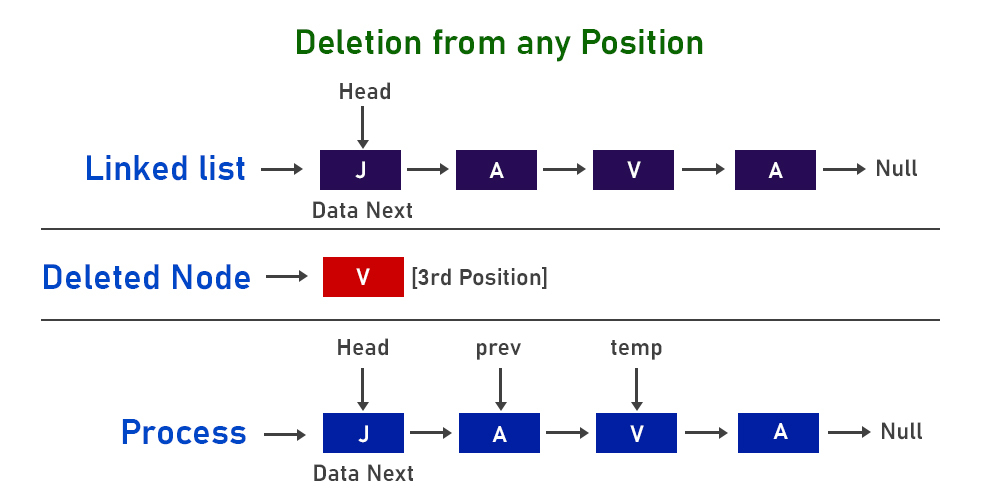
Types of remove() method present inside this class:
- With no arguments inside
- Passing index as in arguments
- Passing object as in arguments
let us discuss each of them alongside implementing by providing a clean java program which is as follows:
Type 1: remove() Method
It is used to remove an element from a linked list. The element is removed from the beginning or head of the linked list.
Syntax:
LinkedList.remove()
Parameters: This function does not take any parameter.
Return Value: This method returns the head of the list or the element present at the head of the list.
Example:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("for");
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("10");
list.add("20");
System.out.println("LinkedList:" + list);
list.remove();
System.out.println("Final LinkedList:" + list);
}
}
|
Output:
LinkedList:[Geeks, for, Geeks, 10, 20]
Final LinkedList:[for, Geeks, 10, 20]
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Type 2: remove(int index) Method
It is used to remove an element from a linked list from a specific position or index.
Syntax:
LinkedList.remove(int index)
Parameters: The parameter index is of integer data type and specifies the position of the element to be removed from the LinkedList.
Return Value: The element that has just been removed from the list.
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("for");
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("10");
list.add("20");
System.out.println("LinkedList:" + list);
list.remove(4);
System.out.println("Final LinkedList:" + list);
}
}
|
Output:
LinkedList:[Geeks, for, Geeks, 10, 20]
Final LinkedList:[Geeks, for, Geeks, 10]
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Type 3: remove(Object O) Method
It is used to remove any particular element from the linked list.
Syntax:
LinkedList.remove(Object O)
Parameters: The parameter O is of the object type of linked list and specifies the element to be removed from the list.
Return Value: Returns true if the specified element is found in the list.
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("for");
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("10");
list.add("20");
System.out.println("LinkedList:" + list);
list.remove("Geeks");
list.remove("20");
System.out.println("Final LinkedList:" + list);
}
}
|
Output:
LinkedList:[Geeks, for, Geeks, 10, 20]
Final LinkedList:[for, Geeks, 10]
Time complexity : O(n)
Auxiliary Space : O(n)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...