Linear Search vs Binary Search
Last Updated :
19 Dec, 2023
Prerequisite:
LINEAR SEARCH
Assume that item is in an array in random order and we have to find an item. Then the only way to search for a target item is, to begin with, the first position and compare it to the target. If the item is at the same, we will return the position of the current item. Otherwise, we will move to the next position. If we arrive at the last position of an array and still can not find the target, we return -1. This is called the Linear search or Sequential search.
Below is the code syntax for the linear search.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int search(int array[], int n, int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int search(int array[], int n, int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static int liner(int arr[], int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
}
|
Python
def linearSearch(array, n, x):
for i in range(0, n):
if (array[i] == x):
return i
return -1
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public static int search(int[] array, int n, int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function search(array, n, x)
{
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (array[i] == x){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
</script>
|
BINARY SEARCH
In a binary search, however, cut down your search to half as soon as you find the middle of a sorted list. The middle element is looked at to check if it is greater than or less than the value to be searched. Accordingly, a search is done to either half of the given list
Below is the code syntax for the binary search.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high)
{
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (array[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high)
{
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (array[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
public static int binary(int[] arr, int x)
{
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
}
else if (x > arr[mid]) {
start = mid + 1;
}
else {
end = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
|
Python
def binarySearch(array, x, low, high):
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low)//2
if array[mid] == x:
return mid
elif array[mid] < x:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public static int binary(int[] arr, int x)
{
int start = 0;
int end = arr.Length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
}
else if (x > arr[mid]) {
start = mid + 1;
}
else {
end = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function binarySearch(array, x, low, high)
{
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x){
return mid;
}
if (array[mid] < x){
low = mid + 1;
}
else{
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
</script>
|
Important Differences
|
Linear Search
|
Binary Search
|
| In linear search input data need not to be in sorted. |
In binary search input data need to be in sorted order. |
| It is also called sequential search. |
It is also called half-interval search. |
| The time complexity of linear search O(n). |
The time complexity of binary search O(log n). |
| Multidimensional array can be used. |
Only single dimensional array is used. |
| Linear search performs equality comparisons |
Binary search performs ordering comparisons |
| It is less complex. |
It is more complex. |
| It is very slow process. |
It is very fast process. |
Let us look at an example to compare the two:
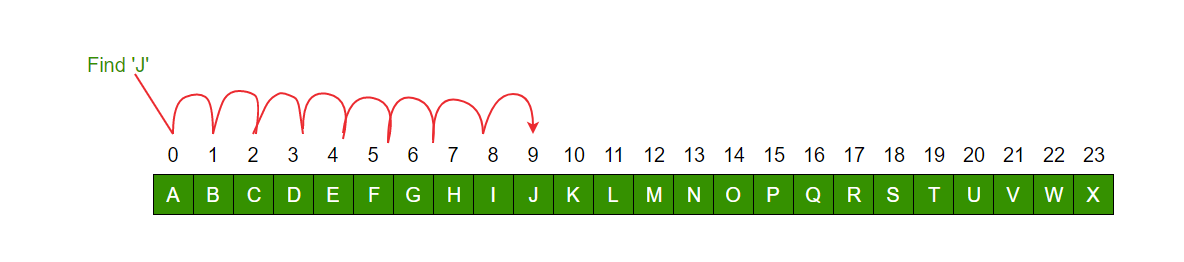
Linear Search to find the element “J” in a given sorted list from A-X
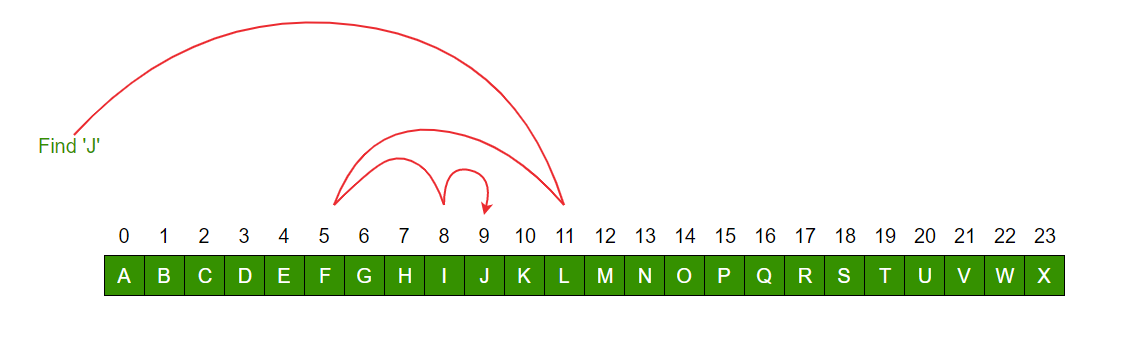
Binary Search to find the element “J” in a given sorted list from A-X
LINEAR SEARCHING EXAMPLE:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int search(int array[], int n, int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int array[] = { 12, 114, 0, 4, 9 };
int x = 4;
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int result = search(array, n, x);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element not found"
: cout << "Element found at index: " << result;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int search(int array[], int n, int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int array[] = { 12, 114, 0, 4, 9 };
int x = 4;
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int result = search(array, n, x);
(result == -1)
? printf("Element not found")
: printf("Element found at index: %d", result);
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static int liner(int arr[], int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 12, 114, 0, 4, 9 };
int search = liner(
arr,
4);
System.out.println(search);
}
}
|
Python
def linearSearch(array, n, x):
for i in range(0, n):
if (array[i] == x):
return i
return -1
array = [24, 41, 31, 11, 9]
x = 11
n = len(array)
result = linearSearch(array, n, x)
if(result == -1):
print("Element not found")
else:
print("Element is Present at Index: ", result)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public static int liner(int[] arr, int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public static void Main(string[] args){
int[] arr = { 12, 114, 0, 4, 9 };
int search = liner(arr, 4);
Console.Write(search);
}
}
|
Javascript
function search(array, n, x)
{
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
array = [12, 114, 0, 4, 9 ];
x = 4;
n = array.length;
result = search(array, n, x);
if(result == -1){
console.log("Element not found");
}
else{
console.log("Elementn found at index: ", result);
}
|
Output
Element found at index: 3
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the size of the input array. The worst-case scenario is when the target element is not present in the array, and the function has to go through the entire array to figure that out.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), the function uses only a constant amount of extra space to store variables. The amount of extra space used does not depend on the size of the input array.
BINARY SEARCHING EXAMPLE:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(vector<int> arr,int x,int low,int high){
while(low <= high){
int mid = low + (high - low)/2;
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
else if (arr[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
vector<int> arr = {2, 4, 5, 7, 14, 17, 19, 22};
int x = 22;
int result = binarySearch(arr, x, 0, arr.size()-1);
if (result != -1)
cout << result << endl;
else
cout << "Not found" << endl;
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high)
{
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (array[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main( )
{
int array[] = { 2, 4, 5, 7, 14, 17, 19, 22 };
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int x = 22;
int result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, n - 1);
if (result == -1)
printf("Not found");
else
printf(" %d", result);
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class GFG {
public static int binary(int arr[], int x)
{
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
}
else if (x > arr[mid]) {
start = mid + 1;
}
else {
end = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 4, 5, 7, 14, 17, 19, 22};
int search = binary(arr, 22);
System.out.println(search);
}
}
|
Python
def binarySearch(array, x, low, high):
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low)//2
if array[mid] == x:
return mid
elif array[mid] < x:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1
array = [2, 4, 5, 7, 14, 17, 19, 22]
x = 22
result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, len(array)-1)
if result != -1:
print(str(result))
else:
print("Not found")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public static int binary(int[] arr, int x)
{
int start = 0;
int end = arr.Length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
}
else if (x > arr[mid]) {
start = mid + 1;
}
else {
end = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void Main(string[] args){
int[] arr = { 2, 4, 5, 7, 14, 17, 19, 22 };
int search = binary(arr, 22);
Console.Write(search);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function binarySearch(array, x, low, high){
while(low <= high){
let mid = low + Math.floor((high - low)/2);
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
else if (array[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
let array = [2, 4, 5, 7, 14, 17, 19, 22];
let x = 22;
let result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, array.length-1);
if (result != -1)
console.log(result);
else
console.log("Not found");
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(log n) – Binary search algorithm divides the input array in half at every step, reducing the search space by half, and hence has a time complexity of logarithmic order.
Auxiliary Space: O(1) – Binary search algorithm requires only constant space for storing the low, high, and mid indices, and does not require any additional data structures, so its auxiliary space complexity is O(1).
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...