Linear Congruence method for generating Pseudo Random Numbers
Last Updated :
17 Jul, 2021
Linear Congruential Method is a class of Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG) algorithms used for generating sequences of random-like numbers in a specific range. This method can be defined as:
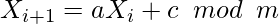
where,
X, is the sequence of pseudo-random numbers
m, ( > 0) the modulus
a, (0, m) the multiplier
c, (0, m) the increment
X0, [0, m) – Initial value of sequence known as seed
m, a, c, and X0 should be chosen appropriately to get a period almost equal to m.
For a = 1, it will be the additive congruence method.
For c = 0, it will be the multiplicative congruence method.
Approach:
- Choose the seed value X0, Modulus parameter m, Multiplier term a, and increment term c.
- Initialize the required amount of random numbers to generate (say, an integer variable noOfRandomNums).
- Define a storage to keep the generated random numbers (here, vector is considered) of size noOfRandomNums.
- Initialize the 0th index of the vector with the seed value.
- For rest of the indexes follow the Linear Congruential Method to generate the random numbers.
randomNums[i] = ((randomNums[i – 1] * a) + c) % m
Finally, return the random numbers.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void linearCongruentialMethod(
int Xo, int m, int a, int c,
vector<int>& randomNums,
int noOfRandomNums)
{
randomNums[0] = Xo;
for (int i = 1; i < noOfRandomNums; i++) {
randomNums[i]
= ((randomNums[i - 1] * a) + c) % m;
}
}
int main()
{
int Xo = 5;
int m = 7;
int a = 3;
int c = 3;
int noOfRandomNums = 10;
vector<int> randomNums(
noOfRandomNums);
linearCongruentialMethod(
Xo, m, a, c,
randomNums, noOfRandomNums);
for (int i = 0; i < noOfRandomNums; i++) {
cout << randomNums[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static void linearCongruentialMethod(int Xo, int m,
int a, int c,
int[] randomNums,
int noOfRandomNums)
{
randomNums[0] = Xo;
for(int i = 1; i < noOfRandomNums; i++)
{
randomNums[i] = ((randomNums[i - 1] * a) + c) % m;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int Xo = 5;
int m = 7;
int a = 3;
int c = 3;
int noOfRandomNums = 10;
int[] randomNums = new int[noOfRandomNums];
linearCongruentialMethod(Xo, m, a, c,
randomNums,
noOfRandomNums);
for(int i = 0; i < noOfRandomNums; i++)
{
System.out.print(randomNums[i] + " ");
}
}
}
|
Python3
def linearCongruentialMethod(Xo, m, a, c,
randomNums,
noOfRandomNums):
randomNums[0] = Xo
for i in range(1, noOfRandomNums):
randomNums[i] = ((randomNums[i - 1] * a) +
c) % m
if __name__ == '__main__':
Xo = 5
m = 7
a = 3
c = 3
noOfRandomNums = 10
randomNums = [0] * (noOfRandomNums)
linearCongruentialMethod(Xo, m, a, c,
randomNums,
noOfRandomNums)
for i in randomNums:
print(i, end = " ")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static void linearCongruentialMethod(int Xo, int m,
int a, int c,
int[] randomNums,
int noOfRandomNums)
{
randomNums[0] = Xo;
for(int i = 1; i < noOfRandomNums; i++)
{
randomNums[i] = ((randomNums[i - 1] * a) + c) % m;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int Xo = 5;
int m = 7;
int a = 3;
int c = 3;
int noOfRandomNums = 10;
int[] randomNums = new int[noOfRandomNums];
linearCongruentialMethod(Xo, m, a, c,
randomNums,
noOfRandomNums);
for(int i = 0; i < noOfRandomNums; i++)
{
Console.Write(randomNums[i] + " ");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function linearCongruentialMethod(Xo, m, a, c,
randomNums, noOfRandomNums)
{
randomNums[0] = Xo;
for(let i = 1; i < noOfRandomNums; i++)
{
randomNums[i] = ((randomNums[i - 1] * a) + c) % m;
}
}
let Xo = 5;
let m = 7;
let a = 3;
let c = 3;
let noOfRandomNums = 10;
let randomNums = new Array(noOfRandomNums).fill(0);
linearCongruentialMethod(Xo, m, a, c,
randomNums,
noOfRandomNums);
for(let i = 0; i < noOfRandomNums; i++)
{
document.write(randomNums[i] + " ");
}
</script>
|
Output: 5 4 1 6 0 3 5 4 1 6
The literal meaning of pseudo is false. These random numbers are called pseudo because some known arithmetic procedure is utilized to generate. Even the generated sequence forms a pattern hence the generated number seems to be random but may not be truly random.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...