LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) approach in Programming
Last Updated :
01 Sep, 2022
Prerequisites – FIFO (First-In-First-Out) approach in Programming, FIFO vs LIFO approach in Programming
LIFO is an abbreviation for last in, first out. It is a method for handling data structures where the first element is processed last and the last element is processed first.
Real-life example:
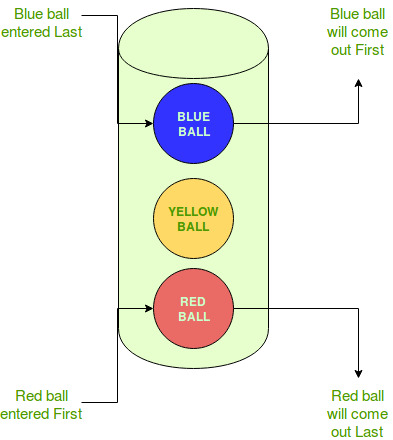
In this example, following things are to be considered:
- There is a bucket that holds balls.
- Different types of balls are entered into the bucket.
- The ball to enter the bucket last will be taken out first.
- The ball entering the bucket next to last will be taken out after the ball above it (the newer one).
- In this way, the ball entering the bucket first will leave the bucket last.
- Therefore, the Last ball (Blue) to enter the bucket gets removed first and the First ball (Red) to enter the bucket gets removed last.
This is known as Last-In-First-Out approach or LIFO.
Where is LIFO used:
- Data Structures:
Certain data structures like Stacks and other variants of Stacks use LIFO approach for processing data.
- Extracting latest information:
Sometimes computers use LIFO when data is extracted from an array or data buffer. When it is required to get the most recent information entered, the LIFO approach is used.
Program Examples for LIFO:
Implementation: Using Stack data structure.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack<int> stack_push(stack<int> stack)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.push(i);
}
return stack;
}
stack<int> stack_pop(stack<int> stack)
{
cout << "Pop :";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int y = (int)stack.top();
stack.pop();
cout << (y) << endl;
}
return stack;
}
void stack_peek(stack<int> stack)
{
int element = (int)stack.top();
cout << "Element on stack top : " << element << endl;
}
void stack_search(stack<int> stack, int element)
{
int pos = -1,co = 0;
while(stack.size() > 0)
{
co++;
if(stack.top() == element)
{
pos = co;
break;
}
stack.pop();
}
if (pos == -1)
cout << "Element not found" << endl;
else
cout << "Element is found at position " << pos << endl;
}
int main()
{
stack<int> stack ;
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack = stack_pop(stack);
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void stack_push(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
stack.push(i);
}
}
static void stack_pop(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
System.out.println("Pop :");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Integer y = (Integer)stack.pop();
System.out.println(y);
}
}
static void stack_peek(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
Integer element = (Integer)stack.peek();
System.out.println("Element on stack top : " + element);
}
static void stack_search(Stack<Integer> stack, int element)
{
Integer pos = (Integer)stack.search(element);
if (pos == -1)
System.out.println("Element not found");
else
System.out.println("Element is found at position " + pos);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack_push(stack);
stack_pop(stack);
stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
}
}
|
Python3
def stack_push(stack):
for i in range(5):
stack.append(i)
return stack
def stack_pop(stack):
print("Pop :")
for i in range(5):
y = stack[-1]
stack.pop()
print(y)
return stack
def stack_peek(stack):
element = stack[-1]
print("Element on stack top :", element)
def stack_search(stack, element):
pos = -1
co = 0
while(len(stack) > 0):
co+=1
if(stack[-1] == element):
pos = co
break
stack.pop()
if (pos == -1):
print( "Element not found")
else:
print("Element is found at position", pos)
stack = []
stack_push(stack)
stack_pop(stack)
stack_push(stack)
stack_peek(stack)
stack_search(stack, 2)
stack_search(stack, 6)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static void stack_push(Stack<int> stack)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.Push(i);
}
}
static void stack_pop(Stack<int> stack)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pop :");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int y = (int)stack.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
static void stack_peek(Stack<int> stack)
{
int element = (int)stack.Peek();
Console.WriteLine("Element on stack top : " + element);
}
static void stack_search(Stack<int> stack, int element)
{
bool pos = stack.Contains(element);
if (pos == false)
Console.WriteLine("Element not found");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element is found at position " + pos);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
stack_push(stack);
stack_pop(stack);
stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function stack_push(stack)
{
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.push(i);
}
return stack;
}
function stack_pop(stack)
{
document.write( "Pop :<br>");
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
var y = parseInt(stack[stack.length-1]);
stack.pop();
document.write( y + "<br>");
}
return stack;
}
function stack_peek(stack)
{
var element = parseInt(stack[stack.length-1]);
document.write( "Element on stack top : " + element +
"<br>");
}
function stack_search( stack, element)
{
var pos = -1,co = 0;
while(stack.length > 0)
{
co++;
if(stack[stack.length-1] == element)
{
pos = co;
break;
}
stack.pop();
}
if (pos == -1)
document.write( "Element not found" + "<br>");
else
document.write("Element is found at position "
+ pos + "<br>");
}
stack=[] ;
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack = stack_pop(stack);
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
</script>
|
Output
Pop :4
3
2
1
0
Element on stack top : 4
Element is found at position 3
Element not found
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...