json.load() in Python
Last Updated :
23 Mar, 2020
The full-form of JSON is JavaScript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called json. To use this feature, we import the json package in Python script. The text in JSON is done through quoted-string which contains the value in key-value mapping within { }. It is similar to the dictionary in Python.
Note: For more information, refer to Working With JSON Data in Python
json.load()
json.load() takes a file object and returns the json object. A JSON object contains data in the form of key/value pair. The keys are strings and the values are the JSON types. Keys and values are separated by a colon. Each entry (key/value pair) is separated by a comma.
Syntax :
json.load(file_object)
Argument : It takes file object as a parameter.
Return : It return json object.
Example: Let’s suppose the JSON looks like this.
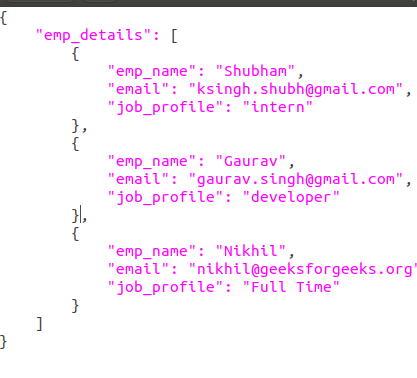
We want to read the content of this file. Below is the implementation.
import json
f = open('data.json',)
data = json.load(f)
for i in data['emp_details']:
print(i)
f.close()
|
Output:

Here, we have used the open() function to read the JSON file. Then, the file is parsed using json.load() method which gives us a dictionary named data.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...