Javascript Program To Write Your Own atoi()
Last Updated :
05 May, 2023
The atoi() function in C takes a string (which represents an integer) as an argument and returns its value of type int. So basically the function is used to convert a string argument to an integer.
Syntax:
int atoi(const char strn)
Parameters: The function accepts one parameter strn which refers to the string argument that is needed to be converted into its integer equivalent.
Return Value: If strn is a valid input, then the function returns the equivalent integer number for the passed string number. If no valid conversion takes place, then the function returns zero.
Now let’s understand various ways in which one can create their own atoi() function supported by various conditions:
Approach 1: Following is a simple implementation of conversion without considering any special case.
- Initialize the result as 0.
- Start from the first character and update result for every character.
- For every character update the answer as result = result * 10 + (s[i] – ‘0’)
Javascript
<script>
function myAtoi(str)
{
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; ++i)
res = res * 10 + str[i].charCodeAt(0) - '0'.charCodeAt(0);
return res;
}
let str = "89789";
let val = myAtoi(str);
document.write(val);
</script>
|
Time Complexity : O(N) , as only one traversal of string.
Auxiliary Space : O(1), as no extra space needed.
Approach 2: This implementation handles the negative numbers. If the first character is ‘-‘ then store the sign as negative and then convert the rest of the string to number using the previous approach while multiplying sign with it.
Javascript
<script>
function myAtoi(str)
{
var res = 0;
var sign = 1;
var i = 0;
if (str[0] == '-') {
sign = -1;
i++;
}
for (; i < str.length; ++i)
res = res * 10 + str[i].charCodeAt(0) - '0'.charCodeAt(0);
return sign * res;
}
var str = "-129";
var val=myAtoi(str);
document.write(val);
</script>
<! --This code is contributed by nirajgusain5 -->
|
Time complexity of the above code is O(n) where n is the length of the input string. This is because the code iterates through each character in the string and performs a constant time operation for each character.
The space complexity of the code is also O(n), where n is the length of the input string. This is because the code uses a single integer variable to store the numerical result, and this variable will have at most n digits in its binary representation. Additionally, the code does not use any additional data structures that would contribute to the space complexity.
Approach 3: This implementation handles various type of errors. If str is NULL or str contains non-numeric characters then return 0 as the number is not valid.
Approach 4: Four corner cases needs to be handled:
- Discards all leading whitespaces
- Sign of the number
- Overflow
- Invalid input
To remove the leading whitespaces run a loop until a character of the digit is reached. If the number is greater than or equal to INT_MAX/10. Then return INT_MAX if the sign is positive and return INT_MIN if the sign is negative. The other cases are handled in previous approaches.
Dry Run:
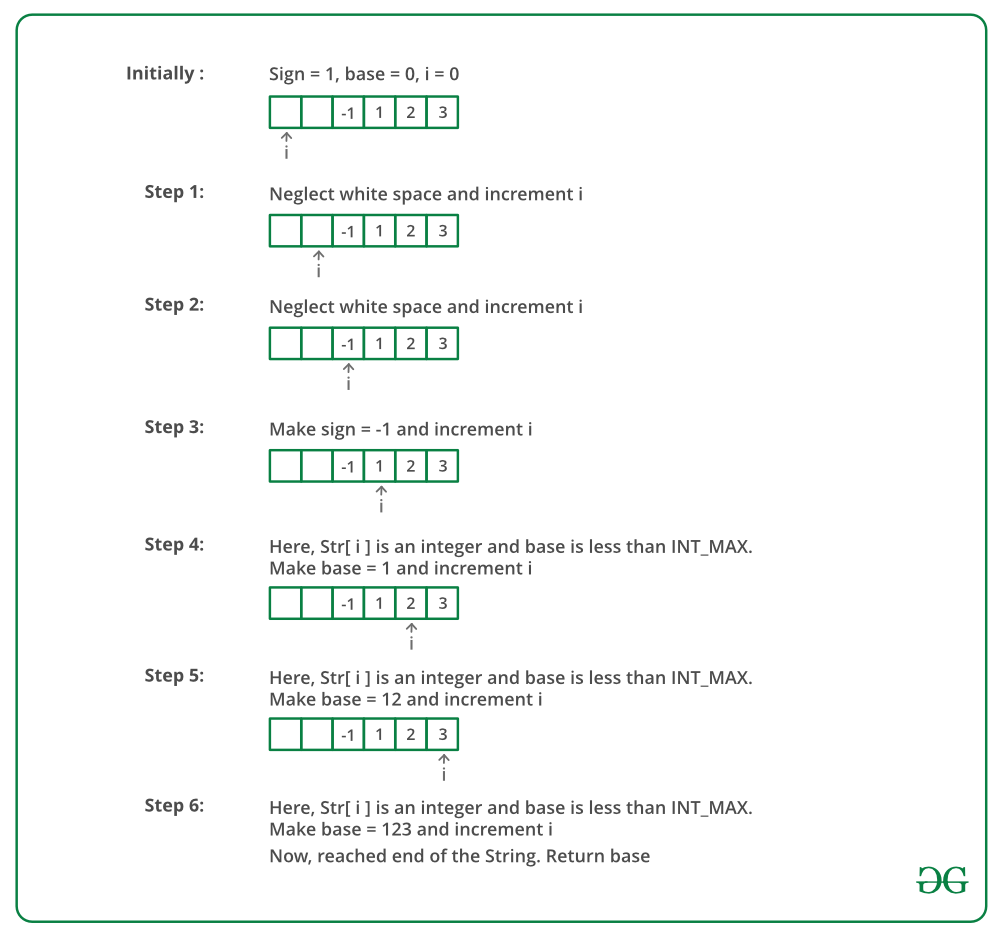
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Javascript
<script>
function myAtoi(str)
{
var sign = 1, base = 0, i = 0;
while (str[i] == ' ')
{
i++;
}
if (str[i] == '-' || str[i] == '+')
{
sign = 1 - 2 * (str[i++] == '-');
}
while (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
{
if (base > Number.MAX_VALUE/ 10
|| (base == Number.MAX_VALUE / 10
&& str[i] - '0' > 7))
{
if (sign == 1)
return Number.MAX_VALUE;
else
return Number.MAX_VALUE;
}
base = 10 * base + (str[i++] - '0');
}
return base * sign;
}
var str = " -123";
var val = myAtoi(str);
document.write(" ", val);
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis for all the above Approaches:
- Time Complexity: O(n).
Only one traversal of string is needed.
- Space Complexity: O(1).
As no extra space is required.
Recursive program for atoi().
Exercise:
Write your won atof() that takes a string (which represents an floating point value) as an argument and returns its value as double.
Please refer complete article on Write your own atoi() for more details!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...