Javascript Program For Merge Sort Of Linked Lists
Last Updated :
10 Nov, 2022
Merge sort is often preferred for sorting a linked list. The slow random-access performance of a linked list makes some other algorithms (such as quicksort) perform poorly, and others (such as heapsort) completely impossible.
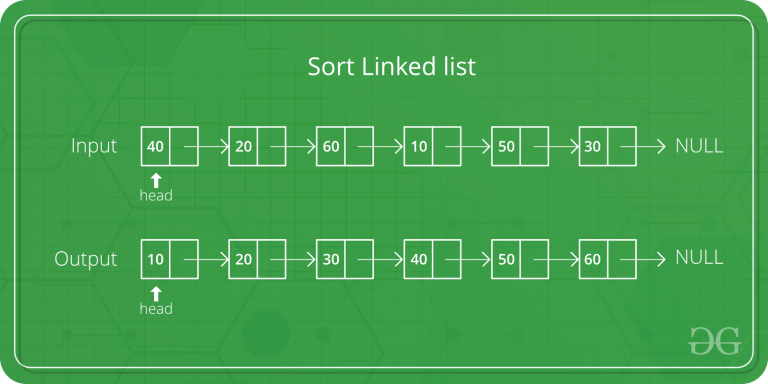
Let the head be the first node of the linked list to be sorted and headRef be the pointer to head. Note that we need a reference to head in MergeSort() as the below implementation changes next links to sort the linked lists (not data at the nodes), so the head node has to be changed if the data at the original head is not the smallest value in the linked list.
MergeSort(headRef)
1) If the head is NULL or there is only one element in the Linked List
then return.
2) Else divide the linked list into two halves.
FrontBackSplit(head, &a, &b); /* a and b are two halves */
3) Sort the two halves a and b.
MergeSort(a);
MergeSort(b);
4) Merge the sorted a and b (using SortedMerge() discussed here)
and update the head pointer using headRef.
*headRef = SortedMerge(a, b);
Javascript
<script>
var head = null;
class node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
function sortedMerge( a, b)
{
var result = null;
if (a == null)
return b;
if (b == null)
return a;
if (a.val <= b.val) {
result = a;
result.next = sortedMerge(a.next, b);
} else {
result = b;
result.next = sortedMerge(a, b.next);
}
return result;
}
function mergeSort( h) {
if (h == null || h.next == null) {
return h;
}
var middle = getMiddle(h);
var nextofmiddle = middle.next;
middle.next = null;
var left = mergeSort(h);
var right = mergeSort(nextofmiddle);
var sortedlist = sortedMerge(left, right);
return sortedlist;
}
function getMiddle( head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
var slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
function push(new_data) {
var new_node = new node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
function printList( headref) {
while (headref != null) {
document.write(headref.val + " ");
headref = headref.next;
}
}
push(15);
push(10);
push(5);
push(20);
push(3);
push(2);
head = mergeSort(head);
document.write("
Sorted Linked List is:
");
printList(head);
</script>
|
Output:
Sorted Linked List is:
2 3 5 10 15 20
Time Complexity: O(n*log n)
Space Complexity: O(n*log n)
Approach 2: This approach is simpler and uses log n space.
mergeSort():
- If the size of the linked list is 1 then return the head
- Find mid using The Tortoise and The Hare Approach
- Store the next of mid in head2 i.e. the right sub-linked list.
- Now Make the next midpoint null.
- Recursively call mergeSort() on both left and right sub-linked list and store the new head of the left and right linked list.
- Call merge() given the arguments new heads of left and right sub-linked lists and store the final head returned after merging.
- Return the final head of the merged linkedlist.
merge(head1, head2):
- Take a pointer say merged to store the merged list in it and store a dummy node in it.
- Take a pointer temp and assign merge to it.
- If the data of head1 is less than the data of head2, then, store head1 in next of temp & move head1 to the next of head1.
- Else store head2 in next of temp & move head2 to the next of head2.
- Move temp to the next of temp.
- Repeat steps 3, 4 & 5 until head1 is not equal to null and head2 is not equal to null.
- Now add any remaining nodes of the first or the second linked list to the merged linked list.
- Return the next of merged(that will ignore the dummy and return the head of the final merged linked list)
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
function mergeSort(head) {
if (head.next == null)
return head;
var mid = findMid(head);
var head2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
var newHead1 = mergeSort(head);
var newHead2 = mergeSort(head2);
var finalHead = merge(newHead1, newHead2);
return finalHead;
}
function merge(head1, head2) {
var merged = new Node(-1);
var temp = merged;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.data < head2.data) {
temp.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
temp.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
while (head1 != null) {
temp.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
while (head2 != null) {
temp.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
return merged.next;
}
function findMid(head) {
var slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
function printList(head) {
while (head != null) {
document.write(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
var head = new Node(7);
var temp = head;
temp.next = new Node(10);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(5);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(20);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(3);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(2);
temp = temp.next;
head = mergeSort(head);
document.write("Sorted Linked List is: <br/>");
printList(head);
</script>
|
Output:
Sorted Linked List is:
2 3 5 7 10 20
Time Complexity: O(n*log n)
Space Complexity: O(log n)
Please refer complete article on Merge Sort for Linked Lists for more details!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...