JavaScript Output
Last Updated :
18 Apr, 2024
JavaScript output refers to the information, results, or content that a JS program displays for users. Output in JavaScript can be displayed in various forms, and developers often use different methods to display the output of a given code.
JavaScript Output Display Properties
There are primarily four distinct methods for displaying output in JavaScript. Although there are other methods for output display, they are not advisable, so it is recommended to refrain from using alternative output approaches.
- innerHTML – Display the HTML output on an element.
- Using console.log() Method – Display the content on the browser console.
- document.write() method – Displays the content on an HTML element.
- window.alert() Method – Display the HTML element to the output.
JavaScript innerHTML Property
The innerHTML property is used with HTML element. JavaScript can be used to select an element using the document.getElementById(id) method, and then use the innerHTML property to display the output on the specified element (selected element).
Syntax:
document.getElementById("id").innerHTML;Example: The document.getElementById(id) method with innerHTML property is used to display the output.
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JavaScript Output</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>
Display Output using innerHTML Property
</h2>
<p id="GFG"></p>
<!-- Script to use innerHTML -->
<script>
document.getElementById("GFG").innerHTML
= "Hello Geeks!";
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

JavaScript console.log() Method
The console.log() method is used for logging messages to the console. It is a debugging tool available in most web browsers. It is used during development to output information about the state of the program.
Syntax:
console.log();
Example: This example uses the console.log() property to display data.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JavaScript Output</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>
Display Output using console.log() Method
</h2>
<!-- Script to use console.log() -->
<script>
console.log("Hello Geeks!");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

JavaScript document.write() Method
To use the document.write(), simply call this method and provide the content you want to be written to the document. This method is often used for directly adding content to the HTML document while it is being parsed.
Note: If we use document.write() after the HTML document is loaded, it will delete all existing HTML.
Syntax:
document.write();
Example: The document.write() method display the output.
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JavaScript Output</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>
Display Output using document.write() Method
</h2>
<!-- Script to uses document.write() -->
<script>
document.write("Hello Geeks!");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

JavaScript window.alert() Method
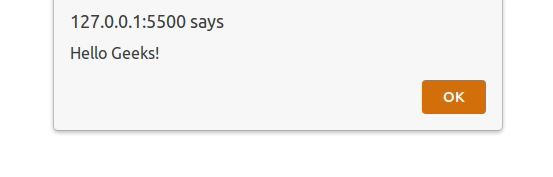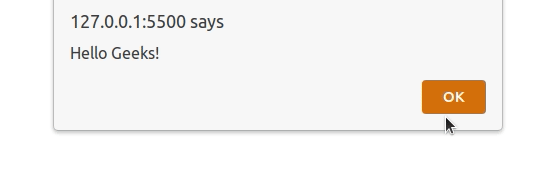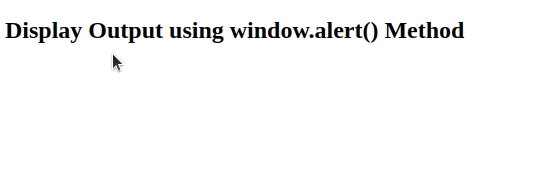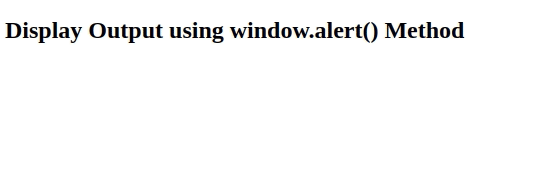
The window.alert() method is used to display an alert box with a specified outut (or message) and an OK button.
Syntax:
window.alert();
Note: We can skip the window keyword in this method.
Example: The window.alert() method display the output data.
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JavaScript Output</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>
Display Output using window.alert() Method
</h2>
<!-- Script to use window.alert() -->
<script>
window.alert("Hello Geeks!");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
JavaScript window.print() Method
The window.print() method is used to open the browser’s print dialog, allowing the user to print the current page. JavaScript does not contain any default print object or methods.
Syntax:
window.print();
Example: The window.print() method prints the current page.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript window.print() Method</h2>
<button onclick="window.print()">
Click here to Print
</button>
</body>
</html>
Output:

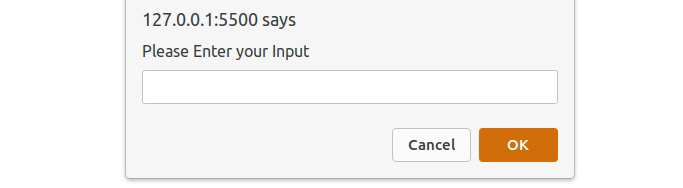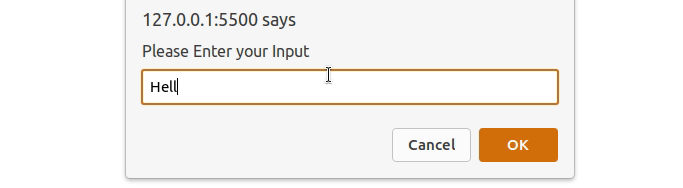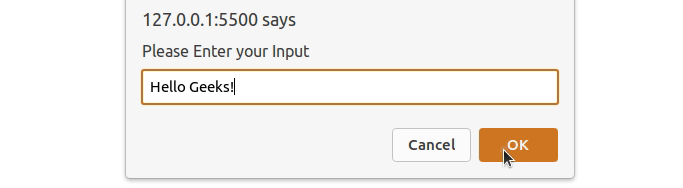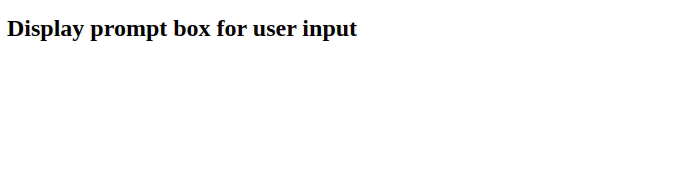
JavaScript window.prompt() Method
The window.prompt() method is used to display a dialog box that prompts the user input. It returns the text entered by the user as a string. It doesn’t display output directly but captures user input.
Note: This method is not used for output, it only use to take input from user.
Syntax:
window.prompt();
Example: The window.prompt() method to take user input and display the entered data used alert() method.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JavaScript Output</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>
Display prompt box for user input
</h2>
<script>
let userInput = window.prompt("Please Enter your Input");
if (userInput !== null) {
window.alert("Hello, " + userInput + "!");
} else {
window.alert("You clicked Cancel or closed the prompt.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...