JavaScript Date setUTCMilliseconds() Method
Last Updated :
19 May, 2023
The date.setUTCMilliseconds() method is used to set milliseconds according to universal time into a date object which is created using Date() constructor.
Syntax:
DateObj.setUTCMilliseconds(milliseconds_Value);
Parameter: This method accepts a single parameter as mentioned above and described below:
- milliseconds_Value: This parameter holds the value of millisecond which is used to set in Date() constructor.
Return Values: It returns the new i.e. updated millisecond which is set by the setUTCMilliseconds() method.
Note: The DateObj is a valid Date object created using the Date() constructor in which we want to set the millisecond according to universal time. The value of milliseconds is from 0 to 999.
Below are examples of the Date.setUTCMilliseconds() method.
Example 1:
Javascript
let dateobj =
new Date('October 13, 1996 05:35:32:77 GMT-3:00');
dateobj.setUTCMilliseconds(52);
let B = dateobj.getUTCMilliseconds();
console.log(B);
|
Output:
52
Example 2: If in the Date() constructor we do not give a millisecond while creating the Date object, still setUTCMilliseconds() method will be able to set new millisecond which is given as its parameter in the created Date object.
Javascript
let dateobj = new Date('October 13, 1996 GMT-3:00');
dateobj.setUTCMilliseconds(51);
let B = dateobj.getUTCMilliseconds();
console.log(B);
|
Output:
51
Example 3: If nothing as a parameter is given in the Date() constructor, still setUTCMilliseconds() method will be able to set milliseconds but a month, year, date, etc remains current according to universal time.
Here 42 is the new milliseconds, 3 is the current month i.e. April, 1 is the current date and 2018 is the current year according to universal time.
Javascript
let dateobj = new Date();
dateobj.setUTCMilliseconds(42);
let B = dateobj.getUTCMilliseconds();
let C = dateobj.getUTCMonth();
let D = dateobj.getUTCDate();
let E = dateobj.getUTCFullYear();
console.log(B);
console.log(C);
console.log(D);
console.log(E);
|
Output:
42
3
1
2018
Example 4: If the value of millisecond 1006 is given as the parameter of the setUTCMilliseconds() method, It will set 6 as the millisecond because the millisecond range is from 0 to 999, and hence 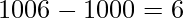 here 1000 is subtracted because 0 to 999 is 1000.
here 1000 is subtracted because 0 to 999 is 1000.
Javascript
let dateobj =
new Date('October 13, 1996 05:35:32:45 GMT-3:00');
dateobj.setUTCMilliseconds(1006);
let B = dateobj.getUTCMilliseconds();
let C = dateobj.getUTCSeconds();
console.log(B);
console.log(C);
|
Output:
6
33
We have a complete list of Javascript Date Objects, to check those please go through this Javascript Date Object Complete reference article.
Supported Browsers: The browsers supported by the JavaScript Date setUTCMilliseconds() method are listed below:
- Google Chrome
- Internet Explorer
- Mozilla Firefox
- Opera
- Safari
We have a Cheat Sheet on Javascript where we covered all the important topics of Javascript to check those please go through Javascript Cheat Sheet-A Basic guide to JavaScript.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...