Java Program For Reversing A Doubly Linked List
Last Updated :
18 Apr, 2023
Given a Doubly Linked List, the task is to reverse the given Doubly Linked List.
See below diagrams for example.
(a) Original Doubly Linked List
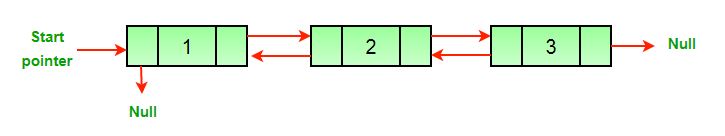
(b) Reversed Doubly Linked List
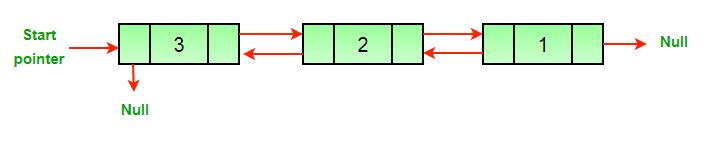
Here is a simple method for reversing a Doubly Linked List. All we need to do is swap prev and next pointers for all nodes, change prev of the head (or start) and change the head pointer in the end.
Java
class LinkedList
{
static Node head;
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
void reverse()
{
Node temp = null;
Node current = head;
while (current != null)
{
temp = current.prev;
current.prev = current.next;
current.next = temp;
current = current.prev;
}
if (temp != null)
{
head = temp.prev;
}
}
void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.prev = null;
new_node.next = head;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
head = new_node;
}
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.push(2);
list.push(4);
list.push(8);
list.push(10);
System.out.println(
"Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(
"The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
|
Output:
Original linked list
10 8 4 2
The reversed Linked List is
2 4 8 10
Time Complexity: O(N), where N denotes the number of nodes in the doubly linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
We can also swap data instead of pointers to reverse the Doubly Linked List. Method used for reversing array can be used to swap data. Swapping data can be costly compared to pointers if the size of the data item(s) is more.
Please write comments if you find any of the above codes/algorithms incorrect, or find better ways to solve the same problem.
Method 2:
The same question can also be done by using Stacks.
Steps:
- Keep pushing the node’s data in the stack. -> O(n)
- The keep popping the elements out and updating the Doubly Linked List
Java
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList
{
static Node head;
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
void reverse()
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
stack.push(temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
temp.data = stack.pop();
temp = temp.next;
}
}
void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.prev = null;
new_node.next = head;
if (head != null)
{
head.prev = new_node;
}
head = new_node;
}
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.push(2);
list.push(4);
list.push(8);
list.push(10);
System.out.println(
"Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(
"The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
|
Output:
Original linked list
10 8 4 2
The reversed Linked List is
2 4 8 10
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
In this method, we traverse the linked list once and add elements to the stack, and again traverse the whole for updating all the elements. The whole takes 2n time, which is the time complexity of O(n).
Please refer complete article on Reverse a Doubly Linked List for more details!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...