Java Program for Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray
Last Updated :
31 May, 2022
Write an efficient program to find the sum of contiguous subarray within a one-dimensional array of numbers that has the largest sum.
Kadane’s Algorithm:
Initialize:
max_so_far = INT_MIN
max_ending_here = 0
Loop for each element of the array
(a) max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
(b) if(max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here
(c) if(max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0
return max_so_far
Explanation:
The simple idea of Kadane’s algorithm is to look for all positive contiguous segments of the array (max_ending_here is used for this). And keep track of maximum sum contiguous segment among all positive segments (max_so_far is used for this). Each time we get a positive-sum compare it with max_so_far and update max_so_far if it is greater than max_so_far
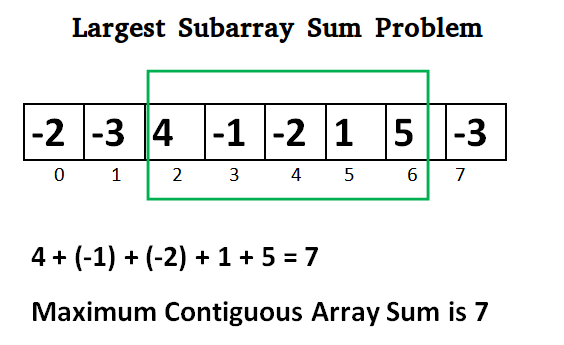
Lets take the example:
{-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3}
max_so_far = max_ending_here = 0
for i=0, a[0] = -2
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0
for i=1, a[1] = -3
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0
for i=2, a[2] = 4
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (4)
max_ending_here = 4
max_so_far is updated to 4 because max_ending_here greater
than max_so_far which was 0 till now
for i=3, a[3] = -1
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-1)
max_ending_here = 3
for i=4, a[4] = -2
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
max_ending_here = 1
for i=5, a[5] = 1
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (1)
max_ending_here = 2
for i=6, a[6] = 5
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (5)
max_ending_here = 7
max_so_far is updated to 7 because max_ending_here is
greater than max_so_far
for i=7, a[7] = -3
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
max_ending_here = 4
Program:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Kadane
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int [] a = {-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3};
System.out.println("Maximum contiguous sum is " +
maxSubArraySum(a));
}
static int maxSubArraySum(int a[])
{
int size = a.length;
int max_so_far = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max_ending_here = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0;
}
return max_so_far;
}
}
|
Output:
Maximum contiguous sum is 7
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Another approach:
Java
static int maxSubArraySum(int a[],int size)
{
int max_so_far = a[0], max_ending_here = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0;
else if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
}
return max_so_far;
}
|
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Algorithmic Paradigm: Dynamic Programming
Following is another simple implementation suggested by Mohit Kumar. The implementation handles the case when all numbers in the array are negative.
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int maxSubArraySum(int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = a[0];
int curr_max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++)
{
curr_max = Math.max(a[i], curr_max+a[i]);
max_so_far = Math.max(max_so_far, curr_max);
}
return max_so_far;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[] = {-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3};
int n = a.length;
int max_sum = maxSubArraySum(a, n);
System.out.println("Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ max_sum);
}
}
|
Output:
Maximum contiguous sum is 7
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
To print the subarray with the maximum sum, we maintain indices whenever we get the maximum sum.
Java
class GFG {
static void maxSubArraySum(int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = Integer.MIN_VALUE,
max_ending_here = 0,start = 0,
end = 0, s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
{
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0)
{
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
System.out.println("Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ max_so_far);
System.out.println("Starting index " + start);
System.out.println("Ending index " + end);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[] = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = a.length;
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
}
}
|
Output:
Maximum contiguous sum is 7
Starting index 2
Ending index 6
Kadane’s Algorithm can be viewed both as a greedy and DP. As we can see that we are keeping a running sum of integers and when it becomes less than 0, we reset it to 0 (Greedy Part). This is because continuing with a negative sum is way more worse than restarting with a new range. Now it can also be viewed as a DP, at each stage we have 2 choices: Either take the current element and continue with previous sum OR restart a new range. These both choices are being taken care of in the implementation.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Now try the below question
Given an array of integers (possibly some elements negative), write a C program to find out the *maximum product* possible by multiplying ‘n’ consecutive integers in the array where n ? ARRAY_SIZE. Also, print the starting point of the maximum product subarray.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...