Java.io.FilterOutputStream Class in Java
Last Updated :
29 Oct, 2022
java.io.FilterInputStream Class in Java
Java.io.FilterOutputStream class is the superclass of all those classes which filters output streams. The write() method of FilterOutputStream Class filters the data and write it to the underlying stream, filtering which is done depending on the Streams.
Declaration :
public class FilterOutputStream
extends OutputStream
Constructors :
- FilterOutputStream(OutputStream geekout) : Creates an output stream filter.
Methods:
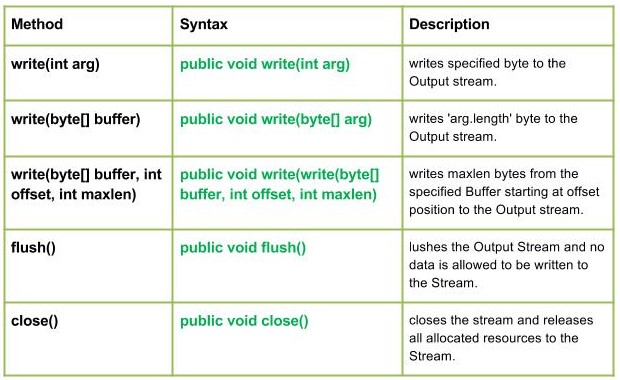
- write(int arg) : java.io.FilterOutputStream.write(int arg) writes specified byte to the Output stream.
Syntax :
public void write(int arg)
Parameters :
arg : Source Bytes
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
char c;
int a;
try
{
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("GEEKS.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
geek_filter.write(77);
geek_filter.flush();
geekinput = new FileInputStream("GEEKS.txt");
a = geekinput.read();
c = (char)a;
System.out.println("Character written by" +
" FilterOutputStream : " + c);
}
catch(IOException except)
{
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally{
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}
|
- Note :
In the program I have used GEEKS.txt file, the program will create a new file of the name given in the code and write in it.
Output :
Character written by FilterOutputStream : M
- write(byte[] buffer) : java.io.FilterOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer) writes ‘arg.length’ byte to the Output stream.
Syntax :
public void write(byte[] arg)
Parameters :
buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
byte[] buffer = {77, 79, 72, 73, 84};
char c;
int a;
try
{
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
geek_filter.write(buffer);
geek_filter.flush();
geekinput = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
while ((a=geekinput.read())!=-1)
{
c = (char)a;
System.out.print(c);
}
}
catch(IOException except)
{
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally
{
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}
|
- Note :
In the program I have use GEEKS.txt file, the program will create a new file of the name given in the code and write in it.
Output :
MOHIT
- write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) : java.io.FilterOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) writes maxlen bytes from the specified Buffer starting at offset position to the Output stream.
Syntax :
public void write(write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)
Parameters :
buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream
Return :
buffer : Source Buffer to be written
offset : Starting offset
maxlen : max no. of bytes to be written to the Output Stream
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.
- flush() : java.io.FilterOutputStream.flush() flushes the Output Stream and no data is allowed to be written to the Stream.
Syntax :
public void flush()
Parameters :
------
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.
- close() : java.io.FilterOutputStream.close() closes the stream and releases all allocated resources to the Stream.
Syntax :
public void close()
Parameters :
------
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.
Java program illustrating : write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen), flush(), close() methods
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
byte[] buffer = {65, 66, 77, 79, 72, 73, 84};
char c;
int a;
try
{
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
geek_filter.write(buffer, 2, 5);
geek_filter.flush();
geekinput = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
while ((a = geekinput.read())!=-1)
{
c = (char)a;
System.out.print(c);
}
}
catch(IOException except)
{
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally
{
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}
|
Note :
In the program I have use GEEKS.txt file, the program will create a new file of the name given in the code and write in it.
Output :
MOHIT
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...