Internet Service Provider (ISP) hierarchy
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2020
Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a company which provides internet connection to end user, but there are basically three levels of ISP. There are 3 levels of Internet Service Provider (ISP): Tier-1 ISP, Tier-2 ISP, and Tier-3 ISP.
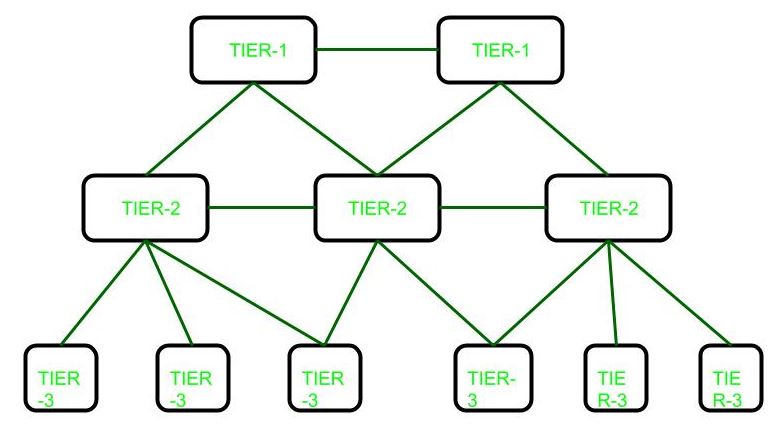
These are explained as following below.
Cogent Communications,
Hibernia Networks,
AT&T
Vodafone,
Easynet,
BT
Comcast,
Deutsche Telekom,
Verizon Communications
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...