Integers are groups of numbers that are defined as the union of positive numbers, and negative numbers, and zero is called an Integer. ‘Integer’ comes from the Latin word ‘whole’ or ‘intact’. Integers do not include fractions or decimals. Integers are denoted by the symbol “Z“.
An Integer is a whole number that can be positive, negative, or zero. Examples of integers are 3,70,-92,234, -3567 etc. Examples of numbers that are not integers are -1.3, 3/4, 2.78, and 345.97
In this article, we have covered everything about what are integers in maths, integers definition, types of integers, etc. to Integers classes 6 and 7.
What are Integers?
If a set is constructed using all-natural numbers, zero, and negative natural numbers, then that set is referred to as Integer. Integers range from negative infinity to positive infinity.
- Natural Numbers: Numbers greater than zero are called positive numbers. Example: 1, 2, 3, 4…
- Negative of Natural Numbers: Numbers less than zero are called negative numbers. Example: -1, -2, -3, -4…
- Zero (0) is neither positive nor negative.
Integers Definition
Integers are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a set of whole numbers that includes both positive and negative numbers, along with zero. In other words, integers are numbers that can be expressed without fractional or decimal components.
Symbol of Integers
Integers are represented by the symbol Z such that,
Z = {… -7, -6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7…}
Types of Integers
Integers are classified into three categories:
- Zero (0)
- Positive Integers (i.e. Natural numbers)
- Negative Integers (i.e. Additive inverses of Natural Numbers)
 Zero
Zero
Zero is a unique number that does not belong to the category of positive or negative integers. It is considered a neutral number and is represented as “0” without any plus or minus sign.
Positive Integers
Positive integers, also known as natural numbers or counting numbers, are often represented as Z+. Positioned to the right of zero on the number line, these integers encompass the realm of numbers greater than zero.
Z+ → 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30,….
Negative Integers
Negative integers mirror the values of natural numbers but with opposing signs. They are symbolized as Z–. Positioned to the left of zero on the number line, these integers form a collection of numbers less than zero.
Z– → -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8, -9, -10, -11, -12, -13, -14, -15, -16, -17, -18, -19, -20, -21, -22, -23, -24, -25, -26, -27, -28, -29, -30,…..
How to Represent Integers on Number Line?
As we have discussed previously, it is possible to visually represent the three categories of integers – positive, negative, and zero – on a number line.
Zero serves as the midpoint for integers on the number line. Positive integers occupy the right side of zero, while negative integers populate the left side. Refer to the diagram below for a visual representation.
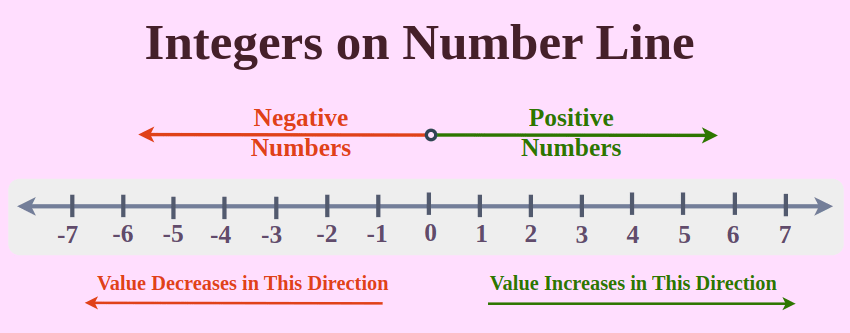
Rules of Integers
Various rules of integers are,
- Addition of Positive Integers
When two positive integers are added together, the result is always an integer.
- Addition of Negative Integers
Sum of two negative integers results in an integer.
- Multiplication of Positive Integers
Product of two positive integers yields an integer.
- Multiplication of Negative Integers
Similarly, when two negative integers are multiplied, the outcome is an integer.
- Sum of an Integer and Its Inverse
Sum of integer and its inverse is alays zero.
- Product of an Integer and Its Reciprocal
Product of an Integer and Its Reciprocal is always 1.
Arithmetic Operations on Integers
Four basic Maths operations performed on integers are:
- Addition of Integers
- Subtraction of Integers
- Multiplication of Integers
- Division of Integers
Addition of Integers
Addition of integers is similar to finding the sum of two integers. Read the rules discussed below to find the sum of integers.
Example: Add the given integers
Subtraction of Integers
Subtraction of integers is similar to finding the difference between two integers. Read the rules discussed below to find the difference between integers.
Example: Add the given integers
- (-5) – (-11) = -5 + 11 = 6
Multiplication of Integers
Multiplication of integers is achieved by following the rule:
- When both integers have same sign, the product is positive.
- When both integers have different signs, the product is negative.
| Product of Sign |
Resultant Sign |
Example |
| (+) × (+) |
+ |
9 × 3 = 27 |
| (+) × (–) |
– |
9 × (-3) = -27 |
| (–) × (+) |
– |
(-9) × 3 = -27 |
| (–) × (–) |
+ |
(-9) × (-3) = 27 |
Division of Integers
Division of integers is achieved by following the rule:
- When both integers have the same sign, the division is positive.
- When both integers have different signs, the division is negative.
| Division of Sign |
Resultant Sign |
Example |
| (+) ÷ (+) |
+ |
9 ÷ 3 = 3 |
| (+) ÷ (–) |
– |
9 ÷ (-3) = -3 |
| (–) ÷ (+) |
– |
(-9) ÷ 3 = -3 |
| (–) ÷ (–) |
+ |
(-9) ÷ (-3) = 3 |
Properties of Integers
Integers have various properties, the major properties of integers are:
- Closure Property
- Associative Property
- Commutative Property
- Distributive Property
- Identity Property
- Additive Inverse
- Multiplicative Inverse
Closure Property
Closure property of integers states that if two integers are added or multiplied together their result is always an integer. For integers p and q
- p + q = integer
- p × q = integer
Example:
(-8) + 11 = 3 (An integer)
(-8) × 11 = -88 (An integer)
Commutative Property
Commutative property of integers states that for two integers p and q
- p + q = q + p
- p × q = q × p
Example:
(-8) + 11 = 11 + (-8) = 3
(-8) × 11 = 11 × (-8) = -88
But the commutative property is not applicable to the subtraction and division of integers.
Associative Property
Associative property of integers states that for integers p, q, and r
- p + (q + r) = (p + q) + r
- p × (q × r) = (p × q) × r
Example:
5 + (4 + 3) = (5 + 4) + 3 = 12
5 × (4 × 3) = (5 × 4) × 3 = 60
Distributive Property
Distributive property of integers states that for integers p, q, and r
- p × (q + r) = p × q + p × r
For Example, Prove: 5 × (9 + 6) = 5 × 9 + 5 × 6
LHS = 5 × (9 + 6)
= 5 × 15
= 75
RHS = 5 × 9 + 5 × 6
= 45 + 30
= 75
Thus, LHS = RHS Proved
Identity Property
Integers hold Identity elements both for addition and multiplication. Operation with the Identity element yields the same integers, such that
Here, 0 is Additive Identity, and 1 is Multiplicative Identity.
Additive Inverse
Every integer has its additive inverse. An additive inverse is a number that in addition to the integer gives the additive identity. For integers, Additive Identity is 0. For example, take an integer p then its additive inverse is (-p) such that
Multiplicative Inverse
Every integer has its multiplicative inverse. A multiplicative inverse is a number that when multiplied to the integer gives the multiplicative identity. For integers, Multiplicative Identity is 1. For example, take an integer p then its multiplicative inverse is (1/p) such that
Applications of Integers
Integers extend beyond numbers, finding applications in real life. Positive and negative values represent opposing situations. For instance, they indicate temperatures above and below zero. They facilitate comparisons, measurements, and quantification. Integers feature prominently in sports scores, ratings for movies and songs, and financial transactions like bank credits and debits.
Articles related to Integers:
Integers Examples
Some examples on Integers are,
Example 1: Can we say that 7 is both a whole number and a natural number?
Solution:
Yes, 7 is both whole number and natural number.
Example 2: Is 5 a whole number and a natural number?
Solution:
Yes, 5 is both a natural number and whole number.
Example 3: Is 0.7 a whole number?
Solution:
No, it is a decimal.
Example 4: Is -17 a whole number or a natural number?
Solution:
No, -17 is neither natural number nor whole number.
Example 5: Categorize the given numbers among Integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers,
Solution:
| Numbers |
Integers |
Whole Numbers |
Natural Numbers |
| -3 |
Yes |
No |
No |
| 77 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| 34.99 |
No |
No |
No |
| 1 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| 100 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Practice Questions on Integers
Various Practice Questions on Integers are,
Q1: Sum of three consecutive integers are 125, what are these integers?
Q2: Which of the following numbers is the largest: -6, 2, -3, or 0?
Q3: Calculate the product of -7 and 9.
Q4: Find the sum of -15, 20, and -8.
Q5: If the temperature drops by 10 degrees Celsius and then rises by 7℃, what is the net change in temperature?
Q6: A submarine is at a depth of 120 meters below sea level. If it rises 80 meters, what will its new depth be?
Integers Class 6 Worksheet
Integers are a fundamental concept in mathematics, especially introduced at the class 6 level, aiming to broaden the understanding of numbers beyond natural numbers and whole numbers. Worksheet on Integers for students to solve is added below,
Solve:
- 23 + (-12)
- 15 – 12
- -14 + 14
- (13) × (-17)
- (4) × (12)
- 0 × (-87)
- (114) ÷ (-7)
- (-7) ÷ (-3)
Summary – Integers – Definition, Properties and Worksheet
Integers are a comprehensive set of whole numbers that span from negative infinity to positive infinity, including all positive numbers (natural numbers), their negative counterparts (additive inverses of natural numbers), and zero. Represented by the symbol “Z,” integers are categorized into positive integers (Z+), negative integers (Z–), and zero, with zero acting as a neutral number that is neither positive nor negative. The rules governing integers encompass addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, highlighting behaviors such as the sum of an integer and its inverse always being zero, and the product of an integer and its reciprocal being one. Additionally, integers possess properties like closure, commutativity (except for subtraction and division), associativity, distributivity, identity elements for addition (0) and multiplication (1), and the concepts of additive and multiplicative inverses. These mathematical principles not only facilitate a deeper understanding of arithmetic operations on integers but also have practical applications in real life, such as in temperature measurement, financial transactions, and sports scores, illustrating the ubiquitous nature and significance of integers in both mathematics and everyday contexts.
FAQs on Integers – Definition, Properties and Worksheet
Define Integers
Integers are a set of whole numbers that include both positive and negative numbers, as well as zero. In mathematical terms, integers are numbers without any fractional or decimal parts.
What are Consecutive Integers?
Consecutive Integers are integers that are adjacent to each other on a number line. The difference between the two consecutive integers is “1”.
What are Examples of Integers?
Examples of integers are -1, -9, 0, 1, 87, etc.
Can Integers be Negative?
Yes, integers can be negative. Negative Integers are -1, -4, and -55, etc.
What is a Positive Integer?
An integer is said to be positive if it is greater than zero. For example: 2, 50, 28 etc.
Is 0 an integer?
Yes, zero is considered an integer.
What are Rules of Integers?
Some important integers rules are:
- Sum of Two Integers is an Integer
- Difference of Two Integers is an Integer
- Multiplication Two Integers is an Integer
- Division of Two Integers may of may not be an Integer
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...