Instruction execution and straight line sequencing in CO
Last Updated :
18 Jun, 2021
Introduction :
As instructions are a part of the program which are stored inside the memory, so every time the processor requires to execute an instruction, for that the processor first fetches the instruction from the memory, then decodes the instruction and then executes the instruction. The whole process is known as an instruction cycle.
Instruction cycle state transition diagram
Instruction execution :
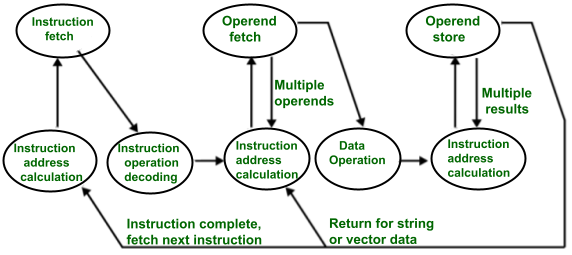
Instruction execution needs the following steps, which are
- PC (program counter) register of the processor gives the address of the instruction which needs to be fetched from the memory.
- If the instruction is fetched then, the instruction opcode is decoded. On decoding, the processor identifies the number of operands. If there is any operand to be fetched from the memory, then that operand address is calculated.
- Operands are fetched from the memory. If there is more than one operand, then the operand fetching process may be repeated (i.e. address calculation and fetching operands).
- After this, the data operation is performed on the operands, and a result is generated.
- If the result has to be stored in a register, the instructions end here.
- If the destination is memory, then first the destination address has to be calculated. Then the result is then stored in the memory. If there are multiple results which need to be stored inside the memory, then this process may repeat (i.e. destination address calculation and store result).
- Now the current instructions have been executed. Side by side, the PC is incremented to calculate the address of the next instruction.
- The above instruction cycle then repeats for further instructions.
Straight line sequencing:
- Straight line sequencing means the instruction of a program is executed in a sequential manner(i.e. every time PC is incremented by a fixed offset).
- And no branch address is loaded on the PC.
Example –
- Here, programs and data are stored in the same memory, i.e. von Neumann architecture.
- First instruction of a program is stored at address i. PC gives address i and instruction stored at that address i is fetched from the memory and then decoded and then operand A is fetched from the memory and stored in a temporary register and then the instruction is executed(i.e. content of address A is copied into processor register R0).
- Side by Side during decoding or execution, the PC gets incremented by 4(i.e. it contains the address of the next instruction) because the instruction and memory segment is of 4 bytes. So the instruction at address i is executed.
- So every time, the PC is incremented by 4. Therefore, the program is executing in a sequential manner. And this process is called straight line sequencing.

Example 2 –
Straight line sequencing program for adding n numbers.
- The addresses of the memory locations containing the n numbers are represented as NUM1,NUM2…..NUMn(i.e. NUM1 address includes first number).
- The first number is stored into processor register R0. And every other number is added to register R0. Finally, when the program ends(i.e. n numbers are added, the result is placed in memory location SUM

Straight line sequencing program for adding n numbers
- The second way is to use a loop to add n number. But here straight line sequencing is not used because every time loop iteration ends, PC has to load the branch address and program execution starts from that address.
- Here the location N stores the value of n. Processor register R1 is used as a counter to determine the number of times the loop gets executed.
- The contents of the location N are moved into R1 at the start of program execution.
- After that, register R0 is cleared.
- The address LOOP is reloaded again and again until R1 becomes 0 (this means all numbers are added).Every time a number is added, then the R1 value is decremented.
- When R1 becomes 0, we come out of the loop and the result which is stored at R1 is copied into memory location SUM.

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...