Insert Node at the End of a Linked List
Last Updated :
22 Feb, 2024
Given a linked list, the task is to insert a new node at the end of the linked list.
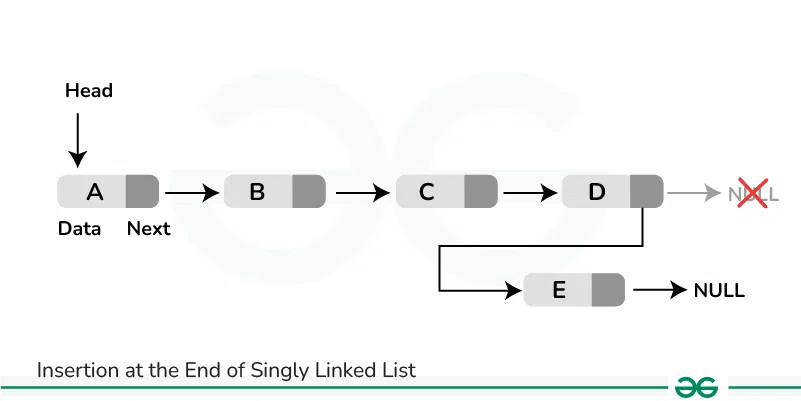
Example:
Input: LinkedList = 2->3->4->5, NewNode = 1
Output: LinkedList = 2->3->4->5->1
Input: LinkedList = , NewNode = 1
Output: LinkedList = 1
Approach:
To insert a node at the end of a Linked List, we need to:
- Go to the last node of the Linked List
- Change the next pointer of last node from NULL to the new node
- Make the next pointer of new node as NULL to show the end of Linked List
Following is the approach to add a new node at the end of the linked list:
- Create a new node
- Store the head reference in a temporary variable
- Set the next pointer of the new node as NULL since it will be the last node
- If the Linked List is empty, make the new node as the head and return
- Else traverse till the last node
- Change the next pointer of the last node to point to the new node
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
Node* last = *head_ref;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
while (last->next != NULL) {
last = last->next;
}
last->next = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << " " << node->data;
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
cout << "Created Linked list is: ";
printList(head);
append(&head, 1);
cout << "\nAfter inserting 1 at the end: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void append(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
struct Node* last = *head_ref;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
while (last->next != NULL) {
last = last->next;
}
last->next = new_node;
}
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf(" %d", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
printf("Created Linked list is: ");
printList(head);
append(&head, 1);
printf("\nAfter inserting 1 at the end: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
void append(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (head == null) {
head = new_node;
return;
}
Node last = head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
last.next = new_node;
}
void printList()
{
Node node = head;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.push(6);
linkedList.push(5);
linkedList.push(4);
linkedList.push(3);
linkedList.push(2);
System.out.print("Created Linked list is: ");
linkedList.printList();
linkedList.append(1);
System.out.print(
"\nAfter inserting 1 at the end: ");
linkedList.printList();
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def push(head_ref, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = head_ref
return new_node
def append(head_ref, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
last = head_ref
new_node.next = None
if head_ref is None:
return new_node
while last.next is not None:
last = last.next
last.next = new_node
return head_ref
def printList(node):
while node is not None:
print(node.data, end=" ")
node = node.next
if __name__ == "__main__":
head = None
head = push(head, 6)
head = push(head, 5)
head = push(head, 4)
head = push(head, 3)
head = push(head, 2)
print("Created Linked list is:")
printList(head)
head = append(head, 1)
print("\nAfter inserting 1 at the end:")
printList(head)
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
}
public class LinkedList {
public static void Push(ref Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.next = head_ref;
head_ref = new_node;
}
public static void Append(ref Node head_ref,
int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
if (head_ref == null) {
head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
Node last = head_ref;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
last.next = new_node;
}
public static void PrintList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(" " + node.data);
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node head = null;
Push(ref head, 6);
Push(ref head, 5);
Push(ref head, 4);
Push(ref head, 3);
Push(ref head, 2);
Console.Write("Created Linked list is:");
PrintList(head);
Append(ref head, 1);
Console.Write("\nAfter inserting 1 at the end:");
PrintList(head);
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
function push(head_ref, new_data) {
const new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head_ref[0];
head_ref[0] = new_node;
}
function append(head_ref, new_data) {
const new_node = new Node(new_data);
let last = head_ref[0];
new_node.next = null;
if (head_ref[0] === null) {
head_ref[0] = new_node;
return;
}
while (last.next !== null) {
last = last.next;
}
last.next = new_node;
}
function printList(node) {
while (node !== null) {
console.log(" " + node.data);
node = node.next;
}
}
function main() {
const head = [null];
push(head, 6);
push(head, 5);
push(head, 4);
push(head, 3);
push(head, 2);
console.log("Created Linked list is:");
printList(head[0]);
append(head, 1);
console.log("\nAfter inserting 1 at the end:");
printList(head[0]);
}
main();
|
Output
Created Linked list is: 2 3 4 5 6
After inserting 1 at the end: 2 3 4 5 6 1
Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the length of the linked list
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...