Inner Join and Outer Join are the types of join. The inner join has the work to return the common rows between the two tables, whereas the Outer Join has the work of returning the work of the inner join in addition to the rows which are not matched.
Let’s discuss both of them in detail in this article. Before moving ahead, let’s discuss what is Join in SQL.
In a relational database management system (RDBMS), there are different types of joins that can be used to combine data from two or more tables in a database. The two most common types of joins are Inner Join and Outer Join.
What is Join in SQL?
SQL Joins are simply a way to combine data from two or more tables based on a common field between them. SQL joins are of two types. We will discuss the types of SQL in detail.
Let’s proceed with an example demonstrating the process of Inner Join and Outer Join.
Student Table
| EnrollNo |
StudentName |
Address |
| 1001 |
geek1 |
geeksquiz1 |
| 1002 |
geek2 |
geeksquiz2 |
| 1003 |
geek3 |
geeksquiz3 |
| 1004 |
geek4 |
geeksquiz4 |
StudentCourse Table
| CourseID |
EnrollNo |
| 1 |
1001 |
| 2 |
1001 |
| 3 |
1001 |
| 1 |
1002 |
| 2 |
1003 |
Inner Join/Simple Join
In an INNER join, it allows retrieving data from two tables with the same ID.
An Inner Join returns only the matching rows between the two tables based on a specified condition. It combines data from two tables based on a common column between them, which is specified using the ON keyword in SQL. Only the rows that meet the join condition from both tables are returned. If a row in one table does not have a matching row in the other table, that row will not be included in the result set.
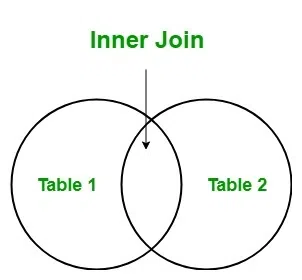
Inner Join
Syntax:
SELECT COLUMN1, COLUMN2 FROM
[TABLE 1] INNER JOIN [TABLE 2]
ON Condition;
The following is a join query that shows the names of students enrolled in different courses.
Query:
SELECT StudentCourse.CourseID,Student.StudentName
FROM Student
INNER JOIN StudentCourse
ON StudentCourse.EnrollNo = Student.EnrollNo
ORDER BY StudentCourse.CourseID;
Note: Inner is optional above. Simple JOIN is also considered as INNER JOIN The above query would produce the following result.
| CourseID |
StudentName |
| 1 |
geek1 |
| 1 |
geek2 |
| 2 |
geek1 |
| 2 |
geek3 |
| 3 |
geek1 |
Example:
For example, let’s say we have two tables, Table1 and Table2, with the following data:
Table 1
| ID |
Name |
| 1 |
John |
| 2 |
Sarah |
| 3 |
David |
Table 2
| ID |
Address |
| 1 |
123 Main St. |
| 2 |
456 Elm St. |
| 4 |
789 Oak St. |
If we perform an Inner Join on these tables using the ID column, the result set would only include the matching rows from both tables, which are the rows with ID values of 1 and 2:
Query:
SELECT Table1.ID,
Table 1. Name, Table 2.Address
FROM Table1
INNER JOIN Table2
ON Table1.ID = Table2.ID
Output:
| ID |
Name |
Address |
| 1 |
John |
123 Main St. |
| 2 |
Sarah |
456 Elm St. |
How To Use Inner Join?
Inner Join is basically performed by just selecting the records having the common values or the matching values in both tables. In case of no common values, no data is shown in the output.
Syntax:
Select Table1.Col_Name, Table2.Col_Name....
From Table1
Inner Join Table2
on Table1.Common_Col = Table2.Common_Col;
If there are 3 Tables present in the database, then the Inner Join works as follows:
Select Table1.Col_Name, Table2.Col_Name, Table3.Col_Name....
From ((Table1
Inner Join Table2
on Table1.Common_Col = Table2.Common_Col)
Inner Join Table3
on Table1.Common_Col = Table3.Common_Col);
Advantages of Inner Join
- Reduced Data Duplication: Inner joins only return rows that have matching values in both tables being joined, which can reduce the amount of duplicate data returned in the result set.
- Efficient Query Execution: Since inner joins only involve rows that match in both tables, they can be more efficient in terms of query execution time compared to outer joins.
- Data Accuracy: Inner joins only return rows that have matching values in both tables, which can improve data accuracy by excluding irrelevant or mismatched data.
Disadvantages of Inner Join
- Data Loss: Since inner joins only return rows that have matching values in both tables, some data may be lost if there are no matching values.
- Query Complexity: Inner joins can become complex and difficult to write and understand when working with multiple tables.
- Overlapping Data: In some cases, inner joins may return overlapping data that needs to be deduplicated in post-processing.
For more, refer to Inner Join in SQL.
Outer Join
An Outer Join returns all the rows from one table and matching rows from the other table based on a specified condition. It combines data from two tables based on a common column between them, which is also specified using the ON keyword in SQL. In addition to the matching rows, it also includes rows from one table that do not have matching rows in the other table.
Outer Join is of three types:
- Left outer join
- Right outer join
- Full Join
1. Left Outer join
Left Outer Join returns all rows of a table on the left side of the join. For the rows for which there is no matching row on the right side, the result contains NULL on the right side.
Left Outer Join returns all the rows from the left table and matching rows from the right table. If a row in the left table does not have a matching row in the right table, the result set will include NULL values for the columns in the right table.
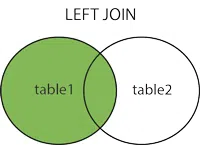
Left Outer Join
Syntax:
SELECT T1.C1, T2.C2
FROM TABLE T1
LEFT JOIN TABLE T2
ON T1.C1= T2.C1;
Query:
SELECT Student.StudentName,StudentCourse.CourseID
FROM Student
LEFT OUTER JOIN StudentCourse
ON StudentCourse.EnrollNo = Student.EnrollNo
ORDER BY StudentCourse.CourseID;
Note: OUTER is optional above. Simple LEFT JOIN is also considered as LEFT OUTER JOIN
| StudentName |
CourseID |
| geek4 |
NULL |
| geek2 |
1 |
| geek1 |
1 |
| geek1 |
2 |
| geek3 |
2 |
| geek1 |
3 |
For more, refer to Inner Join in SQL.
2. Right Outer Join
Right Outer Join is similar to Left Outer Join (Right replaces Left everywhere). Right Outer Join returns all the rows from the right table and matching rows from the left table. If a row in the right table does not have a matching row in the left table, the result set will include NULL values for the columns in the left table.
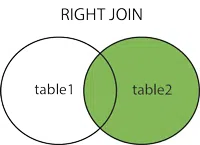
Right Outer Join
Syntax:
SELECT T1.C1, T2.C2
FROM TABLE T1
RIGHT JOIN TABLE T2
ON T1.C1= T2.C1;
Example:
Table Record
| Roll_Number |
Name |
Age |
| 1 |
Harsh |
18 |
| 2 |
Ankesh |
19 |
| 3 |
Rupesh |
18 |
| 4 |
Vaibhav |
15 |
| 5 |
Naveen |
13 |
| 6 |
Shubham |
15 |
| 7 |
Ankit |
19 |
| 8 |
Bhupesh |
18 |
Table Course
| Course_ID |
Roll_Number |
| 1 |
1 |
| 2 |
2 |
| 2 |
3 |
| 3 |
4 |
| 1 |
5 |
| 4 |
9 |
| 5 |
10 |
| 4 |
11 |
Query:
SELECT Record.NAME,Course.COURSE_ID
FROM Record
RIGHT JOIN Course
ON Course.Roll_Number = Record.Roll_Number;
Output:
| Name |
Course_ID |
| Harsh |
1 |
| Ankesh |
2 |
| Rupesh |
2 |
| Vaibhav |
3 |
| Naveen |
1 |
| NULL |
4 |
| NULL |
5 |
| NULL |
4 |
For more, refer to Right Join in SQL.
3. Full Outer Join
Full Outer Join contains the results of both the Left and Right outer joins. It is also known as cross-join. It will provide a mixture of two tables.
Full Outer Join returns all the rows from both tables, including matching and non-matching rows. If a row in one table does not have a matching row in the other table, the result set will include NULL values for the columns in the table that do not have a match.
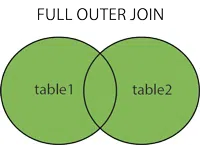
Full Outer Join
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM T1
CROSS-JOIN T2;
Query:
SELECT Record.NAME,Course.COURSE_ID
FROM Record
FULL JOIN Course
ON Course.Roll_Number = Record.Roll_Number;
Output:
| Name |
Course_ID |
| Harsh |
1 |
| Ankesh |
2 |
| Rupesh |
2 |
| Vaibhav |
3 |
| Naveen |
1 |
| Shubham |
NULL |
| Ankit |
NULL |
| Bhupesh |
NULL |
| NULL |
4 |
| NULL |
5 |
| NULL |
4 |
For more, refer to Outer Join in SQL.
How To Use Outer Join?
Outer Join is performed by the selection of the records from all the tables given there. Left Outer Join works by selecting all records from the left table and matching records from the right table. Similarly, Right Outer Join works by selecting all records from the right table and matching records from the left table and the Full Outer Join returns all records if a match occurs in the left or the right table.
Advantages of Outer Join
- Increased Data Retrieval: Outer joins can retrieve more data than inner joins since they include non-matching rows in the result set.
- Data Integrity: Outer joins can help maintain data integrity by ensuring that all records in the primary table are returned, even if there are no corresponding records in the secondary table.
- Data Analysis: Outer joins can be useful for data analysis, especially when exploring relationships between data sets and identifying trends and patterns.
Disadvantages of Outer Join
- Slow Query Execution: Outer joins can be slower to execute than inner joins, especially when dealing with large data sets.
- Data Duplication: Outer joins can return duplicate data when the secondary table has multiple matching records.
- Data Quality: Outer joins may return inaccurate or incomplete data if the tables being joined have incomplete or inconsistent data.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...