Initialize an ArrayList in Java
Last Updated :
28 Feb, 2023
ArrayList is a part of collection framework and is present in java.util package. It provides us dynamic arrays in Java. Though, it may be slower than standard arrays but can be helpful in programs where lots of manipulation in the array is needed.
- ArrayList inherits AbstractList class and implements List interface.
- ArrayList is initialized by a size, however the size can increase if collection grows or shrink if objects are removed from the collection.
- Java ArrayList allows us to randomly access the list.
- ArrayList can not be used for primitive types, like int, char, etc. We need a wrapper class for such cases (see this for details).
- ArrayList in Java can be seen as similar to vector in C++.
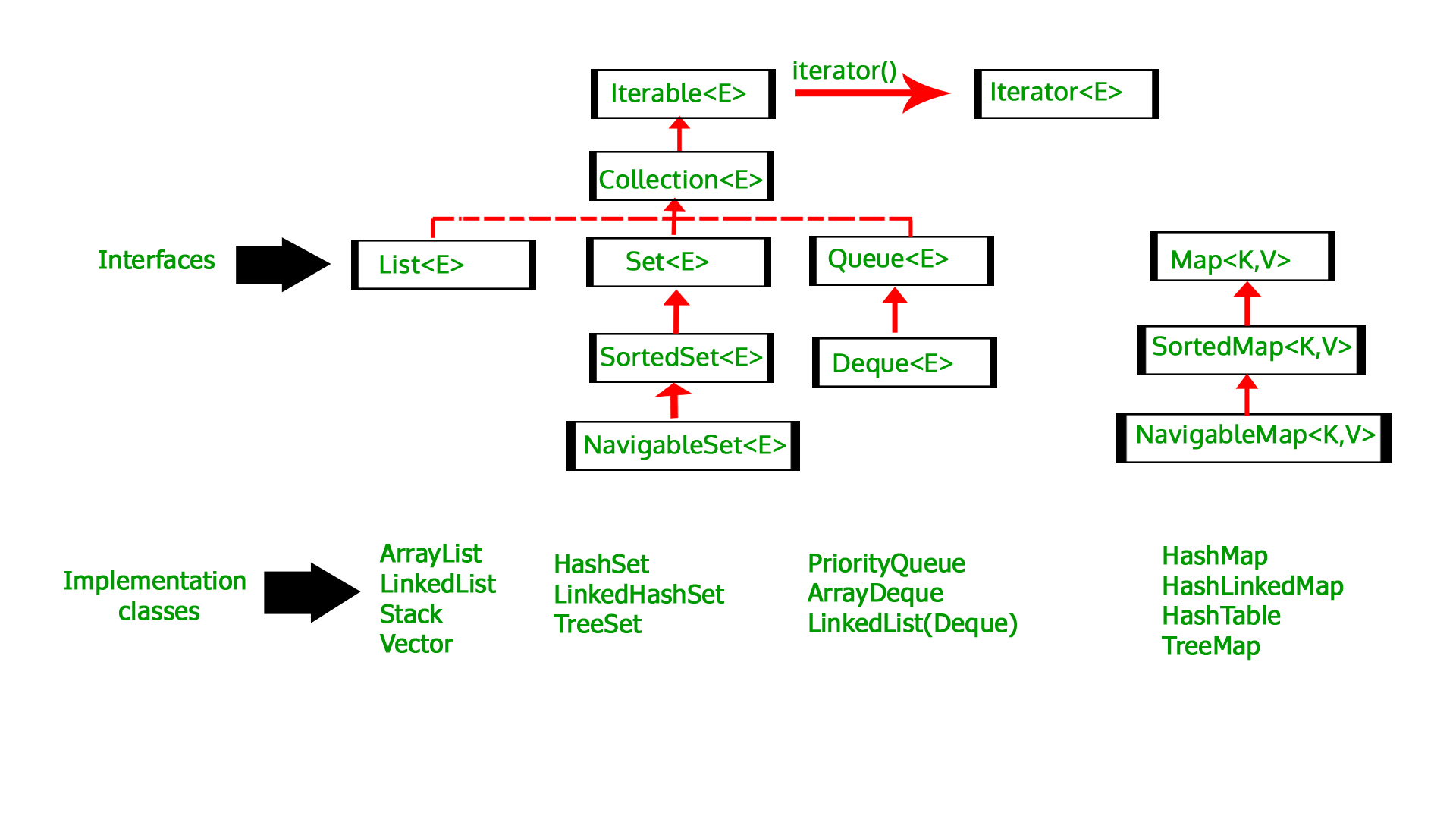 Below are the various methods to initialize an ArrayList in Java:
Below are the various methods to initialize an ArrayList in Java:
Initialization with add()
- Syntax:
ArrayList<Type> str = new ArrayList<Type>();
str.add("Geeks");
str.add("for");
str.add("Geeks");
- Examples:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList<String> gfg = new ArrayList<String>();
gfg.add("Geeks");
gfg.add("for");
gfg.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + gfg);
}
}
|
Output:
ArrayList : [Geeks, for, Geeks]
- Examples: Using shorthand version of this method
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList<String> gfg = new ArrayList<String>() {
{
add("Geeks");
add("for");
add("Geeks");
}
};
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + gfg);
}
}
|
Output:
ArrayList : [Geeks, for, Geeks]
Initialization using asList()
- Syntax:
ArrayList<Type> obj = new ArrayList<Type>(
Arrays.asList(Obj A, Obj B, Obj C, ....so on));
- Examples:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList<String> gfg = new ArrayList<String>(
Arrays.asList("Geeks",
"for",
"Geeks"));
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + gfg);
}
}
|
Output:
ArrayList : [Geeks, for, Geeks]
Initialization using List.of() method
- Syntax:
List<Type> obj = new ArrayList<>(
List.of(Obj A, Obj B, Obj C, ....so on));
- Examples:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
List<String> gfg = new ArrayList<>(
List.of("Geeks",
"for",
"Geeks"));
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + gfg);
}
}
|
Output:
ArrayList : [Geeks, for, Geeks]
Initialization using another Collection
- Syntax:
List gfg = new ArrayList(collection);
- Examples:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(3);
arr.add(4);
arr.add(5);
List<Integer> gfg = new ArrayList<Integer>(arr);
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + gfg);
}
}
|
Output:
ArrayList : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Initialization using stream() and collect() methods
1. Syntax:
ArrayList<Type> listName = Stream.of(element1, element2, ..., elementN).collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
1. Examples:
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList<String> list
= Stream.of("Geeks", "For", "Geeks")
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(
ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
Output
[Geeks, For, Geeks]
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...