Importance of Internet Standardization
Last Updated :
08 May, 2023
In simplest terms, the Internet is a global network comprised of smaller networks that are interconnected using standardized communication protocols. The Internet standards describe a framework known as the Internet protocol suite. This model divides methods into a layered system of protocols.
Many standardization bodies exist today to monitor the internet. There are bodies at the global level and national level. These standardization bodies take the decisions and carry out research for the advancement of the internet. Today the internet is very advanced and it is at the core of the everyday life of each one of us. This would haven’t been possible without the significant contributions made by such standardization bodies all across the globe.
Global level bodies:
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- Internet Research Task Force (IRTF)
IETF: IETF contains many Working Groups (WGs) that do not perform research activities. IETF is an engineering body and handles the implementation part. Example: TCP Maintenance Working Group (TCPM WG).
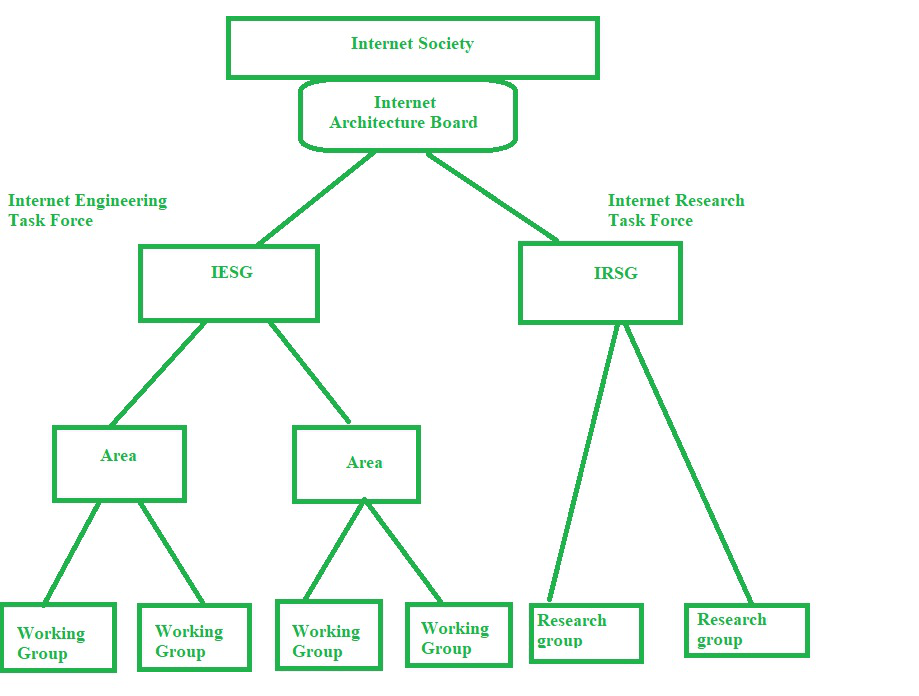
IRTF: IRTF contains many Research Groups (RGs), they intensively focus on the research part and new advancements.Example: Internet Congestion Control Research Group (a.k.a. ICCRG), the congestion control is the open research domain for the last 3.5 decades. Today also many research activities are going on around the world in this domain. Google has done very significant work in this done in the last decade.
How Does it Work?
Researchers (like students/professors of IITs) write ‘Internet Drafts’ or ‘IDs’. The work done by the researcher is called ‘ID’ until it becomes a standard. Researchers submit their ‘ID’ to the corresponding bodies (IETF/IRTF) and seek feedback from the Working Groups/Research Groups. These groups aren’t governed by govt. or any political authority. These are maintained by expert researchers and engineers who have in-depth knowledge of the internet. These WG/RG decides whether to adopt the ‘ID’ or not depending upon what changes it will bring into the existing system and how it is useful for the world. If the WG/RG adopts the ‘ID’, then periodic feedback is provided to the authors and they are expected to revise it. This process is continued until RG/WG are satisfied with the work done by the authors. Once all the changes are done successfully and WG/RG is satisfied with it, the document becomes a standard, it becomes an official ‘RFC’ and a number is given to it (e.g., RFC 791 for IP).
BBR was developed by Google in 2017 and it was submitted to IETF WG. It was submitted as an “Internet-Draft”. It could not satisfy the WG and thus never became an RFC. BBR stands for bottleneck bandwidth round-trip-time. It used Jain’s index for fairness calculation. But Jain’s fairness index is itself ambiguous so BBR suffered from fairness issues and didn’t get the success it was supposed to. But many use the BBR today also. Dropbox is using BBRv1 since 2017 and is adjusted and familiar with its pros and cons. Uber also used BBR. Now Uber is using QUIC which is also designed by google over UDP and is under review by IETF.
Internet Standardization Activities in India:
- India Internet Engineering Society: It conducts two main events. They are as follows:
- RFCsWeLove (every month or once in two months)
- Connections (annual event)
- Statistics of Internet-Drafts and RFCs were written by authors from India.
Here are some of the key importance of Internet Standardization:
- Interoperability: Internet standardization ensures that devices and systems from different manufacturers and vendors can work together seamlessly. This is particularly important in today’s interconnected world, where devices and systems need to be able to communicate and exchange data across different networks and platforms.
- Compatibility: Internet standardization ensures that software and hardware products developed by different vendors can work together, without any compatibility issues. Standardization helps to create a level playing field for vendors and developers, while also promoting competition and innovation in the marketplace.
- Security: Internet standardization plays a critical role in ensuring the security of internet-connected devices and systems. Standardization helps to promote best practices in security and encryption, reducing the risk of cyber attacks and data breaches.
- Accessibility: Standardization can help to make the internet more accessible to users with disabilities. For example, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) provide technical standards for web content accessibility, making it easier for people with disabilities to access and use the internet.
- Global reach: Internet standardization enables communication and collaboration across borders and time zones. By promoting a common language and framework for data exchange, it helps to break down barriers and enable global connectivity and collaboration.
Conclusion :
Internet standardization is crucial for ensuring interoperability, compatibility, security, accessibility, and global reach of the internet. It provides a common language and framework for communication and data exchange, enabling innovation and driving economic growth in the digital age.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...