Implicit differentiation – Advanced Examples
Last Updated :
28 Jan, 2021
In the previous article, we have discussed the introduction part and some basic examples of Implicit differentiation. So in this article, we will discuss some advanced examples of implicit differentiation.
Implicit Differentiation
Implicit differentiation is a method that makes use of the chain rule to differentiate implicitly defined functions. It is generally not easy to find the function explicitly and then differentiate. Instead, we can totally differentiate f(x, y) and then solve the rest of the equation to find the value of 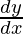 . Even when it is possible to explicitly solve the original equation, the formula resulting from total differentiation is, in general, much simpler and easier to use.
. Even when it is possible to explicitly solve the original equation, the formula resulting from total differentiation is, in general, much simpler and easier to use.
Method to solve
- Differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to x.
- Follow the rules of differentiation.
- Use the chain rule to differentiate expressions involving y.
- Solve the equation for
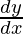
Advanced Examples
Example 1: Find the derivative of y = cos(5x – 3y)?
Solution:
Given equation:
y = cos(5x – 3y)
Step 1: Differentiating both sides wrt x,
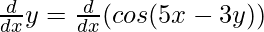
Step 2: Using Chain Rule

Step 3: Expanding the above equation

Step 4: Taking all terms with dy/dx on LHS
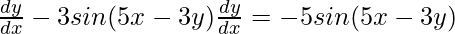
Step 5: Taking dy/dx common from the LHS of equation
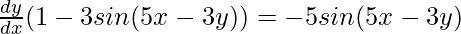
Step 6: Isolate dy/dx
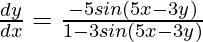
Example 2: Find the derivative of (x² + y²)³ = 5x²y²?
Solution:
Given equation:
(x² + y²)³ = 5x²y²
Differentiating both sides:

Example 3: Find the derivative of 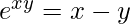 ?
?
Solution:
Given equation:
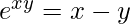
Differentiating both sides:

Example 4: Find the derivative of y = ln(x)?
Solution:
Given equation:
y = ln(x)
=> ey = x
Differentiating both sides:
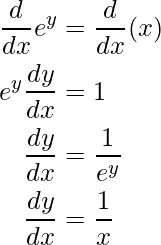
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...