Implementing DFA for no runs of length less than 4 for input (a,b)
Last Updated :
08 Mar, 2023
DFA or Deterministic Finite Automata is a finite state machine, in which on every input alphabet a transition is done from one state to another state according to set of defined rules as per the need of string acceptance.
In this particular problem, runs of length is the factor to think about.The input alphabets are {a, b}. No runs of length less than 4 means any input alphabets repeats itself minimum 4 times.
Example:
Input: n = “aaabab”
Output: string not accepted
Explanation: The starting letter a is not repeated at least 4 times. Hence DFA failed.
Input: n = “aaaabbbbaaaabbbbbaaaaa”
Output: string accepted
Explanation: Every unique occurrence of a and b are repeated at least 4 times. Hence DFA passed.
Designing DFA step by step:
Step-1: First we have to think about what input alphabet is inputted. As this is about minimum 4 runs of length. Take input alphabet is ‘a’ on state “A” and mark this state as initial state. The following transition occur on input ‘a’:
- From state “A” to state “B”
- From state “B” to state “C”
- From state “C” to state “D”
- From state “D” to state “E”
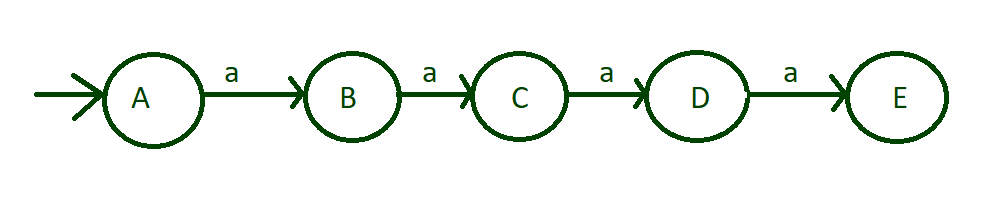
input of run of length 4
Step-2: As in above step, minimum 4 a’s are inputted which is acceptable so make state “E” is final state. Also runs of length more than 4 is acceptable so put self loop of ‘a’ on final state “E”.
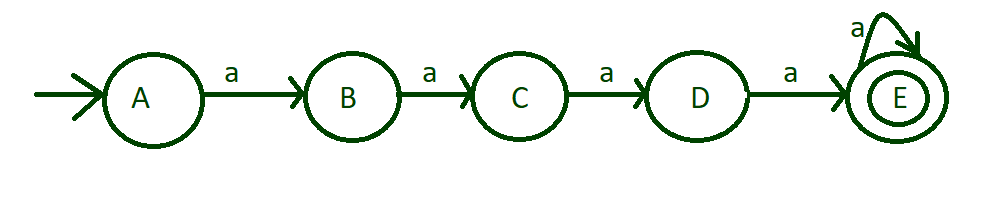
marks state “E” to final state
Step-3: Till now machine design is done with input alphabet ‘a’.But input alphabet ‘b’ of state “A” is left to deal with. Now do the same process with input alphabet ‘b’ on state “A”.The following transition occur on input ‘b’:
- From state “A” to state “F”
- From state “F” to state “G”
- From state “G” to state “H”
- From state “H” to state “Q”
Mark state “Q” to final state. And also runs of length more than 4 is also acceptable so put self loop on final state “Q”.
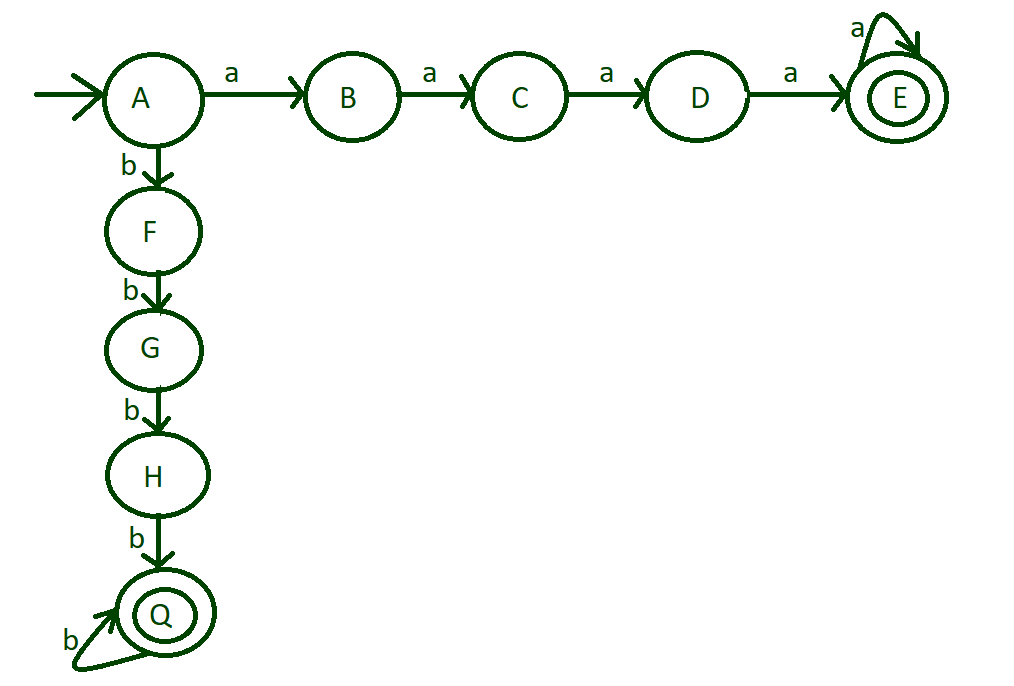
input alphabet ‘b’ transitions
Step-4: Till now we have done with only single input a or b, i.e, aaaa, and bbbb, but now deal with both input such as aaaabbbb or aaaabbbbaaaaa etc.
For this transition of input ‘b’ from state “E” to state “F” and transition of input ‘a’ from state “Q” to state “B”.

Step-5: Now dealing with remaining input alphabets, till now designed machine have covered all possible acceptable cases and nor remaining input alphabets will go to dead state”DS”.
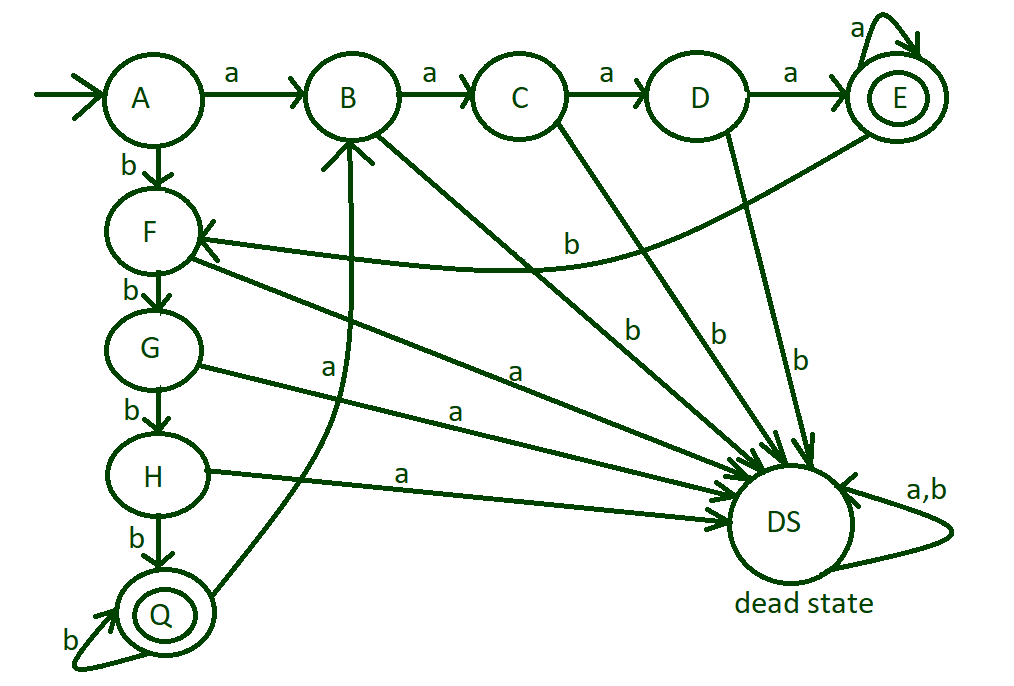
final design
Transition Table of above DFA:
Here “A” is initial state and “E” and “Q” are final states. DS is termed as DEAD STATE
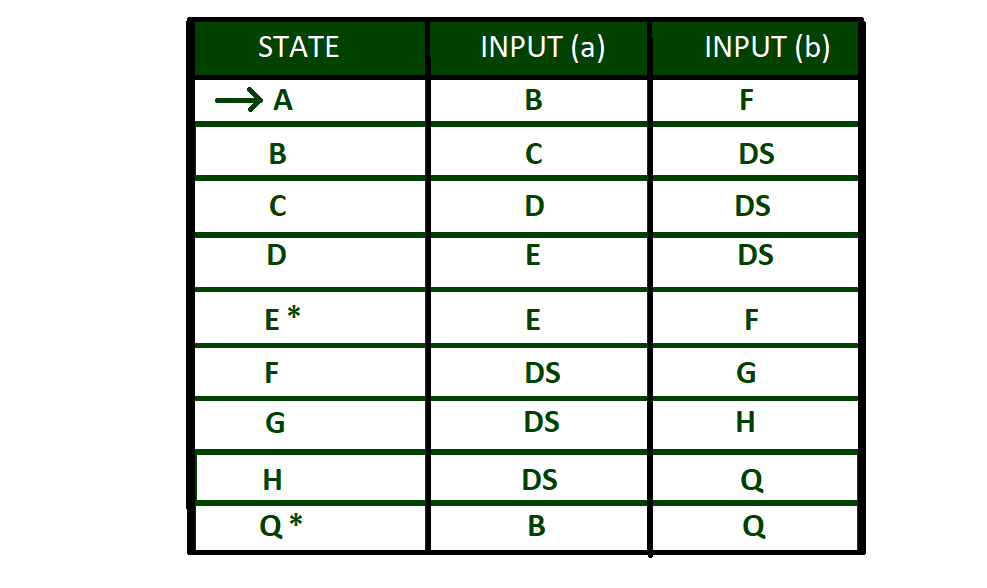
Transition Table
Python implementation of above DFA:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class StateMachine {
public:
static void checkStateA(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String not accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'a') {
stateB(n.substr(1));
}
else {
stateF(n.substr(1));
}
}
}
static void stateB(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String not accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'a') {
stateC(n.substr(1));
}
else {
std::cout << "String not accepted"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
static void stateC(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String not accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'a') {
stateD(n.substr(1));
}
else {
std::cout << "String not accepted"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
static void stateD(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String not accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'a') {
stateE(n.substr(1));
}
else {
std::cout << "String not accepted"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
static void stateE(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String accepted" << std::endl;
}
else if (n.at(0) == 'a') {
stateE(n.substr(1));
}
else if (n.at(0) == 'b') {
stateF(n.substr(1));
}
}
static void stateF(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String not accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'b') {
stateG(n.substr(1));
}
else {
std::cout << "String not accepted"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
static void stateG(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String not accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'b') {
stateH(n.substr(1));
}
else {
std::cout << "String not accepted"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
static void stateH(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String not accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'b') {
stateQ(n.substr(1));
}
else {
std::cout << "String not accepted"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
static void stateQ(std::string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0) {
std::cout << "String accepted" << std::endl;
}
else {
if (n.at(0) == 'b') {
stateQ(n.substr(1));
}
else if (n.at(0) == 'a') {
stateB(n.substr(1));
}
}
}
};
int main()
{
std::string n = "aaaabbbbbaaaa";
StateMachine::checkStateA(n);
n = "aaaabbb";
StateMachine::checkStateA(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class StateMachine {
public static void checkStateA(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'a') {
stateB(n.substring(1));
}
else {
stateF(n.substring(1));
}
}
}
public static void stateB(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'a') {
stateC(n.substring(1));
}
else {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
}
}
public static void stateC(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'a') {
stateD(n.substring(1));
}
else {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
}
}
public static void stateD(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'a') {
stateE(n.substring(1));
}
else {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
}
}
public static void stateE(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String accepted");
}
else if(n.charAt(0) == 'a') {
stateE(n.substring(1));
}
else if(n.charAt(0) == 'b') {
stateF(n.substring(1));
}
}
public static void stateF(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'b') {
stateG(n.substring(1));
}
else {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
}
}
public static void stateG(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'b') {
stateH(n.substring(1));
}
else {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
}
}
public static void stateH(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'b') {
stateQ(n.substring(1));
}
else {
System.out.println("String not accepted");
}
}
}
public static void stateQ(String n) {
if(n.length() == 0) {
System.out.println("String accepted");
}
else {
if(n.charAt(0) == 'b') {
stateQ(n.substring(1));
}
else if(n.charAt(0) == 'a') {
stateB(n.substring(1));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String n = "aaaabbbbbaaaa";
checkStateA(n);
n = "aaaabbb";
checkStateA(n);
}
}
|
Python3
def checkStateA(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateB(n[1:])
else:
stateF(n[1:])
def stateB(n):
if (len(n)== 0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateC(n[1:])
else:
print("string not accepted")
def stateC(n):
if (len(n)== 0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateD(n[1:])
else:
print("string not accepted")
def stateD(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateE(n[1:])
else:
print("string not accepted")
def stateE(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("string accepted")
elif(n[0]=='a'):
stateE(n[1:])
elif(n[0]=='b'):
stateF(n[1:])
def stateF(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='b'):
stateG(n[1:])
else:
print("string not accepted")
def stateG(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='b'):
stateH(n[1:])
else:
print("string not accepted")
def stateH(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='b'):
stateQ(n[1:])
else:
print("string not accepted")
def stateQ(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("string accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='b'):
stateQ(n[1:])
elif(n[0]=='a'):
stateB(n[1:])
if __name__ == '__main__':
n ="aaaabbbbbaaaa"
checkStateA(n)
n ="aaaabbb"
checkStateA(n)
|
C#
using System;
public class StateMachine {
public static void CheckStateA(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
StateB(n.Substring(1));
else
StateF(n.Substring(1));
}
}
public static void StateB(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
else {
if (n[0] == 'a')
StateC(n.Substring(1));
else
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
}
}
public static void StateC(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
else {
if (n[0] == 'a')
StateD(n.Substring(1));
else
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
}
}
public static void StateD(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
else {
if (n[0] == 'a')
StateE(n.Substring(1));
else
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
}
}
public static void StateE(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String accepted");
else if (n[0] == 'a')
StateE(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
StateF(n.Substring(1));
}
public static void StateF(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
else {
if (n[0] == 'b')
StateG(n.Substring(1));
else
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
}
}
public static void StateG(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
else {
if (n[0] == 'b')
StateH(n.Substring(1));
else
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
}
}
public static void StateH(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
else {
if (n[0] == 'b')
StateQ(n.Substring(1));
else
Console.WriteLine("String not accepted");
}
}
public static void StateQ(string n)
{
if (n.Length == 0)
Console.WriteLine("String accepted");
else {
if (n[0] == 'b')
StateQ(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'a')
StateB(n.Substring(1));
}
}
}
public class Program {
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string n = "aaaabbbbbaaaa";
StateMachine.CheckStateA(n);
n = "aaaabbb";
StateMachine.CheckStateA(n);
}
}
|
Javascript
function checkStateA(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string not accepted");
} else {
if (n[0] === 'a') {
stateB(n.substring(1));
} else {
stateF(n.substring(1));
}
}
}
function stateB(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string not accepted");
} else {
if (n[0] === 'a') {
stateC(n.substring(1));
} else {
console.log("string not accepted");
}
}
}
function stateC(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string not accepted");
} else {
if (n[0] === 'a') {
stateD(n.substring(1));
} else {
console.log("string not accepted");
}
}
}
function stateD(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string not accepted");
} else {
if (n[0] === 'a') {
stateE(n.substring(1));
} else {
console.log("string not accepted");
}
}
}
function stateE(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string accepted");
} else if (n[0] === 'a') {
stateE(n.substring(1));
} else if (n[0] === 'b') {
stateF(n.substring(1));
}
}
function stateF(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string not accepted");
} else {
if (n[0] === 'b') {
stateG(n.substring(1));
} else {
console.log("string not accepted");
}
}
}
function stateG(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string not accepted");
} else {
if (n[0] === 'b') {
stateH(n.substring(1));
} else {
console.log("string not accepted");
}
}
}
function stateH(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string not accepted");
} else {
if (n[0] === 'b') {
stateQ(n.substring(1));
} else {
console.log("string not accepted");
}
}
}
function stateQ(n) {
if (n.length === 0) {
console.log("string accepted");
} else if (n[0] === 'b') {
stateQ(n.substring(1));
} else if (n[0] === 'a') {
stateB(n.substring(1));
}
}
let n = "aaaabbbbbaaaa";
checkStateA(n);
n = "aaaabbb";
checkStateA(n);
|
Output
String accepted
String not accepted
Time Complexity: O(N) for given input string of length N
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...