Implementation of Perceptron Algorithm for XNOR Logic Gate with 2-bit Binary Input
Last Updated :
26 Nov, 2022
In the field of Machine Learning, the Perceptron is a Supervised Learning Algorithm for binary classifiers. The Perceptron Model implements the following function:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ \begin{array}{c} \hat{y}=\Theta\left(w_{1} x_{1}+w_{2} x_{2}+\ldots+w_{n} x_{n}+b\right) \\ =\Theta(\mathbf{w} \cdot \mathbf{x}+b) \\ \text { where } \Theta(v)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} 1 & \text { if } v \geqslant 0 \\ 0 & \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right. \end{array} \]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f7626bb7672b45e3187df50ef64cd4bc_l3.png)
For a particular choice of the weight vector
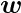
and bias parameter
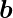
, the model predicts output
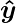
for the corresponding input vector
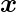
.
XNOR logical function truth table for
2-bit binary variables, i.e, the input vector
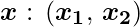
and the corresponding output
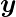
–
We can observe that, 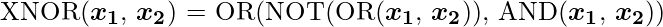 Designing the Perceptron Network:
Designing the Perceptron Network:
- Step1: Now for the corresponding weight vector
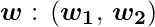 of the input vector
of the input vector 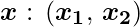 to the OR and AND node, the associated Perceptron Function can be defined as:
to the OR and AND node, the associated Perceptron Function can be defined as: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[$\boldsymbol{\hat{y}_{1}} = \Theta\left(w_{1} x_{1}+w_{2} x_{2}+b_{OR}\right)$ \]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-977101357b34fb859ced599bcefae030_l3.png)
[Tex]\[$\boldsymbol{\hat{y}_{2}} = \Theta\left(w_{1} x_{1}+w_{2} x_{2}+b_{AND}\right)$ \] [/Tex] - Step2: The output
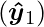 from the OR node will be inputted to the NOT node with weight
from the OR node will be inputted to the NOT node with weight 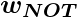 and the associated Perceptron Function can be defined as:
and the associated Perceptron Function can be defined as: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[$\boldsymbol{\hat{y}_{3}} = \Theta\left(w_{NOT} \boldsymbol{\hat{y}_{1}}+b_{NOT}\right)$\]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ba58779f2294aab77613511a51fec2fe_l3.png)
- Step3: The output
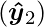 from the AND node and the output
from the AND node and the output 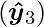 from NOT node as mentioned in Step2 will be inputted to the OR node with weight
from NOT node as mentioned in Step2 will be inputted to the OR node with weight 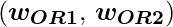 . Then the corresponding output
. Then the corresponding output 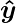 is the final output of the XNOR logic function. The associated Perceptron Function can be defined as:
is the final output of the XNOR logic function. The associated Perceptron Function can be defined as: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[$\boldsymbol{\hat{y}} = \Theta\left(w_{OR1} \boldsymbol{\hat{y}_{3}}+w_{OR2} \boldsymbol{\hat{y}_{2}}+b_{OR}\right)$\]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b4ec4a2e01d87a282e4912f727867ea5_l3.png)
 For the implementation, the weight parameters are considered to be
For the implementation, the weight parameters are considered to be 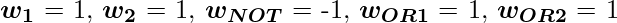 and the bias parameters are
and the bias parameters are 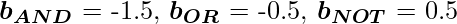 . Python Implementation:
. Python Implementation:
Python3
import numpy as np
def unitStep(v):
if v >= 0:
return 1
else:
return 0
def perceptronModel(x, w, b):
v = np.dot(w, x) + b
y = unitStep(v)
return y
def NOT_logicFunction(x):
wNOT = -1
bNOT = 0.5
return perceptronModel(x, wNOT, bNOT)
def AND_logicFunction(x):
w = np.array([1, 1])
bAND = -1.5
return perceptronModel(x, w, bAND)
def OR_logicFunction(x):
w = np.array([1, 1])
bOR = -0.5
return perceptronModel(x, w, bOR)
def XNOR_logicFunction(x):
y1 = OR_logicFunction(x)
y2 = AND_logicFunction(x)
y3 = NOT_logicFunction(y1)
final_x = np.array([y2, y3])
finalOutput = OR_logicFunction(final_x)
return finalOutput
test1 = np.array([0, 1])
test2 = np.array([1, 1])
test3 = np.array([0, 0])
test4 = np.array([1, 0])
print("XNOR({}, {}) = {}".format(0, 1, XNOR_logicFunction(test1)))
print("XNOR({}, {}) = {}".format(1, 1, XNOR_logicFunction(test2)))
print("XNOR({}, {}) = {}".format(0, 0, XNOR_logicFunction(test3)))
print("XNOR({}, {}) = {}".format(1, 0, XNOR_logicFunction(test4)))
|
Output:XNOR(0, 1) = 0
XNOR(1, 1) = 1
XNOR(0, 0) = 1
XNOR(1, 0) = 0
Here, the model predicted output (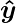 ) for each of the test inputs are exactly matched with the XNOR logic gate conventional output (
) for each of the test inputs are exactly matched with the XNOR logic gate conventional output (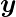 ) according to the truth table. Hence, it is verified that the perceptron algorithm for XNOR logic gate is correctly implemented.
) according to the truth table. Hence, it is verified that the perceptron algorithm for XNOR logic gate is correctly implemented.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...