hwclock command in Linux with examples
Last Updated :
21 May, 2019
hwclock also called Real Time Clock (RTC), is a utility for accessing the hardware clock. The hardware clock is independent of the OS(operating system) you use and works even when the machine is shut down. The hardware clock is also called a BIOS clock. A user can also change the date and time of the hardware clock from the BIOS. The hardware clock stores the values of the second, minute, hour, day, month and year. The hwclock utility saves its settings in the /etc/adjtime file, which is created when a user makes first change.
Syntax:
hwclock [function] [option...]
Functions:
- -r, –show : It will display the RTC time.
- –get : It is used to display the drift corrected RTC time.
- –set : It is used to set the RTC according to –date.
- -s, –hctosys : It will set the system time form the RTC.
- -w, –systohoc : It will set the RTC from the system time i.e. the opposite of -s, –hctosys.
- –systz : Used to send the timescale configurations to the kernel.
- -a, –adjust : Adjust the RTC to account for systematic drift.
- –predict : It will predict the drifted RTC time according to –date.
Options:
- -u, –utc : Shows that RTC timescale is UTC.
- -l, –localtime : Shows that RTC timescale is Local.
- -D, –debug : This is used to display the debug information. Information is shown according to the demands of hwclock command.
- -V, –version : Display version information and exit.
- -h, –help : Display help text and exit.
Note: Use sudo with hwclock command.
Examples:
1. To display the Hardware Clock Date and Time:
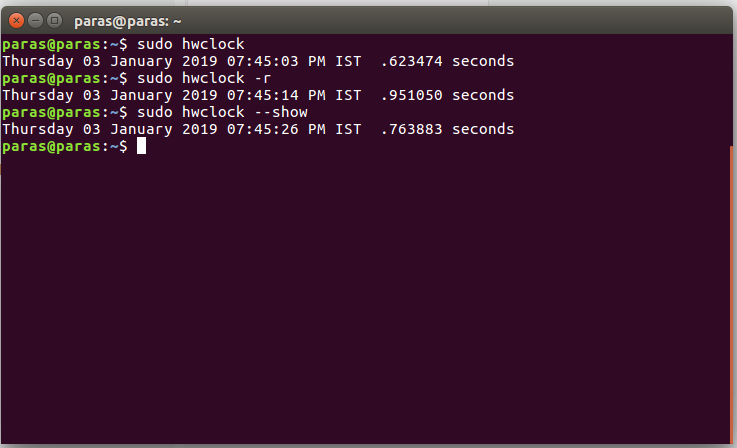
2. Using adjust function:
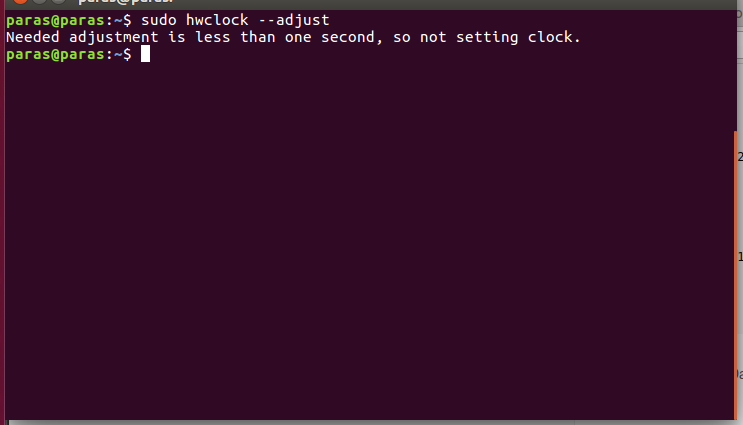
3. Using debug option to get the debug information:
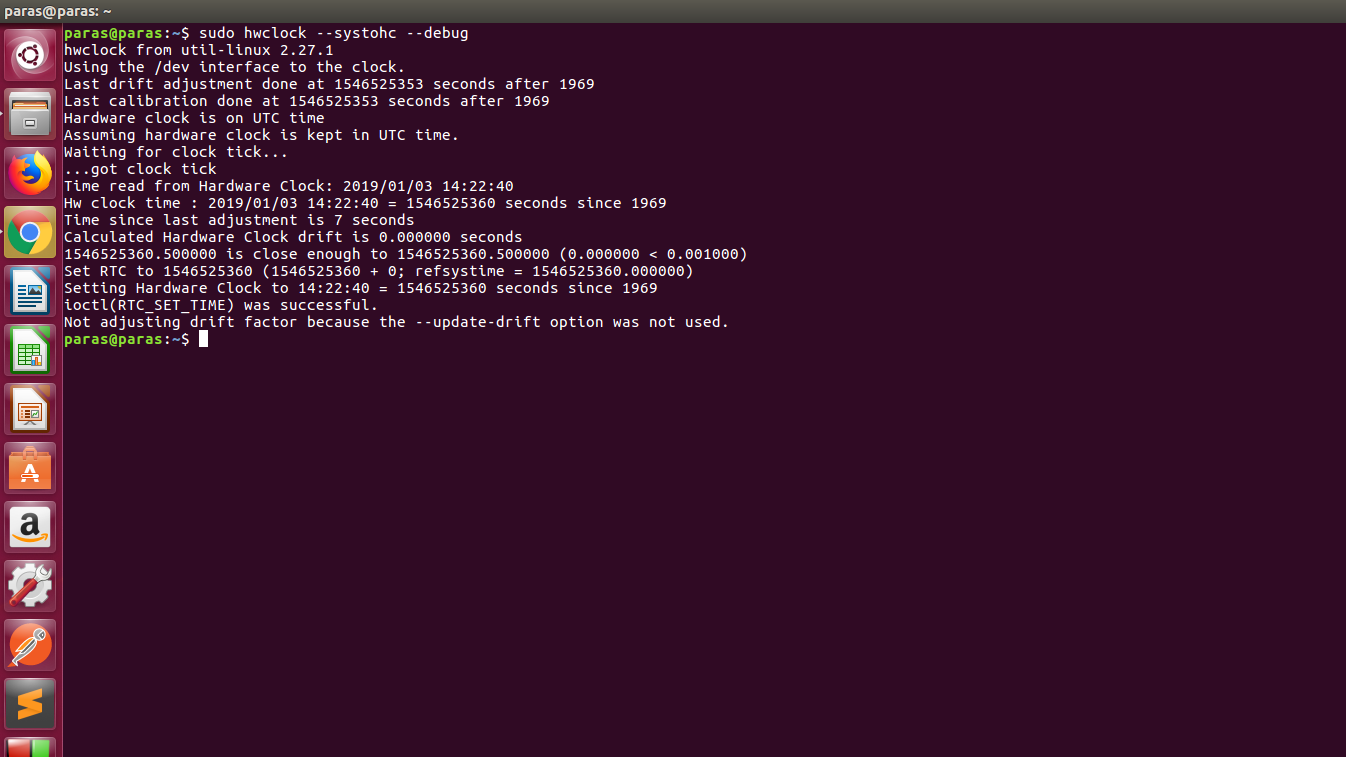
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...